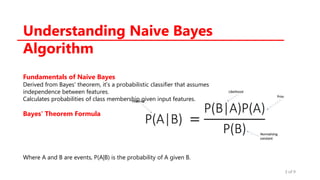
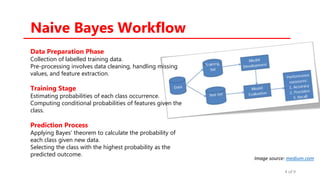
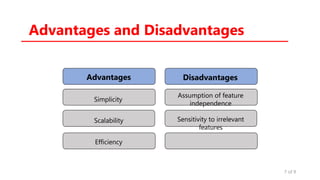
The document provides an overview of the Naïve Bayes classification algorithm, detailing its foundations in Bayesian theory and its application in supervised machine learning for classification tasks. It discusses the workflow involved in data preparation, training, and prediction, as well as the different types of Naïve Bayes classifiers suited for various data forms. Additionally, it highlights the advantages and disadvantages of the method, along with its applications in spam filtering, sentiment analysis, document classification, and recommendation systems.