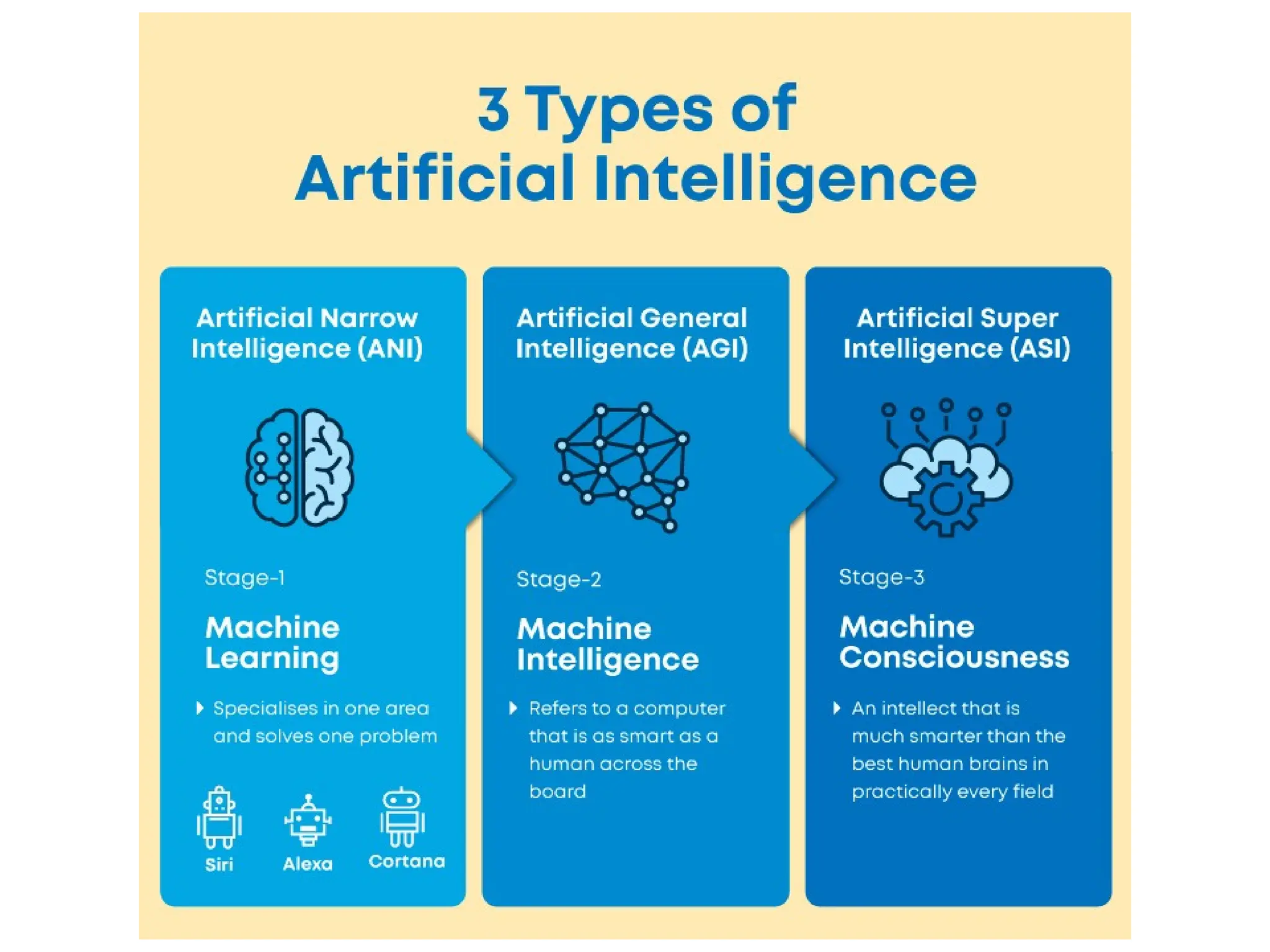
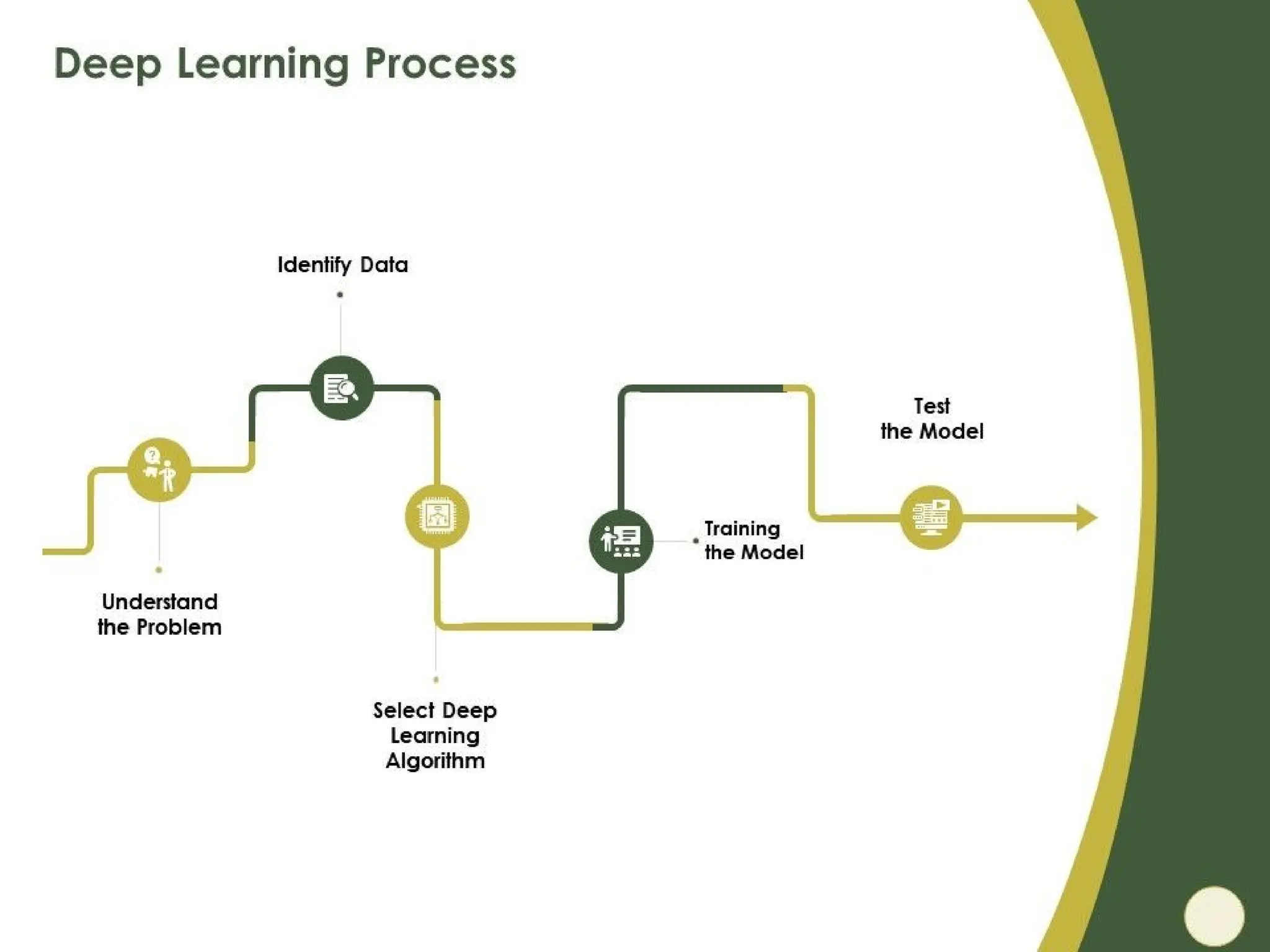
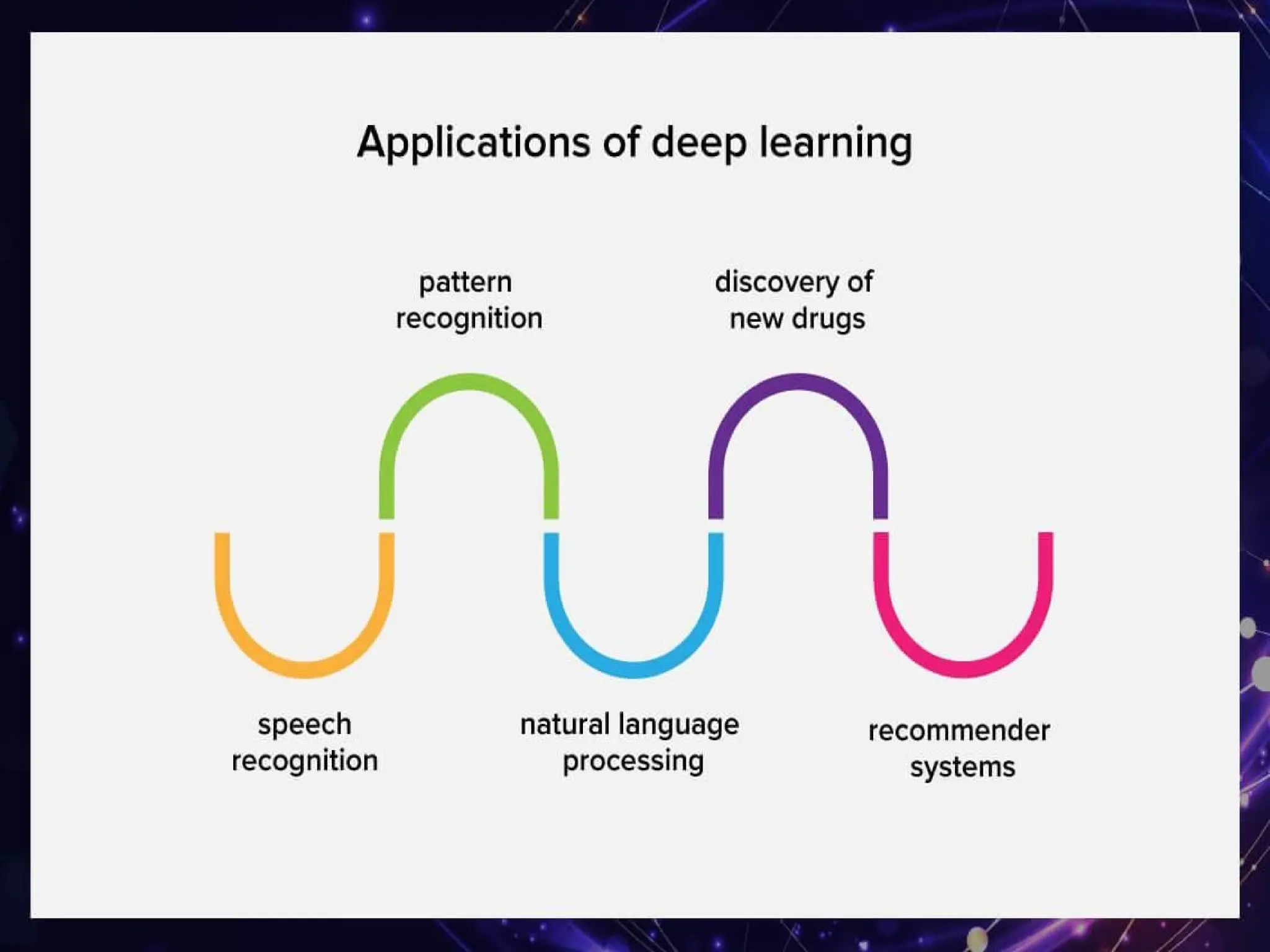
