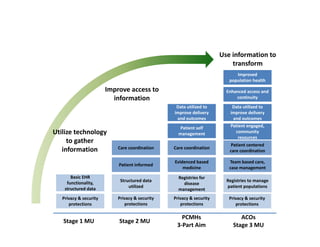
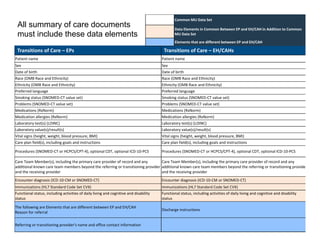
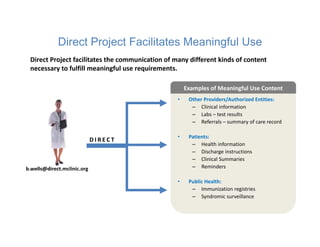
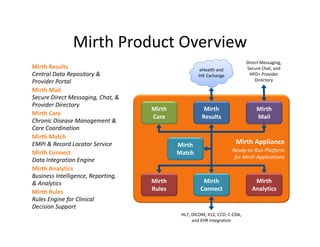
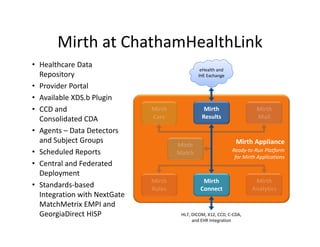
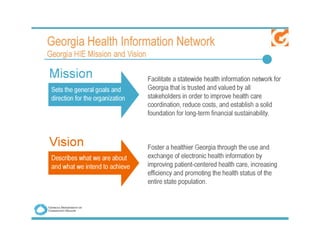
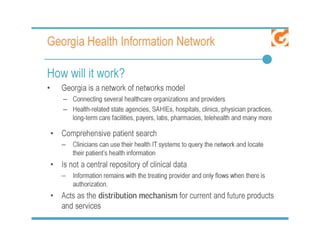
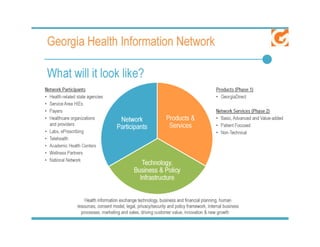
The document discusses meaningful use of health information exchange. It provides context from an IOM report on the need for health IT to support clinical processes. It defines meaningful use as using certified EHR technology to improve care quality, engage patients, improve care coordination, and maintain privacy/security. The stages and objectives of meaningful use are outlined, including core requirements for care coordination/transitions of care and medication reconciliation between providers. Standards for summary of care record contents are also listed.