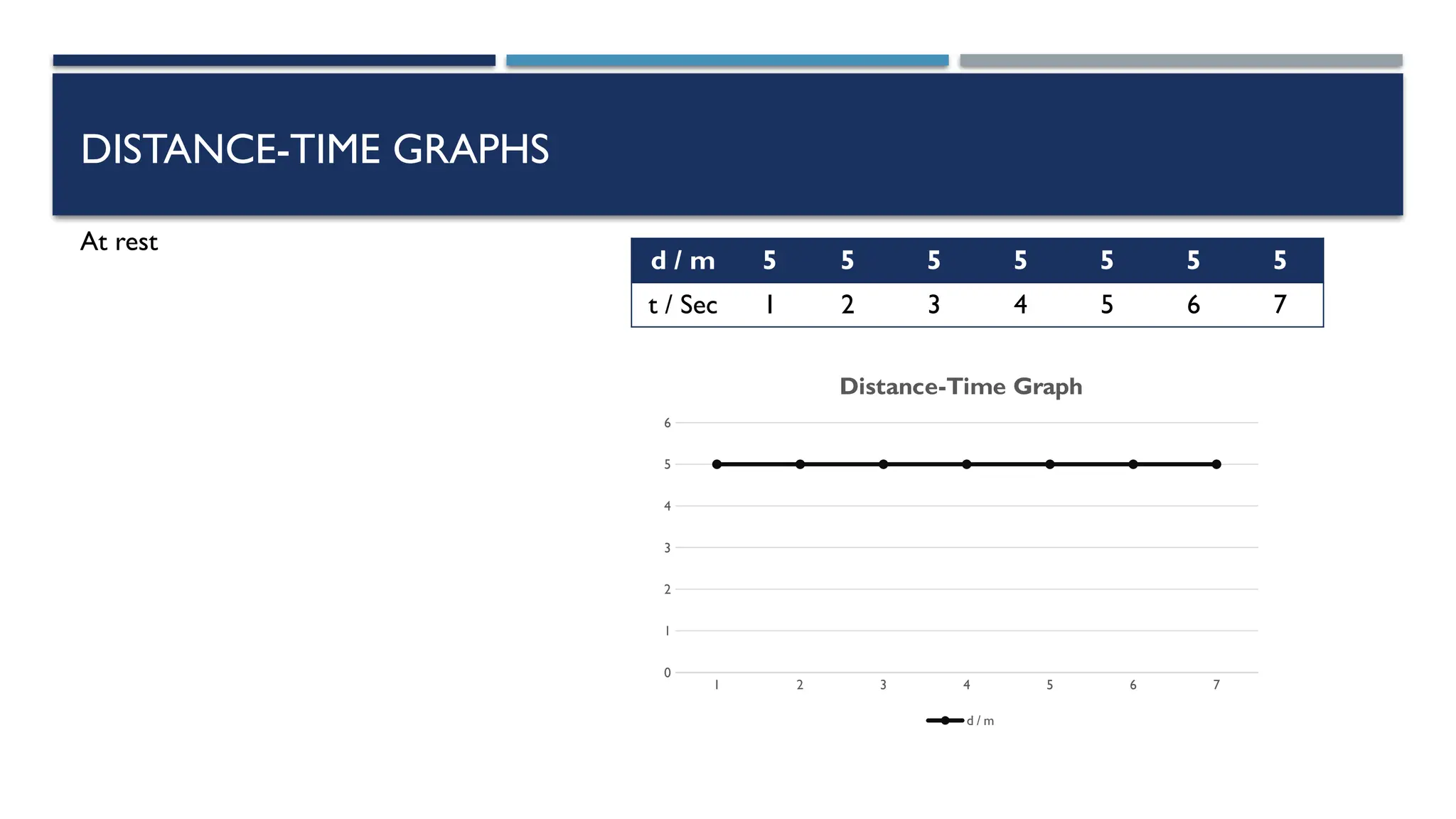
