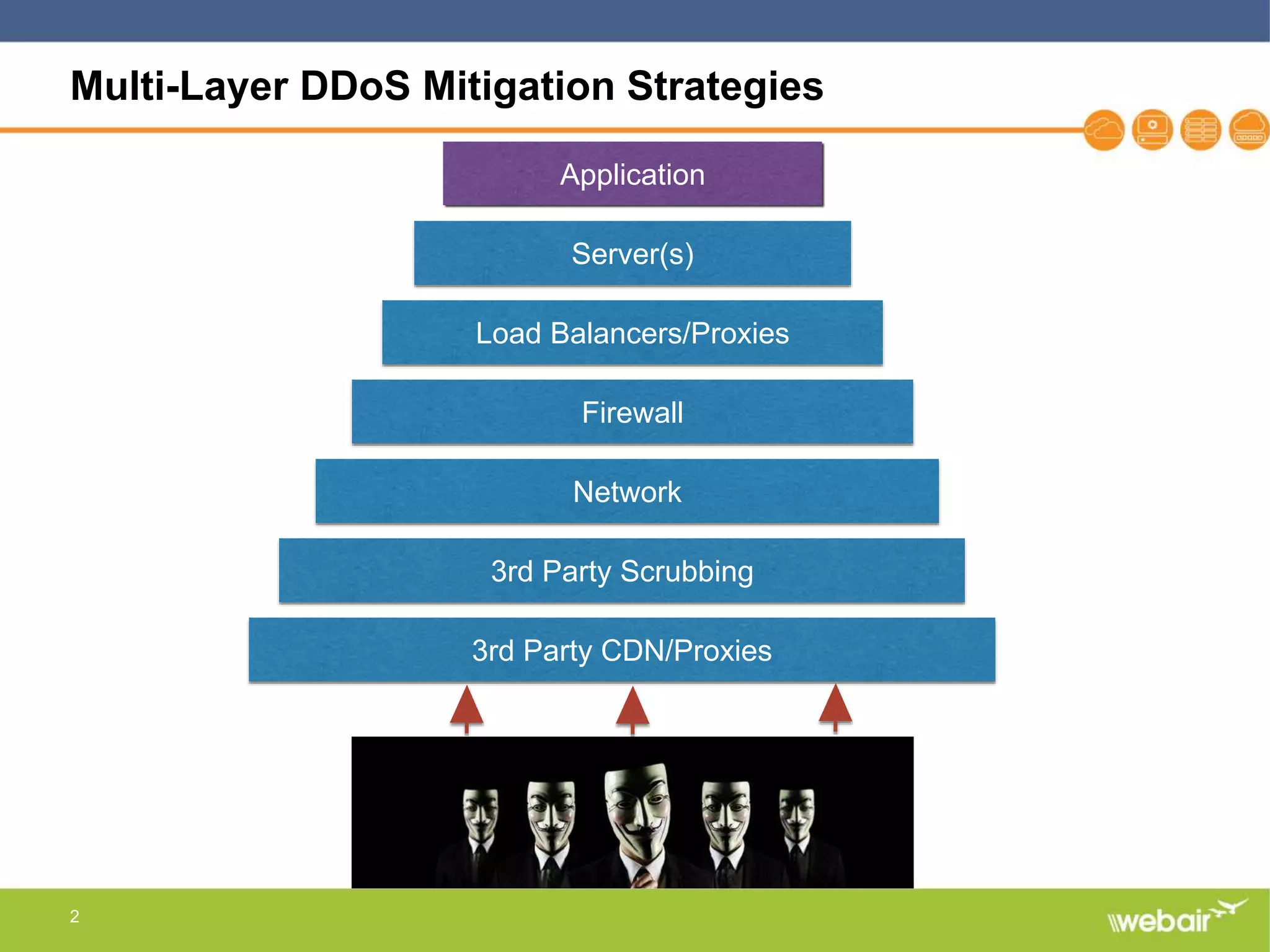
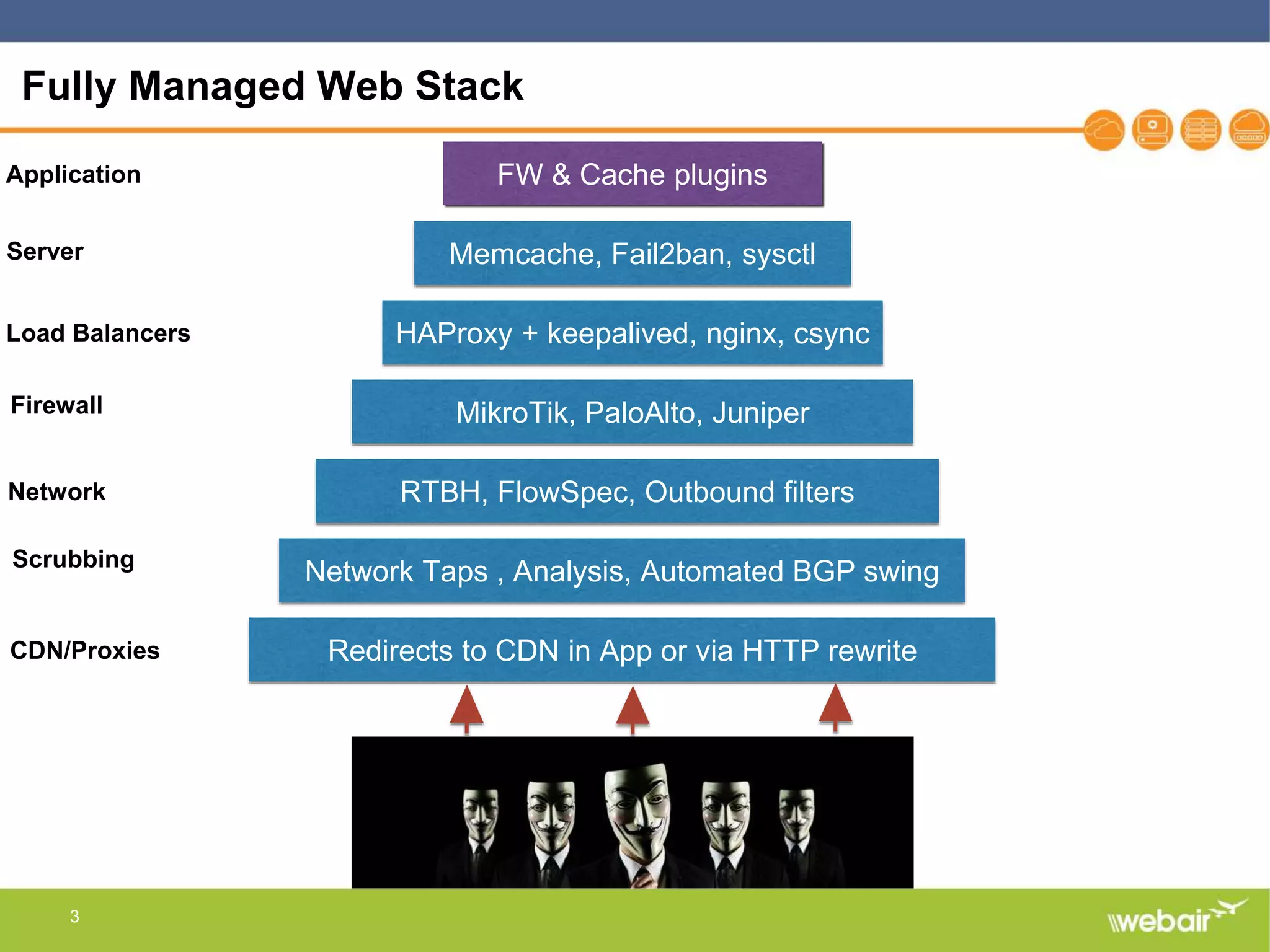
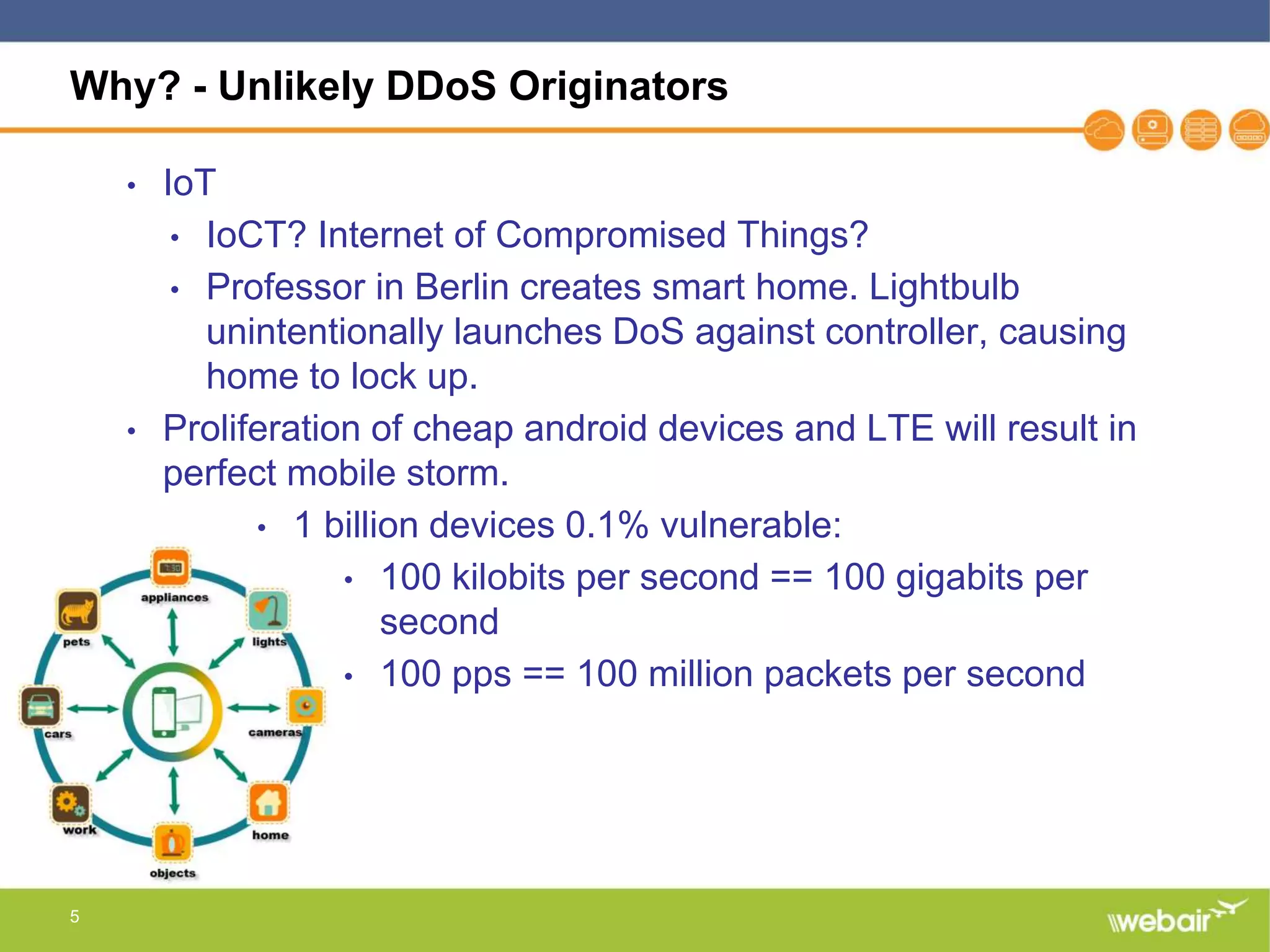
