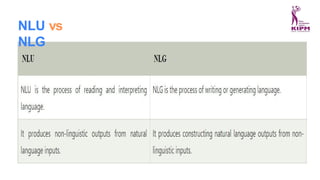
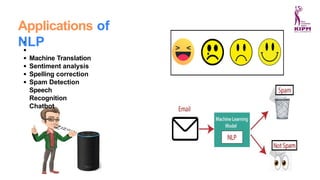
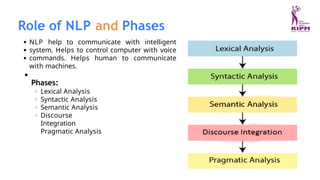
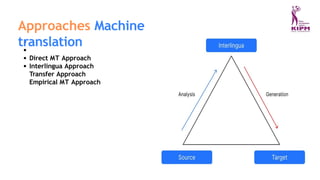
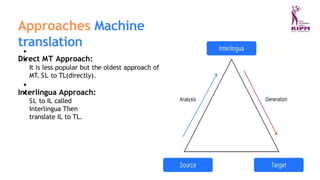
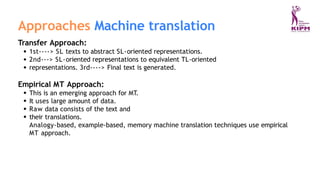
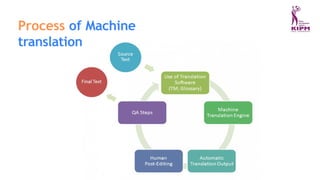
The document discusses various applications and phases of artificial intelligence, focusing on information retrieval, information extraction, and natural language processing (NLP). It explains the workings and advantages of NLP in tasks like machine translation, sentiment analysis, and speech recognition while also addressing its limitations. Additionally, it covers the role of robotics in AI and different types of robot locomotion.