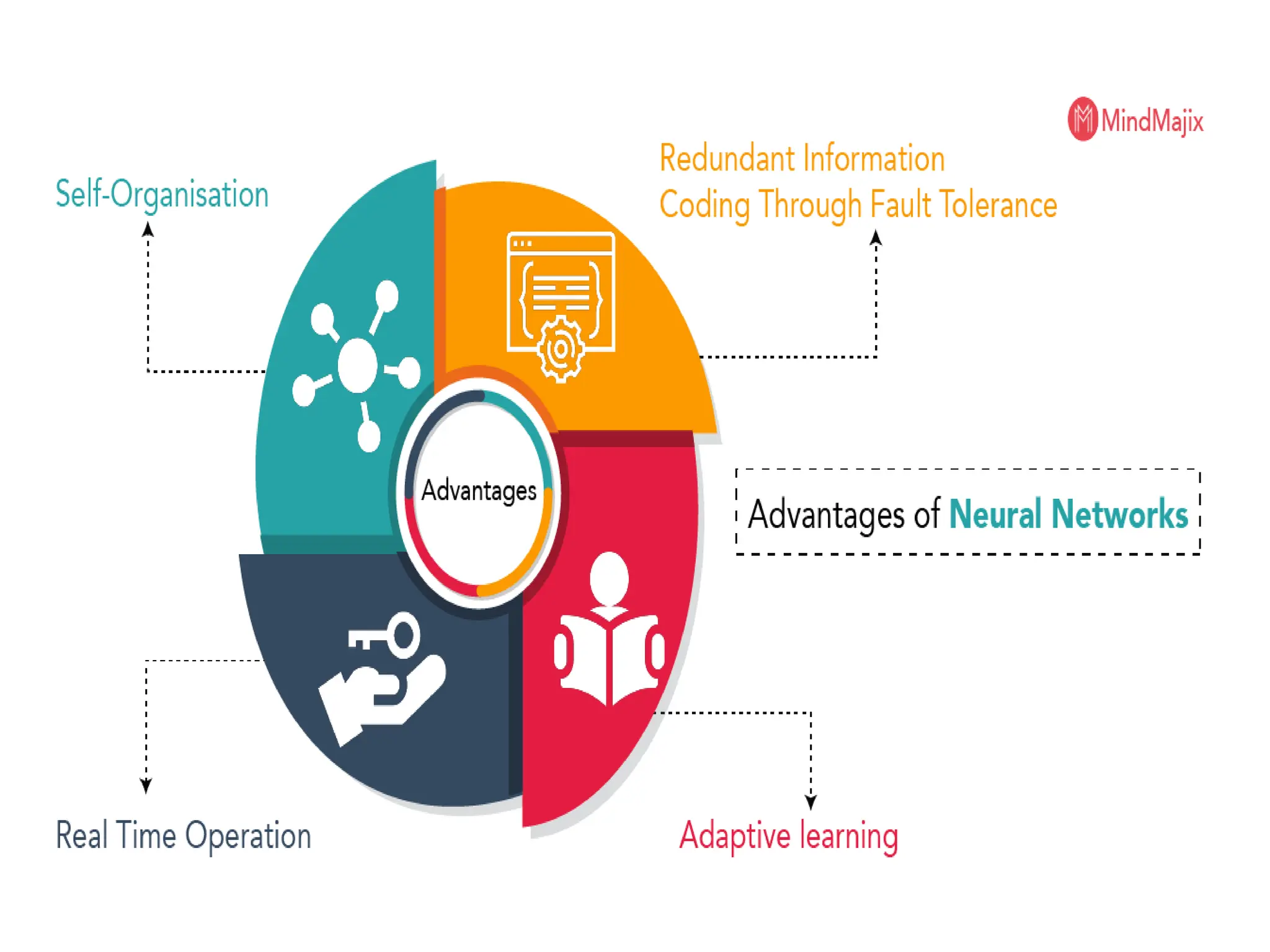
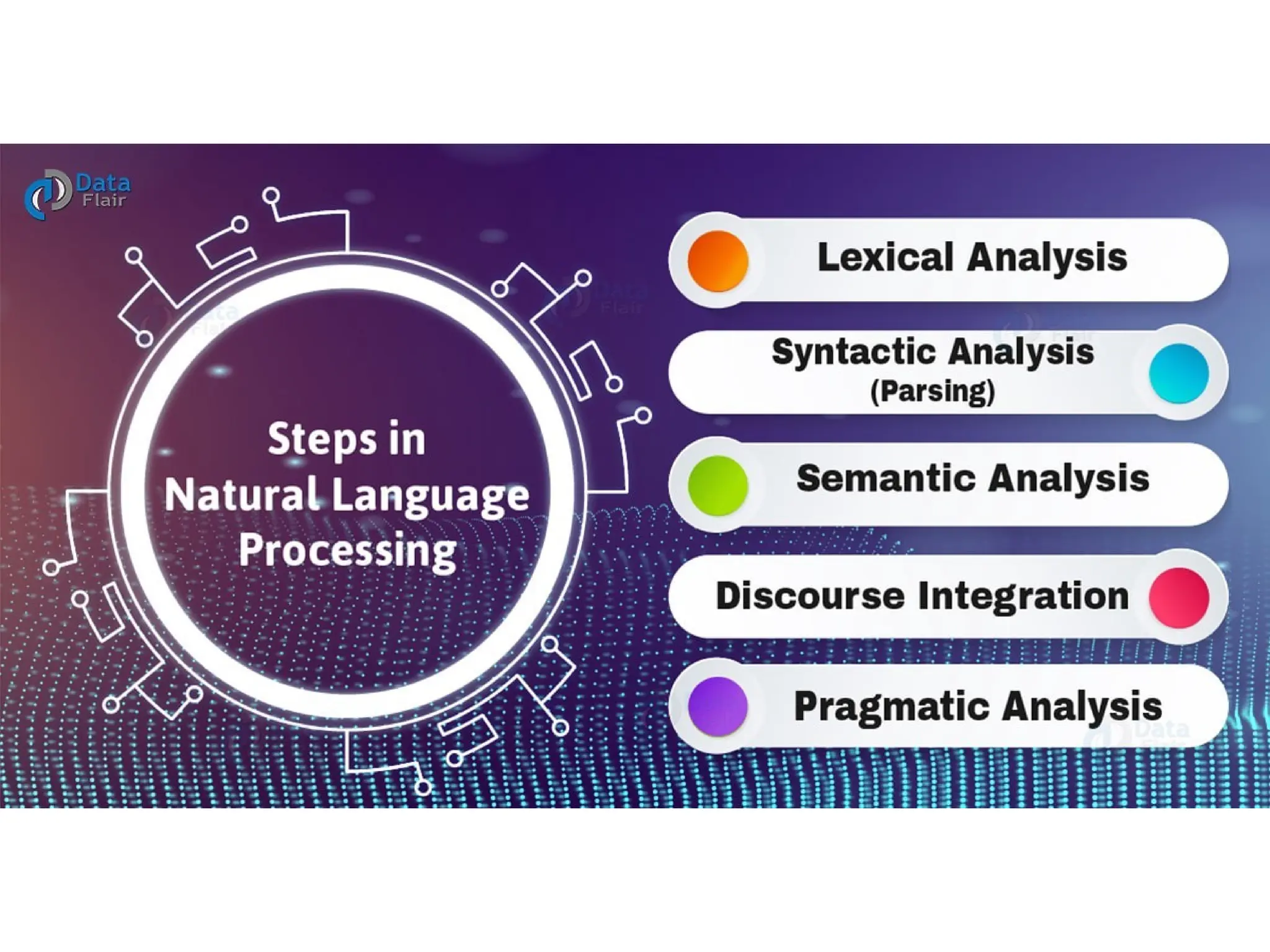