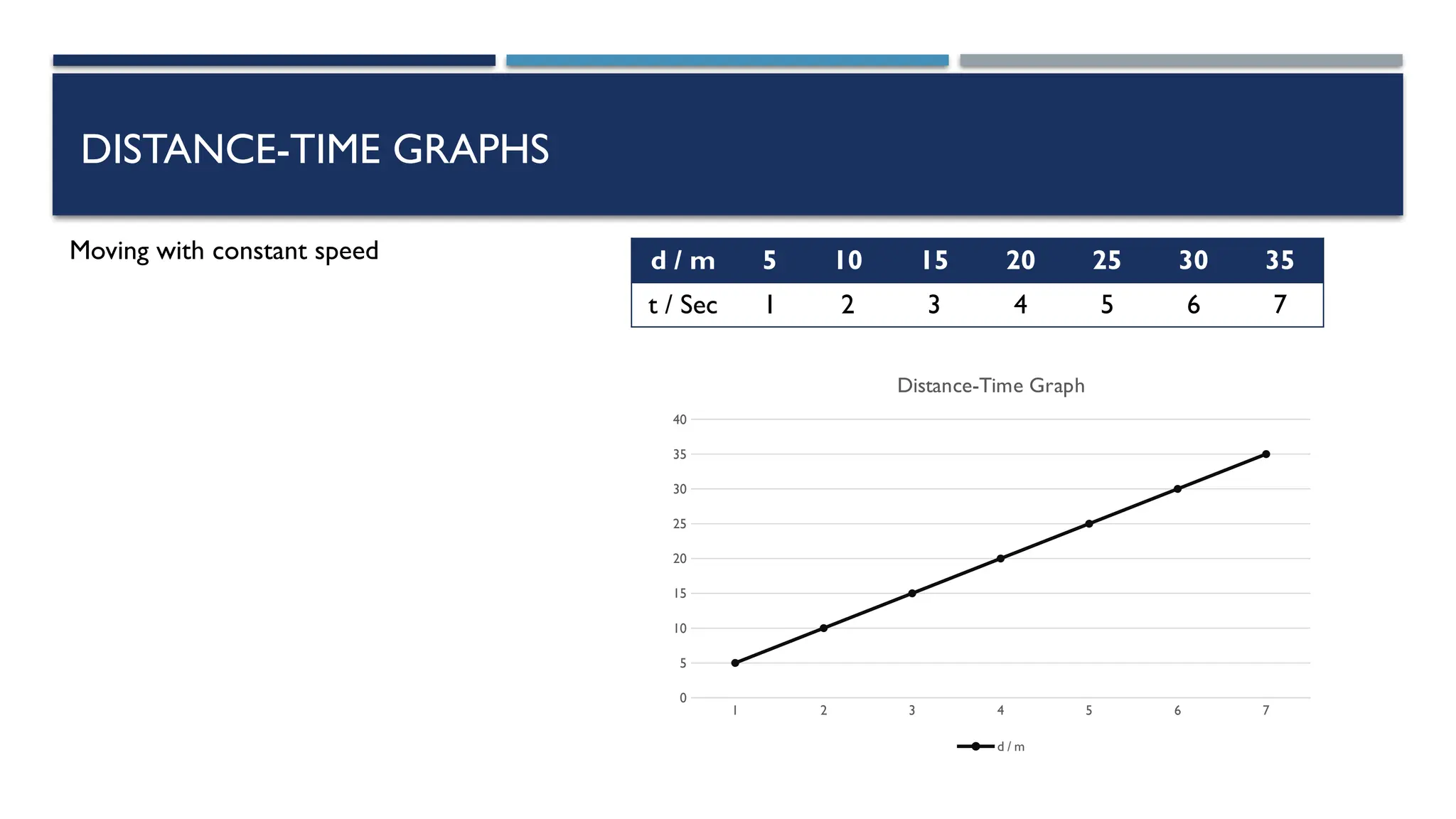
