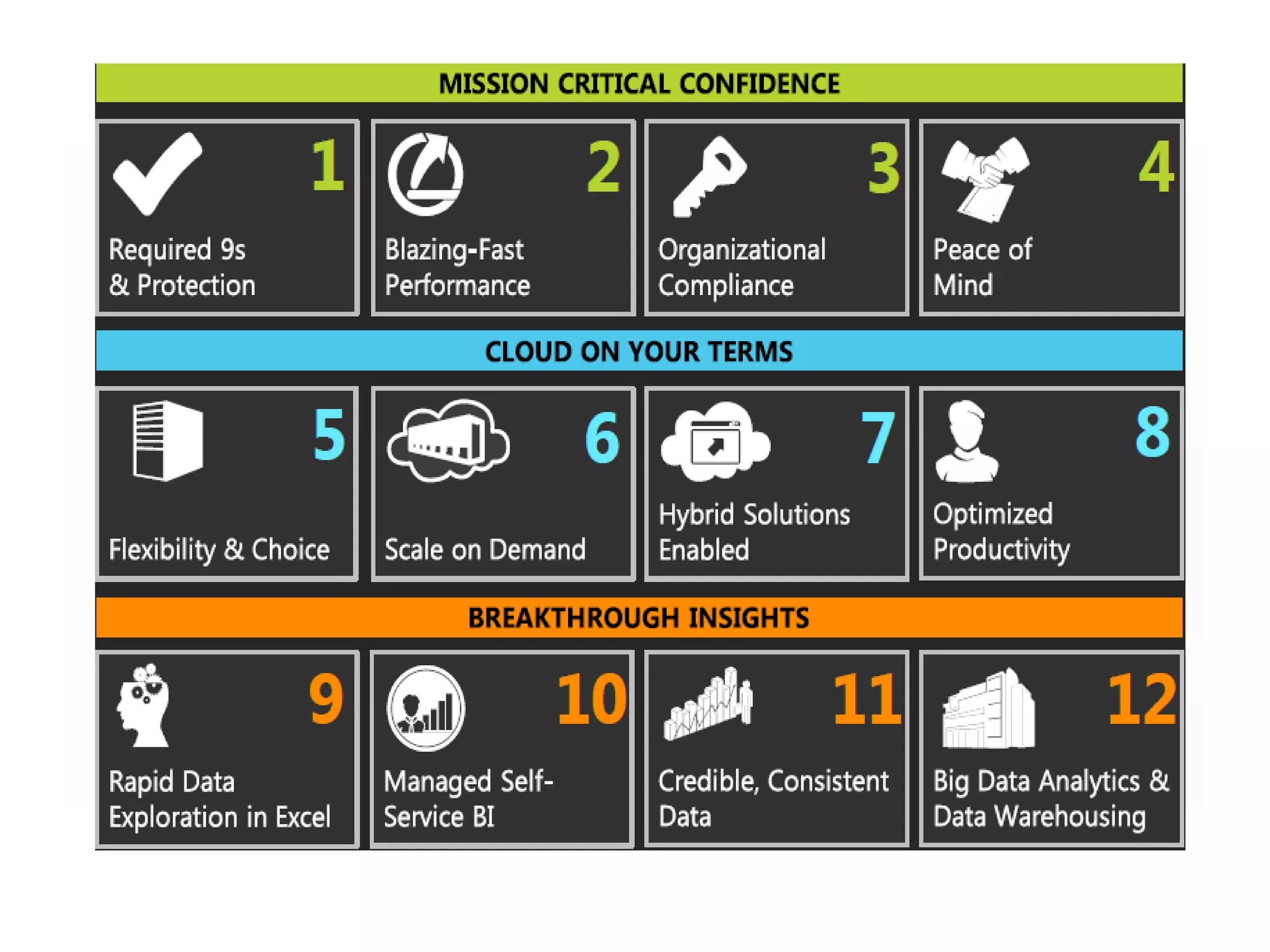
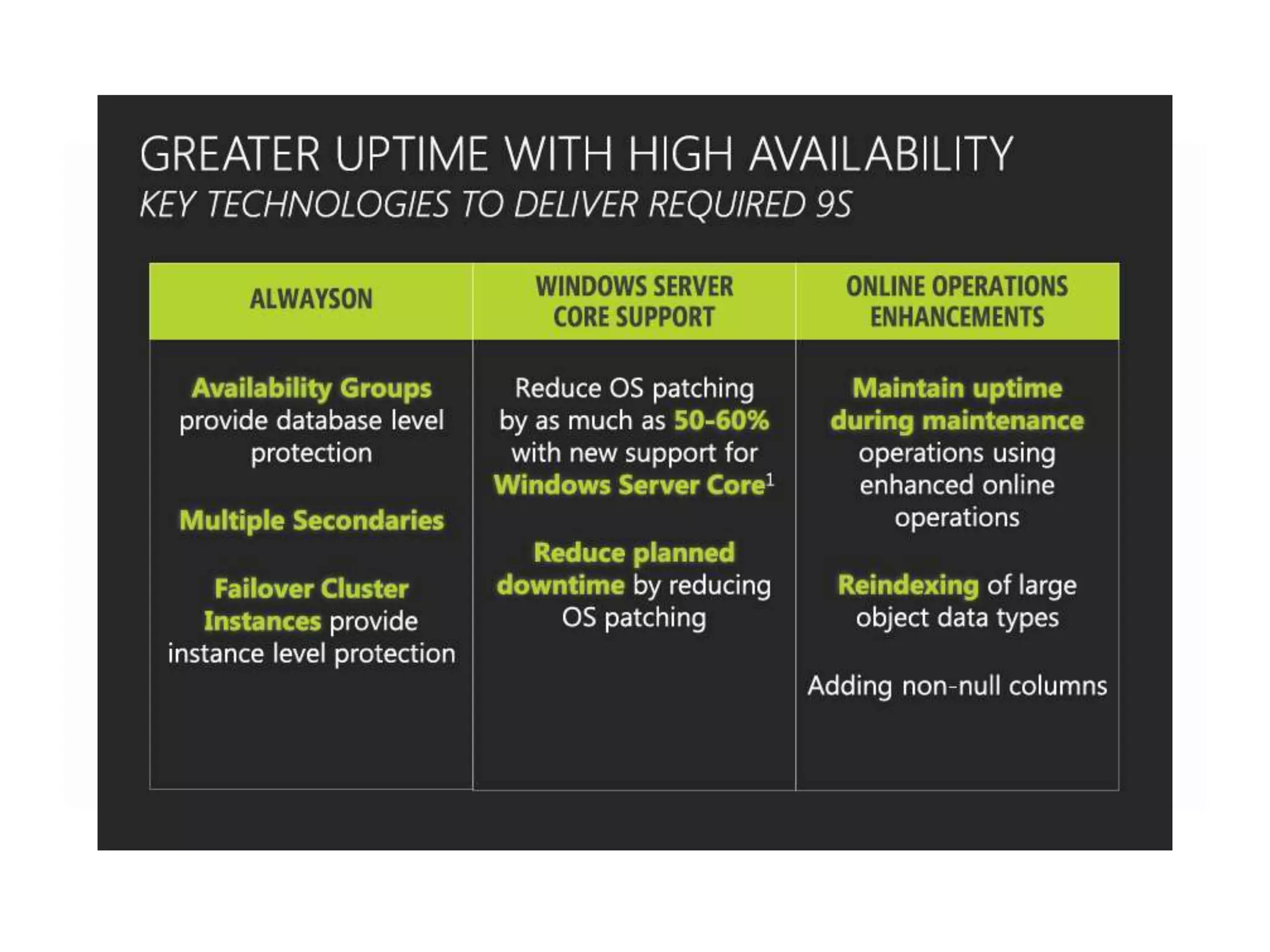
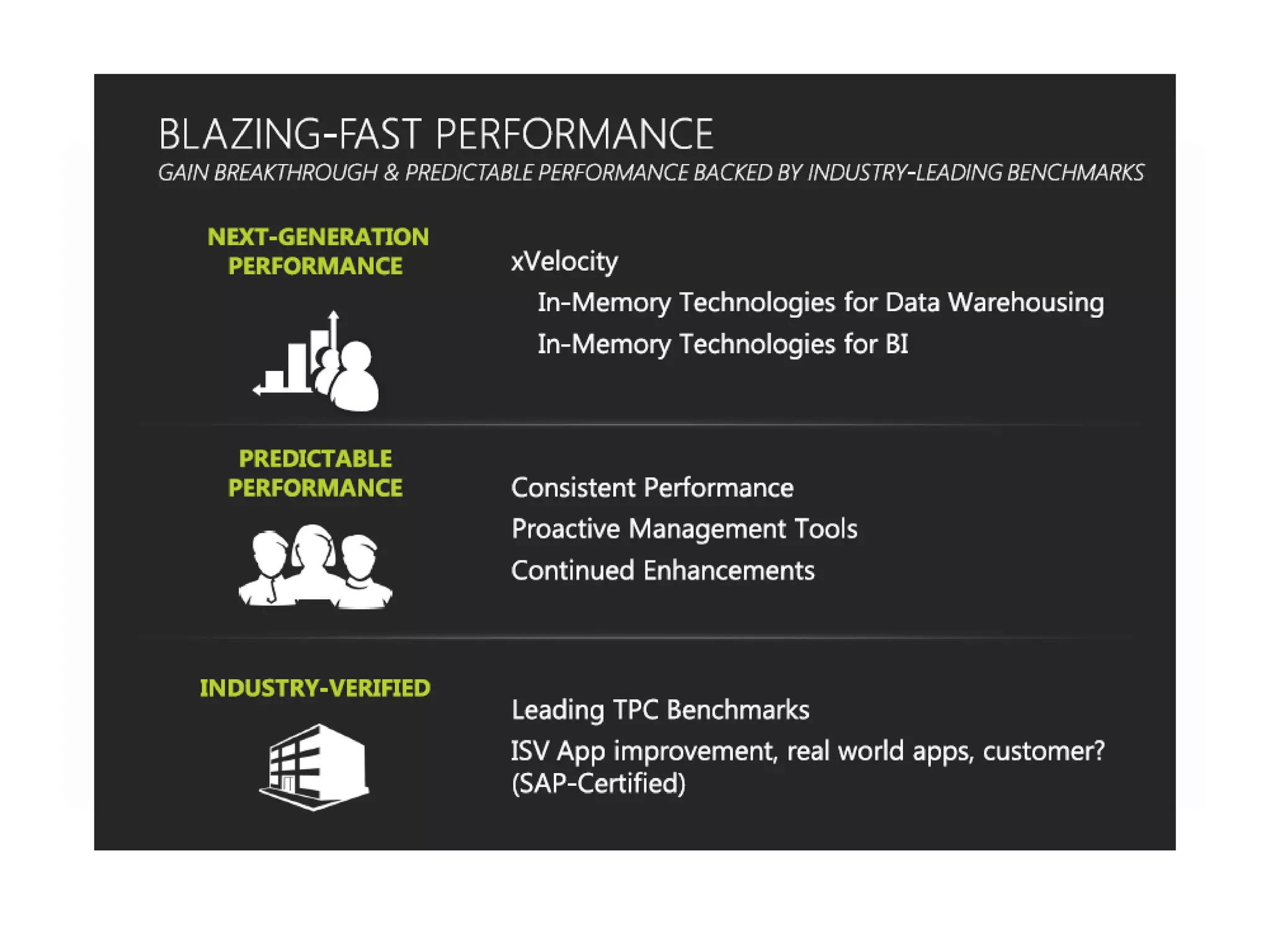