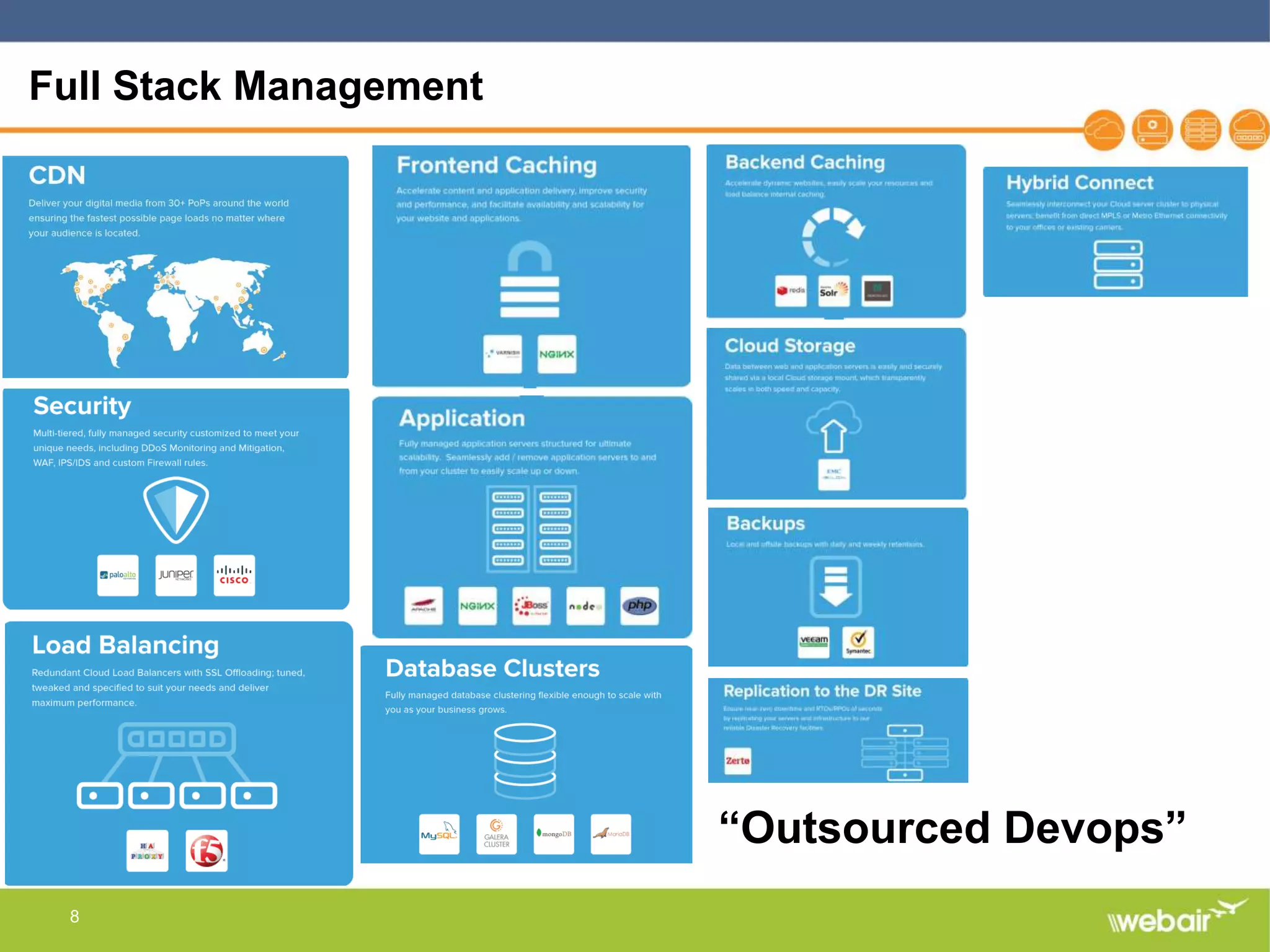
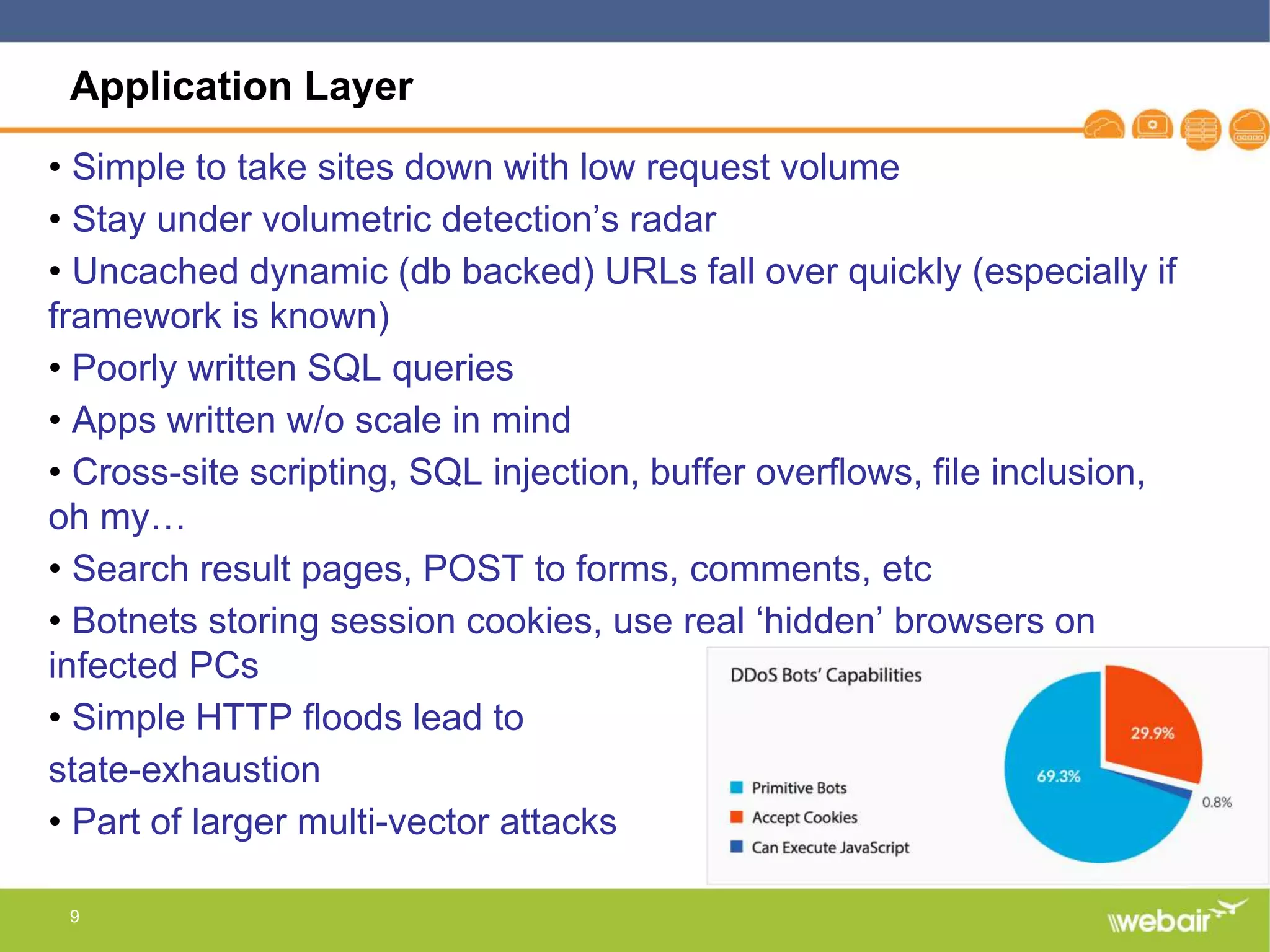
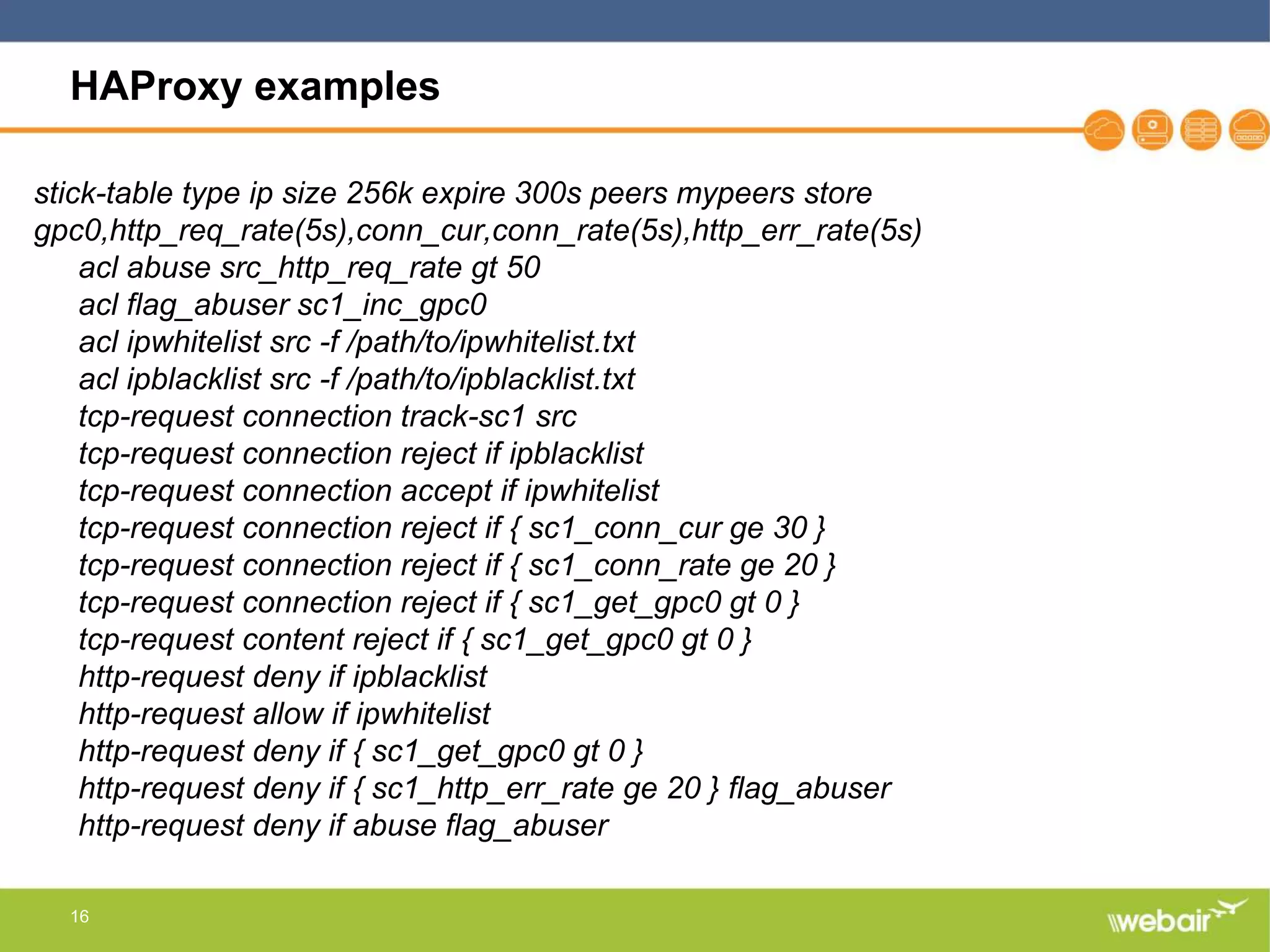
