The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and its subfields, including machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), computer vision, and intelligent robotics. It explains the distinctions between narrow AI and general AI, discusses key NLP processes like segmentation and part-of-speech tagging, and highlights applications across various domains such as chatbots and autonomous vehicles. Real-world examples of intelligent robotics and their applications in industries like healthcare and agriculture are also presented.


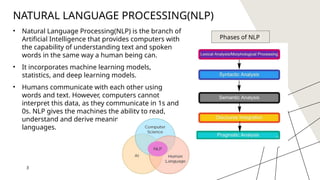
![Lexical analysis: In this phase, the
sentences, paragraphs are broken into
tokens.
For example, The sentence “He goes to
college.” is divided into [ ‘He’ , ‘goes’ , ‘to’ ,
‘college’, ‘.’] .
Syntactic analysis: In this phase, the
sentence is checked whether it is well
formed or not. It is checked for word
arrangements and grammar.
For example, The sentence “Delhi goes to
him” is rejected by the syntactic parser.
Semantic analysis: In this phase, the
sentence is checked for the literal
meaning of each word and their
arrangement together.
For example, The sentence “I ate hot ice
cream” will get rejected by the semantic
analyzer because it doesn’t make sense
4
Discourse integration: In this phase, the
impact of the sentences before a particular
sentence and the effect of the current
sentence on the upcoming sentences is
determined.
For example, the word “that” in the
sentence “He wanted that” depends upon
the prior discourse context.
Pragmatic analysis: The actual effect of
the text is discovered by applying the set of
rules that characterize cooperative
dialogues.
E.g., “close the window?” should be
interpreted as a request instead of an order.
Sometimes the discourse integration phase
and pragmatic analysis phase are
combined.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-250111161114-36f25e8b/85/NATURAL-LANGUAGE-PROCESSING-in-ARTIFICIAL-INTELLIGENCE-pptx-4-320.jpg)