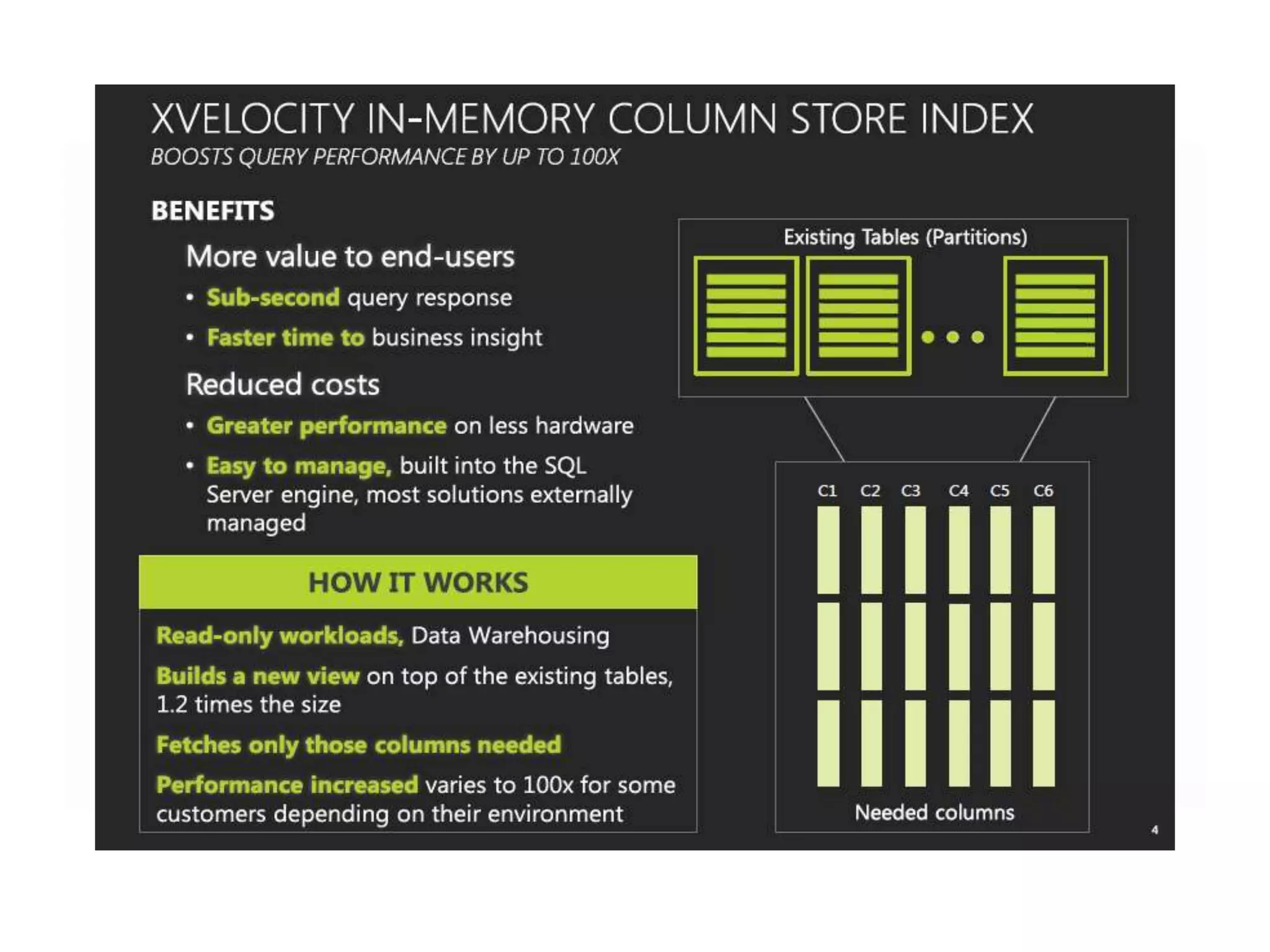
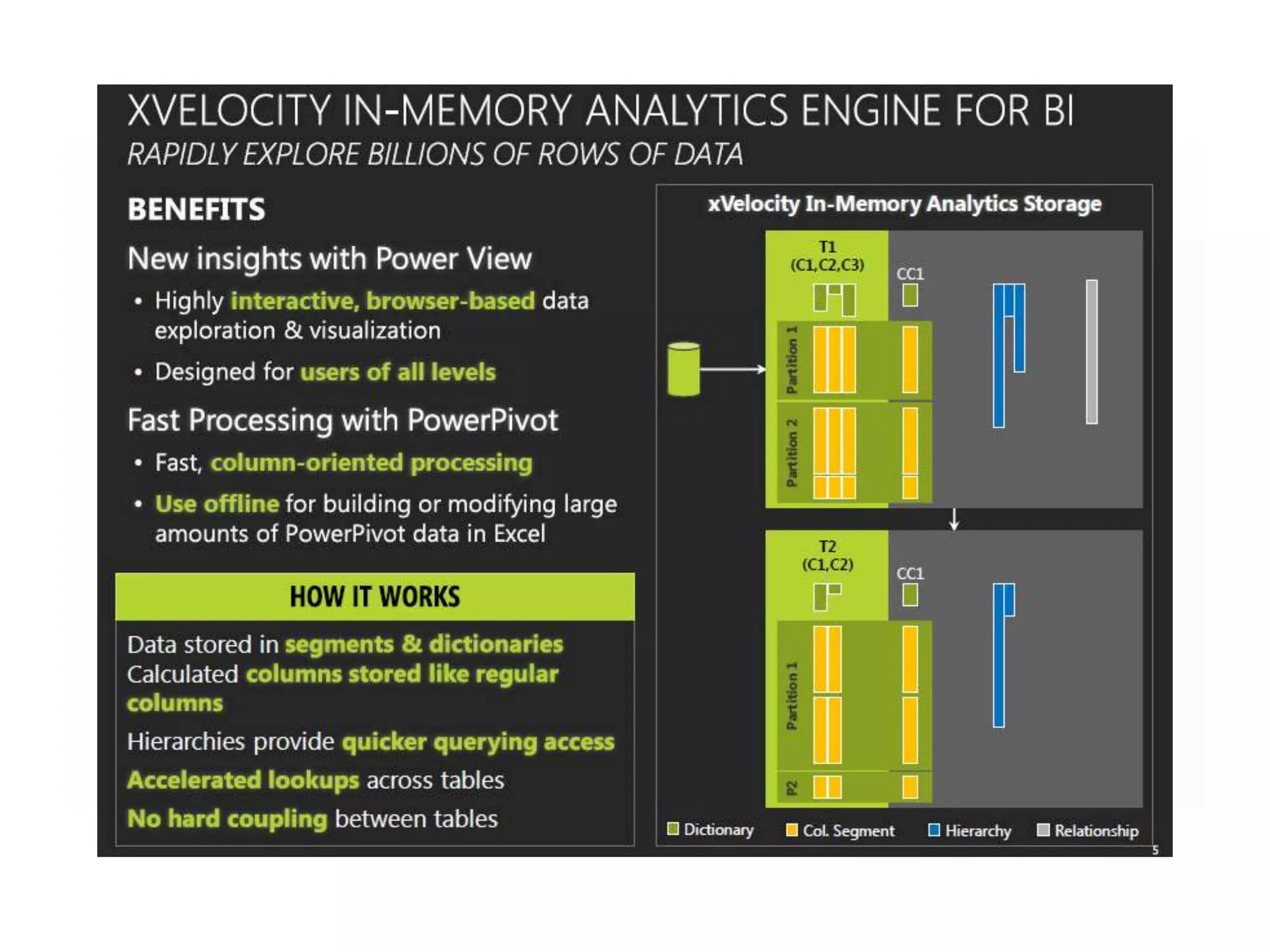
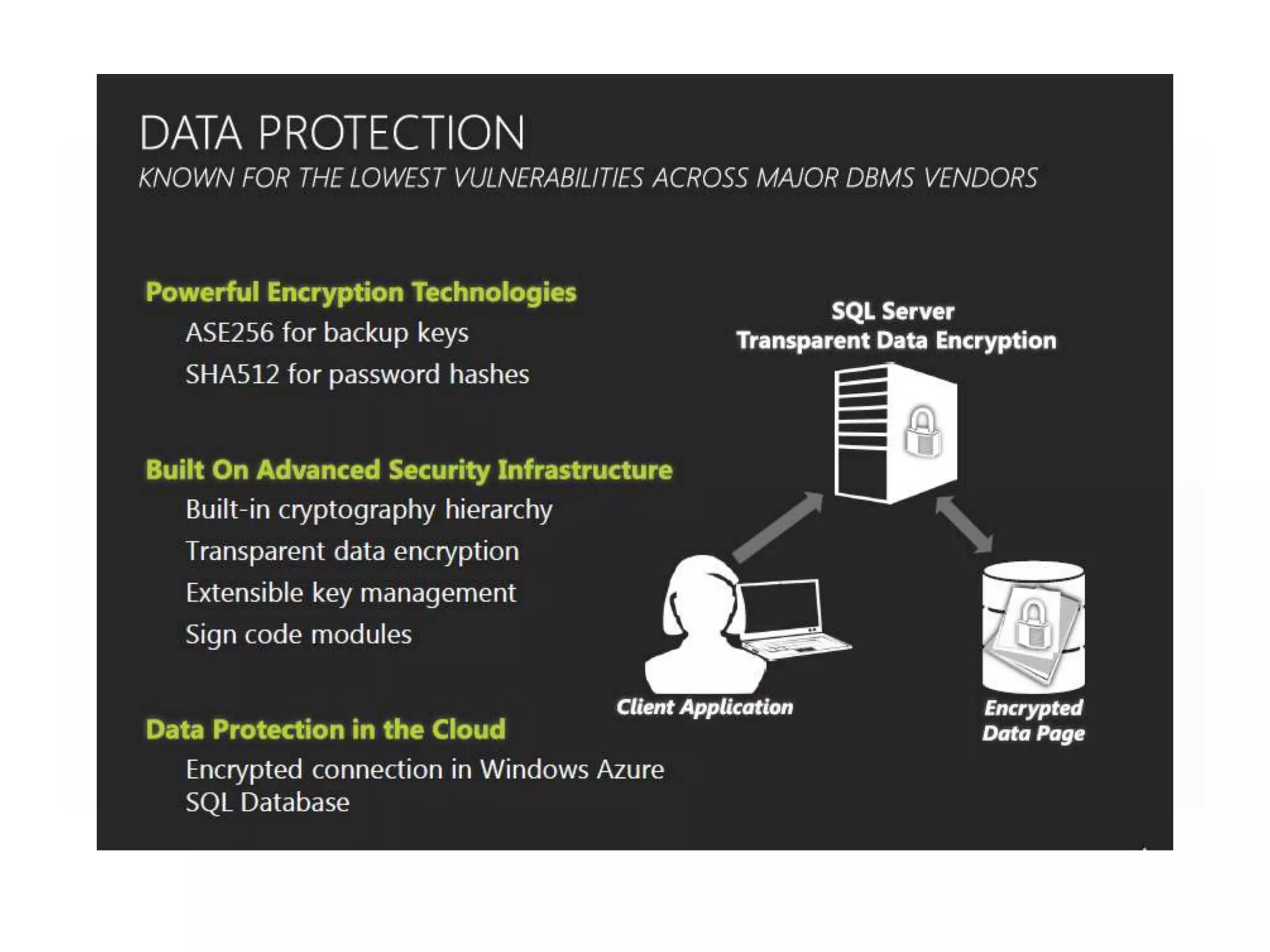
