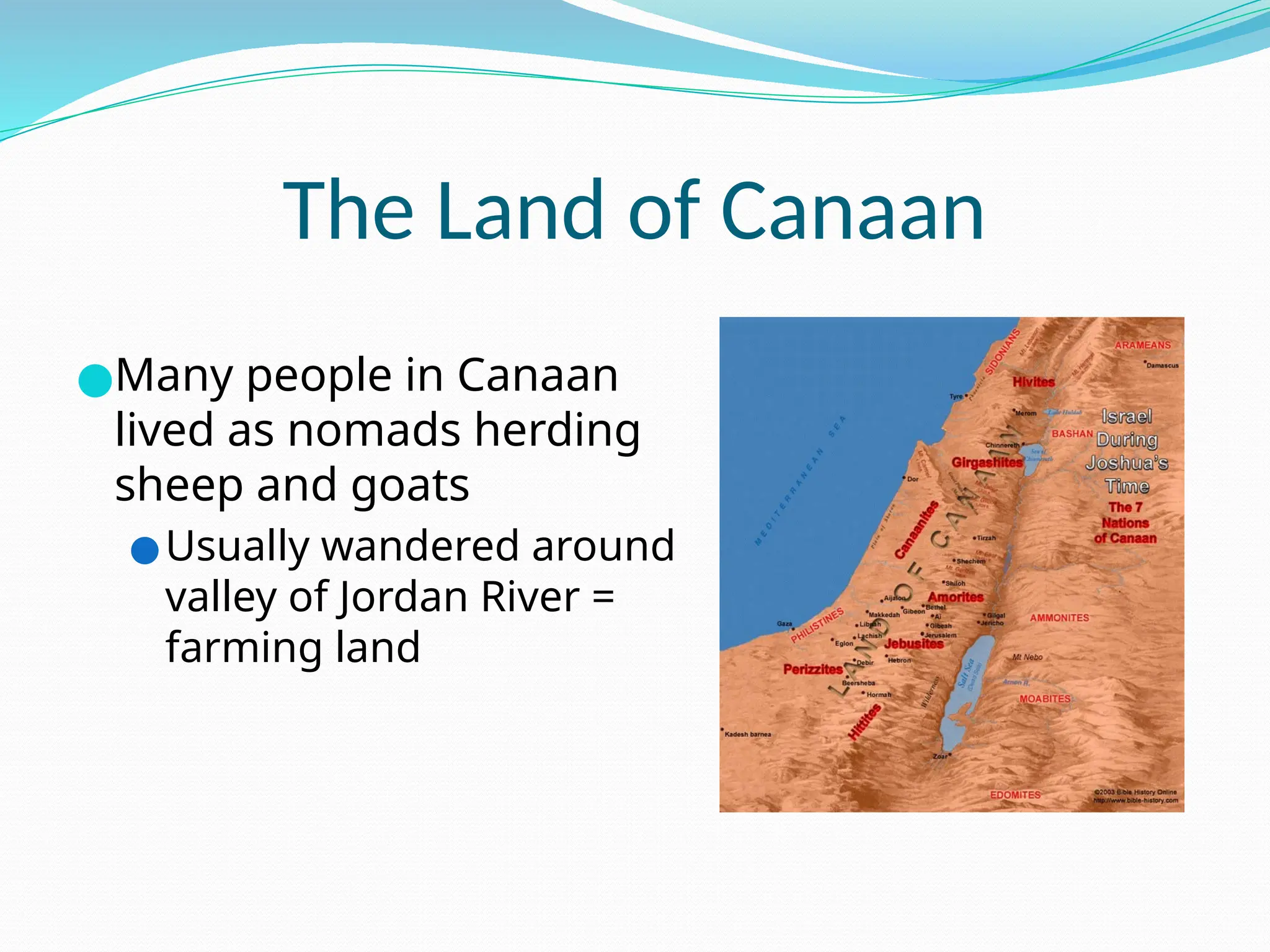
The document outlines the historical development of monotheistic religions, focusing on Zoroastrianism, Judaism, and early Christianity, detailing their beliefs, key figures, and events. It highlights the influences and struggles these faiths faced over time, including the rise of synagogues, the impact of Roman rule, and the eventual formalization of Christianity as a major religion. Additionally, it describes the structural evolution of the Christian church and the significant schism between Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy.