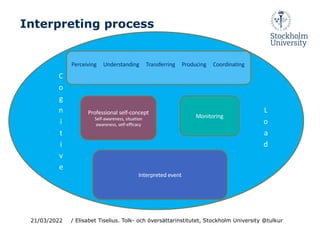
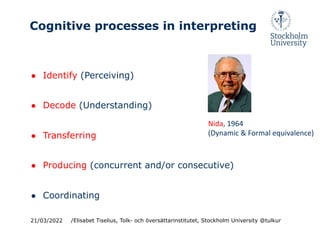
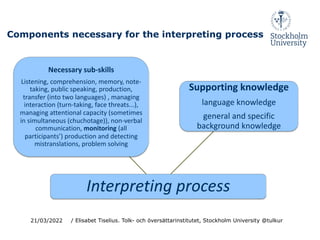
This document discusses cognition and working memory in dialogue interpreting. It begins with an overview of dialogue interpreting as a mode of interpreting involving short consecutive interpreting without notes and quasi-simultaneous interpreting with few participants. It then discusses some key cognitive processes in interpreting like identifying, decoding, transferring, and producing interpretations. It emphasizes the importance of monitoring all participants' contributions and ensuring comprehension between participants. The document also discusses language proficiency models and notes asymmetries in interpreters' language skills. Finally, it examines the cognitive load of monitoring, coordination, and turn-taking in dialogue interpreting.
































![Assumptions about cognitive
processes in dialogue interpreting
The fundamental conditions of [dialogue]
interpreting (i.e., three-party dialogue and
immediate feedback) impact the process
requirements and put more cognitive load on
monitoring, co-ordination, and ethical awareness.
Englund Dimitrova and Tiselius (2016)
21/03/2022 /Elisabet Tiselius /Tolk- och översättarinstitutet, Stockholm University @tulkur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ncihchft52whycognitionmattersvslideshare-220509143709-b971bdda/85/NCIHC-HFT52-Why-Cognition-Matters-v-slideshare-35-320.jpg)






![I* >> gaze to C --------------------------------* *gaze aversion--------------------->* *gaze to C--------->*
51 JS vale y estoy un poquito preocupada por * * las actividades porque son son a* *tiempo completo↑*
good because I’m a little worried for those activities because are are they full time
I* *gaze aversion ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
*y: y: que pasa con los hijos porque yo tengo hijos y los cuido yo sola (.) porque su padre y yo nos
an: an: what happens with the kids because I’m alone with the children because their father and I got
I⧫ ⧫ turn tw JS--->⧫
I* ------------------------------------>* * gaze to JS------------------------------------------------->
separamos durante la huída* ⧫ y hasta el día⧫* de hoy no [sabemos (.) de]
separated during the fleeing and to this day we don’t have any news of
I⧫ ⧫L index to L ear⧫
52 I [perdona no entiendo] eso ⧫de la oída⧫=
sorry I don’t understand this with the heard
I⧫ ⧫nod------------------⧫
I* >----------* *gaze aversion-------------------------------------------->>
53 JS =la huída* ⧫[desde que huímos]⧫
the flight from the time we fled
I [a: vale vale]
[a: okay okay]
21/03/2022 /Elisabet Tiselius /Tolk- och översättarinstitutet, Stockholm University @tulkur](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ncihchft52whycognitionmattersvslideshare-220509143709-b971bdda/85/NCIHC-HFT52-Why-Cognition-Matters-v-slideshare-43-320.jpg)