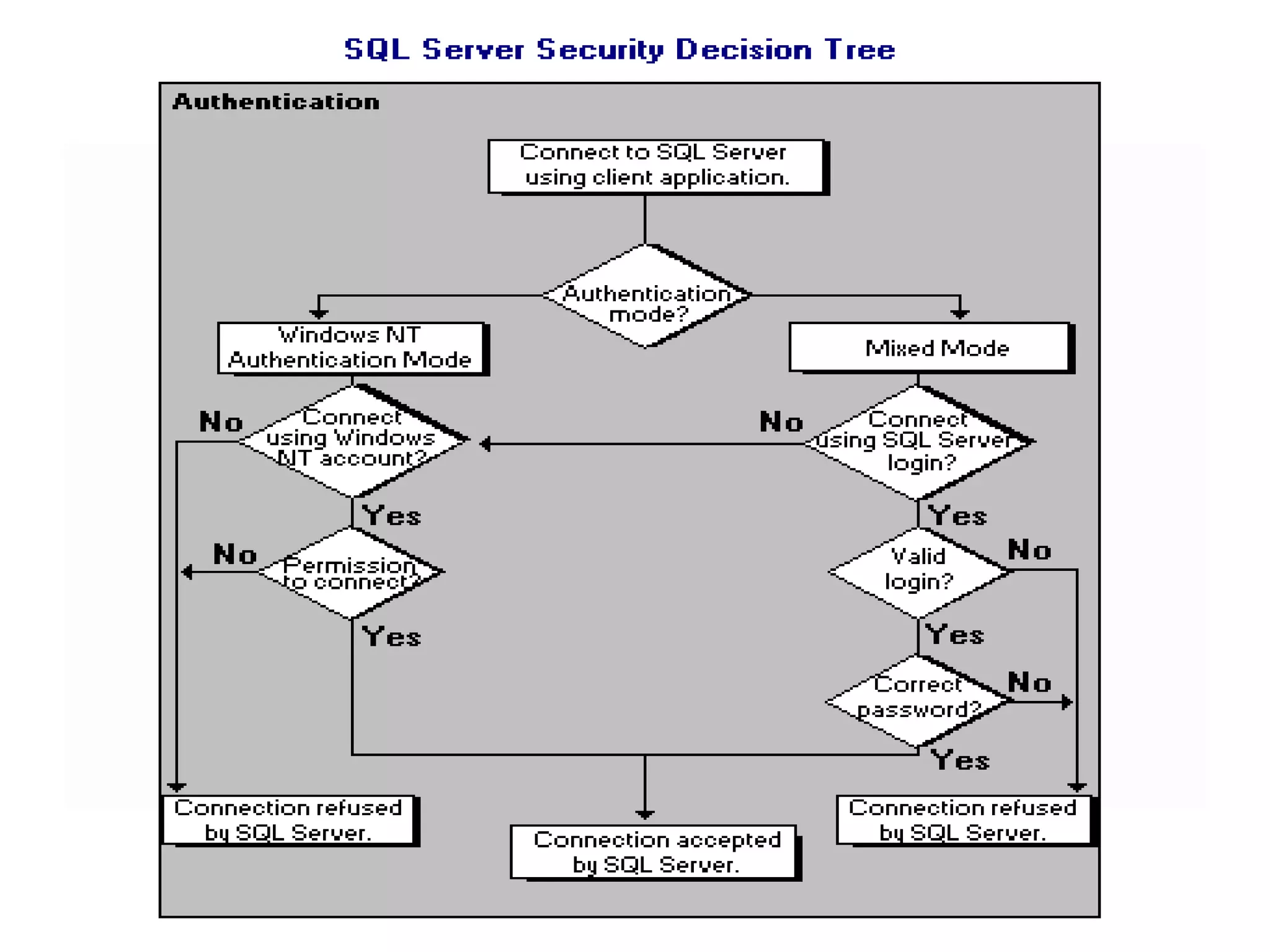
MS SQL is an RDBMS developed by Microsoft in C++ to support IA-32 and x64 platforms. It has evolved over several versions since 1989 when initially developed jointly with Sybase and Ashton-Tate for OS/2. Microsoft later developed versions for Windows including SQL Server 2000 which added features like failover clustering and XML support. The current version is SQL Server 2012 released in 2012 with editions for enterprise, business intelligence and standard use cases. It features high availability and in-memory analytics. The next version, SQL Server 2014, will deliver more in-memory capabilities and integration with Windows Azure.