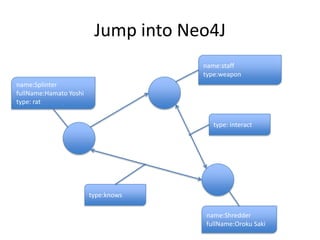
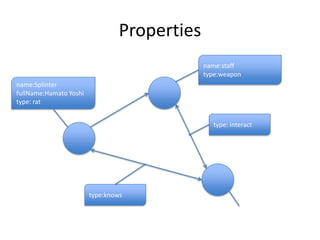
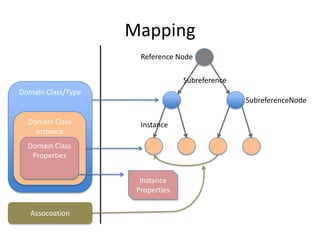
This document discusses using the Neo4J graph database with Grails. It provides an overview of NoSQL databases and why graph databases are useful. It then discusses Neo4J specifically and how its data model is suited to connected data. The document outlines how to install the Neo4J plugin for Grails and use GORM to work with Neo4J. It also discusses advanced configurations like embedded, REST, and high availability modes.




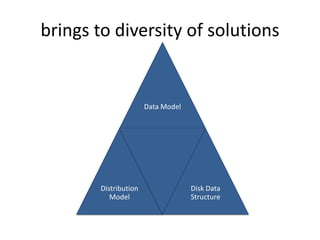















![Advanced Configuration
grails-app/conf/DataSource.groovy
grails {
neo4j {
type = "embedded"
location = "/var/neo4j"
params = []
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4j-120402065725-phpapp01/85/Neo4-Grails-33-320.jpg)

![High Availabile
type = "ha”
grails {
neo4j {
type = "ha"
location = "/var/neo4j"
params = [ // see http://docs.neo4j.org/chunked/stable/ha-configuration.html
'ha.server_id': 1,
'ha.coordinators': 'localhost:2181,localhost:2182,localhost:2183'
]
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neo4j-120402065725-phpapp01/85/Neo4-Grails-35-320.jpg)