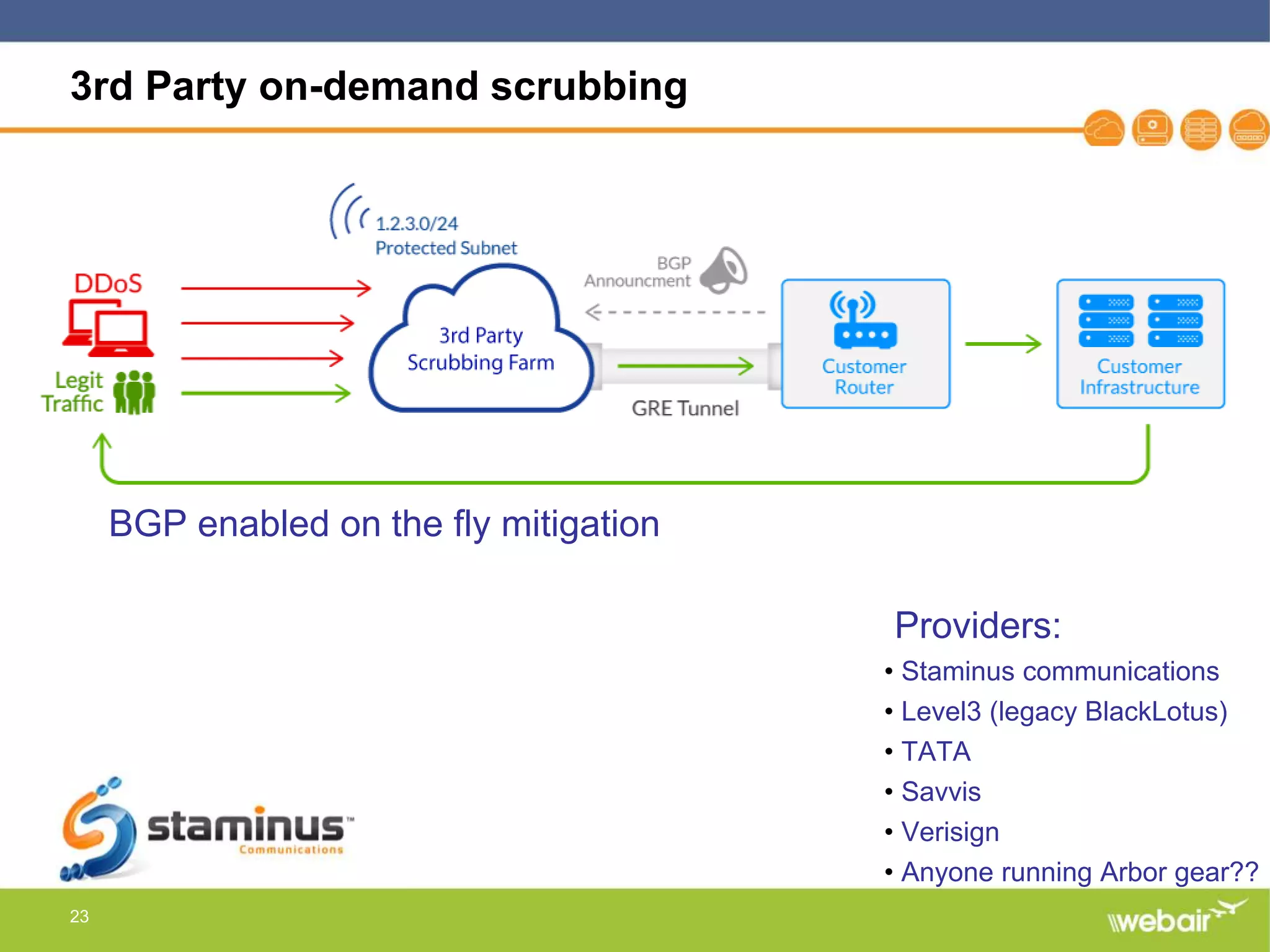
The document discusses multi-layer DDoS mitigation strategies for application servers, load balancers, and firewalls, emphasizing the increasing complexity of DDoS attacks and the rise of DDoS-as-a-service. It outlines various protective measures, including server layer configurations, load balancer features, and the use of third-party scrubbing providers. The content also covers best practices for managing vulnerabilities at the application layer and details on securing network infrastructure to prevent attacks.