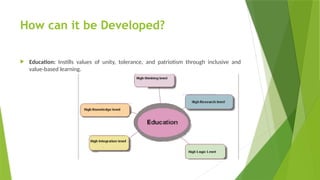
National Integrity refers to the unity, honesty, and collective responsibility of the citizens of a country toward preserving its sovereignty, cultural identity, constitutional values, and social harmony. It ensures that despite differences in religion, language, region, or caste, the people of a nation stand together as one. it also describes components of national integrity