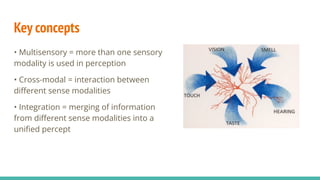
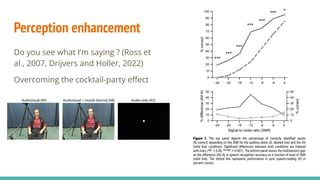
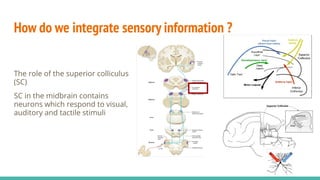
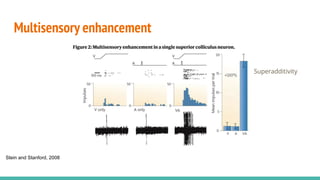
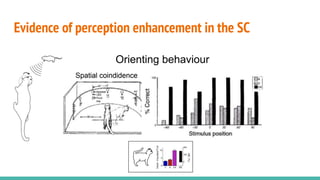
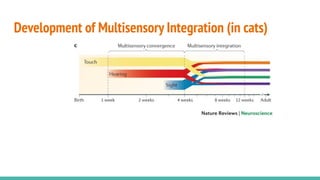
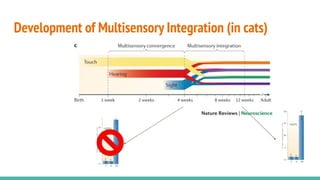
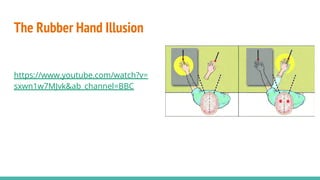
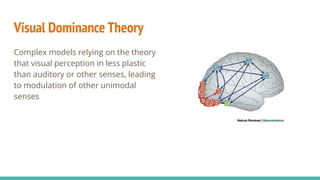
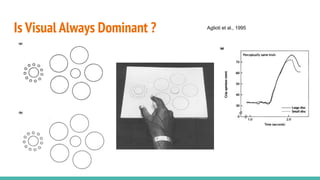
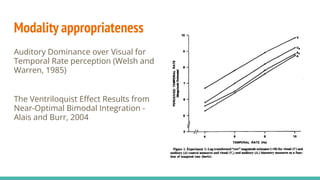
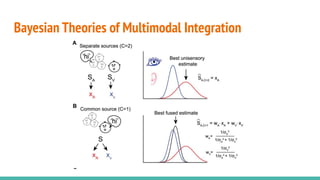
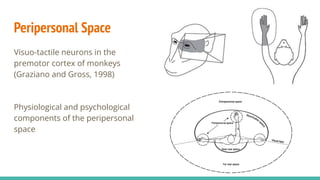
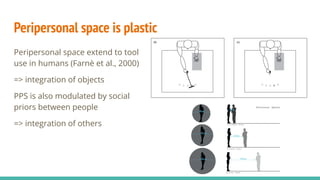
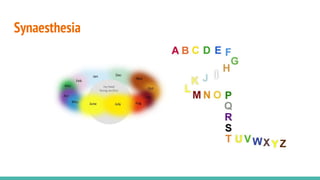
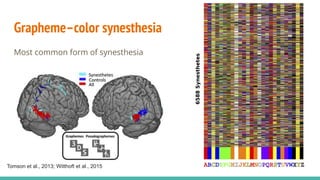
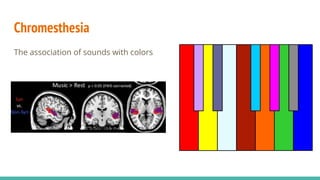
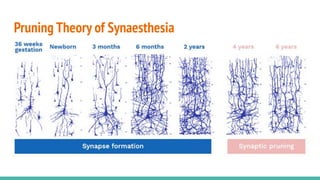
The document discusses the neuroscience of multisensory integration, highlighting that perception is typically multisensory rather than unimodal. It details key concepts such as cross-modal interactions, integration, and the physiological mechanisms involved, particularly focusing on the superior colliculus. Additionally, it addresses principles of multisensory integration, the binding problem, and phenomena like the McGurk effect and synaesthesia.