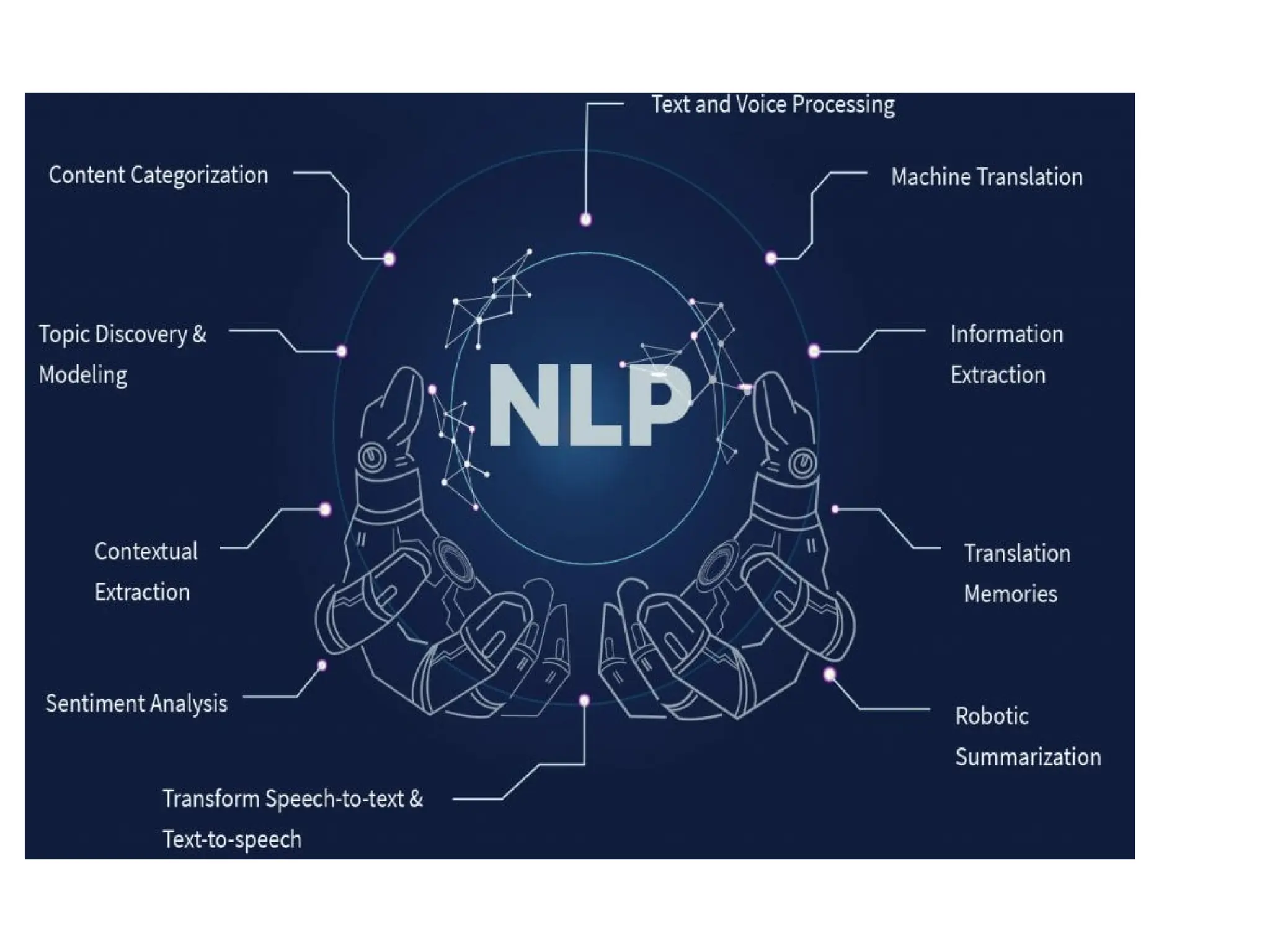
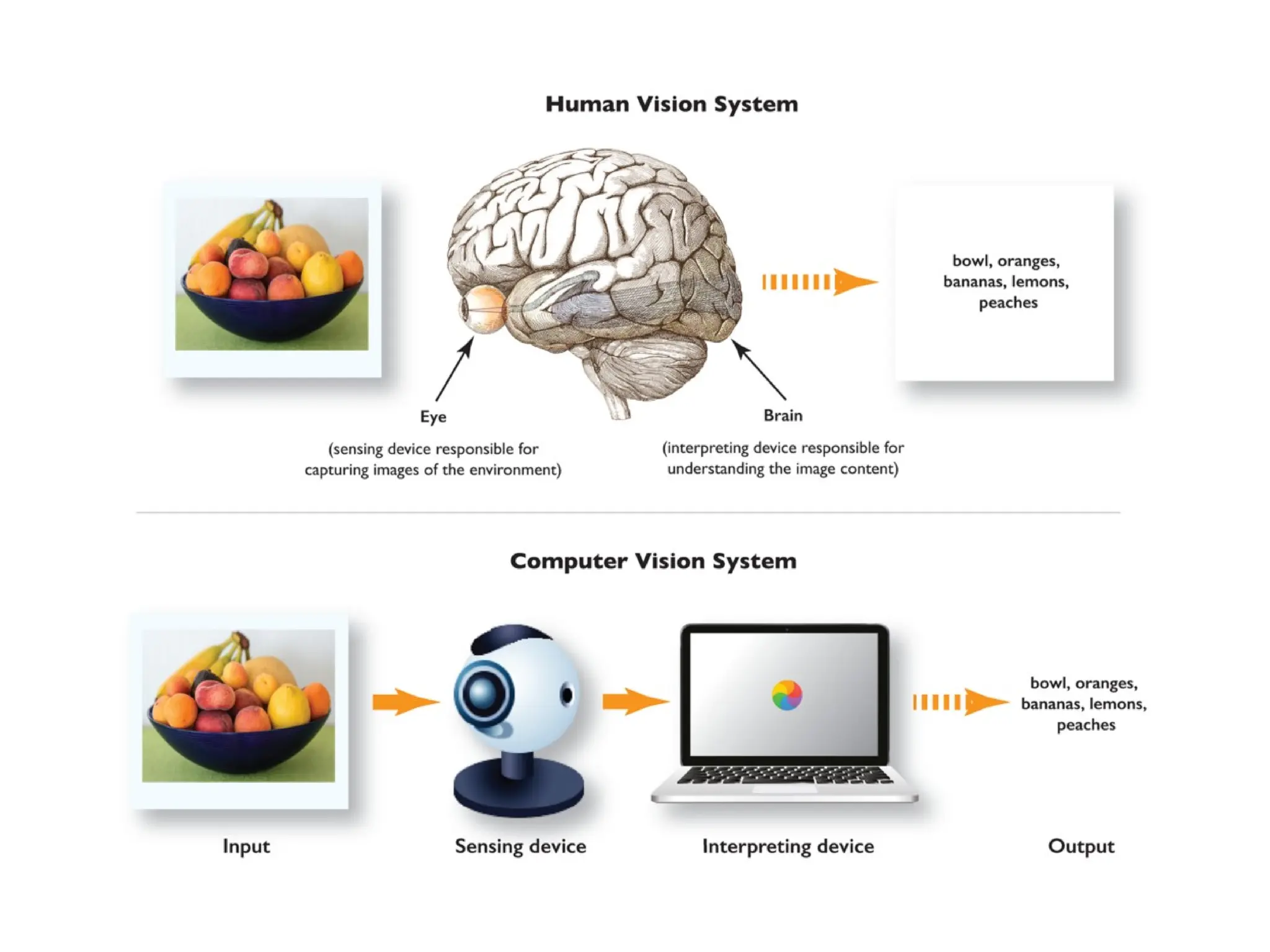
The document outlines the need for artificial intelligence (AI) in solving real-life problems, its applications like virtual assistants, and its ability to improve productivity. It discusses the advantages and disadvantages of AI, types of AI, and various related terminologies such as machine learning and natural language processing. Additionally, it highlights components of AI like computer vision, emphasizing their role in automating tasks and enhancing operational efficiency.