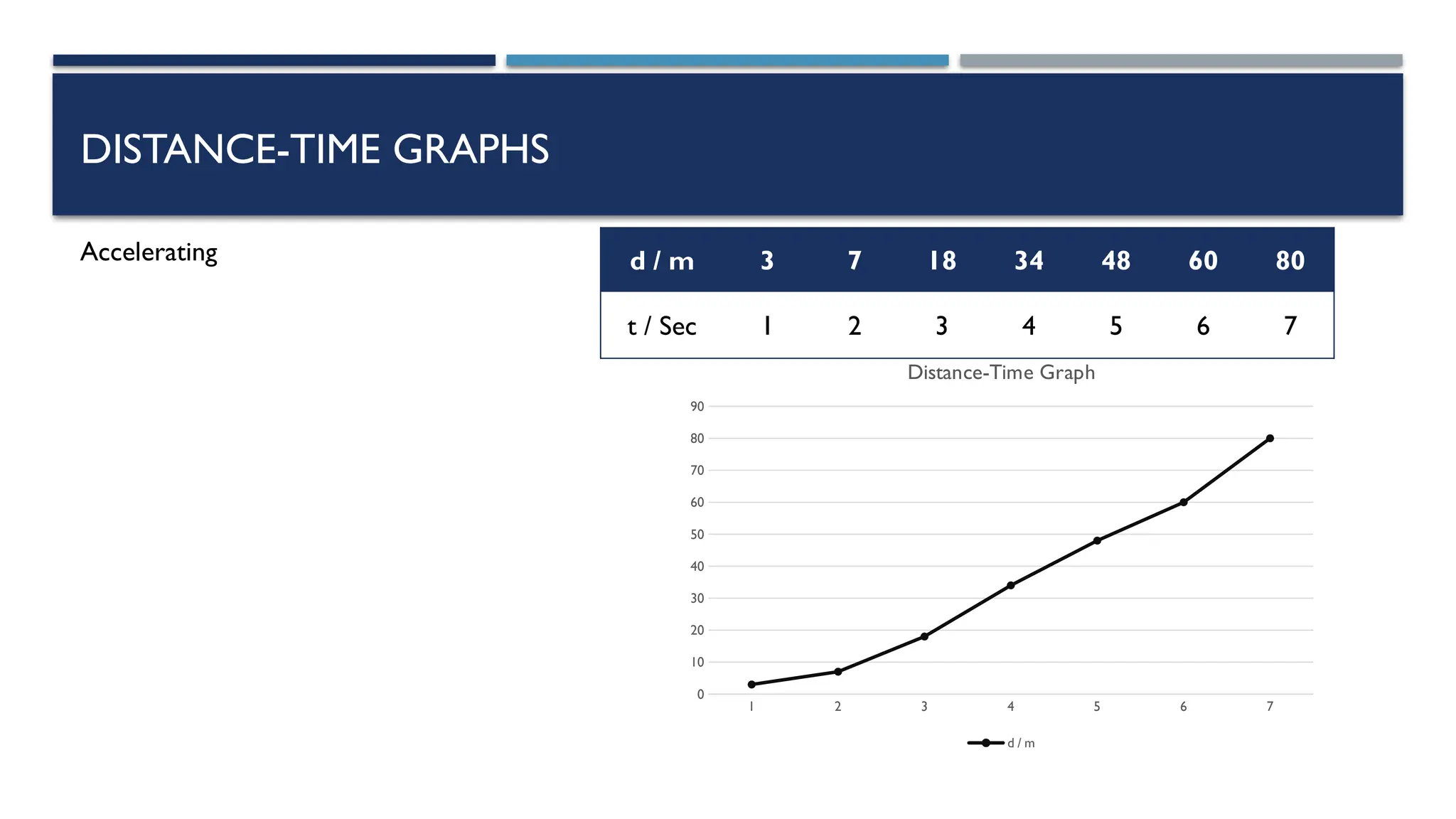
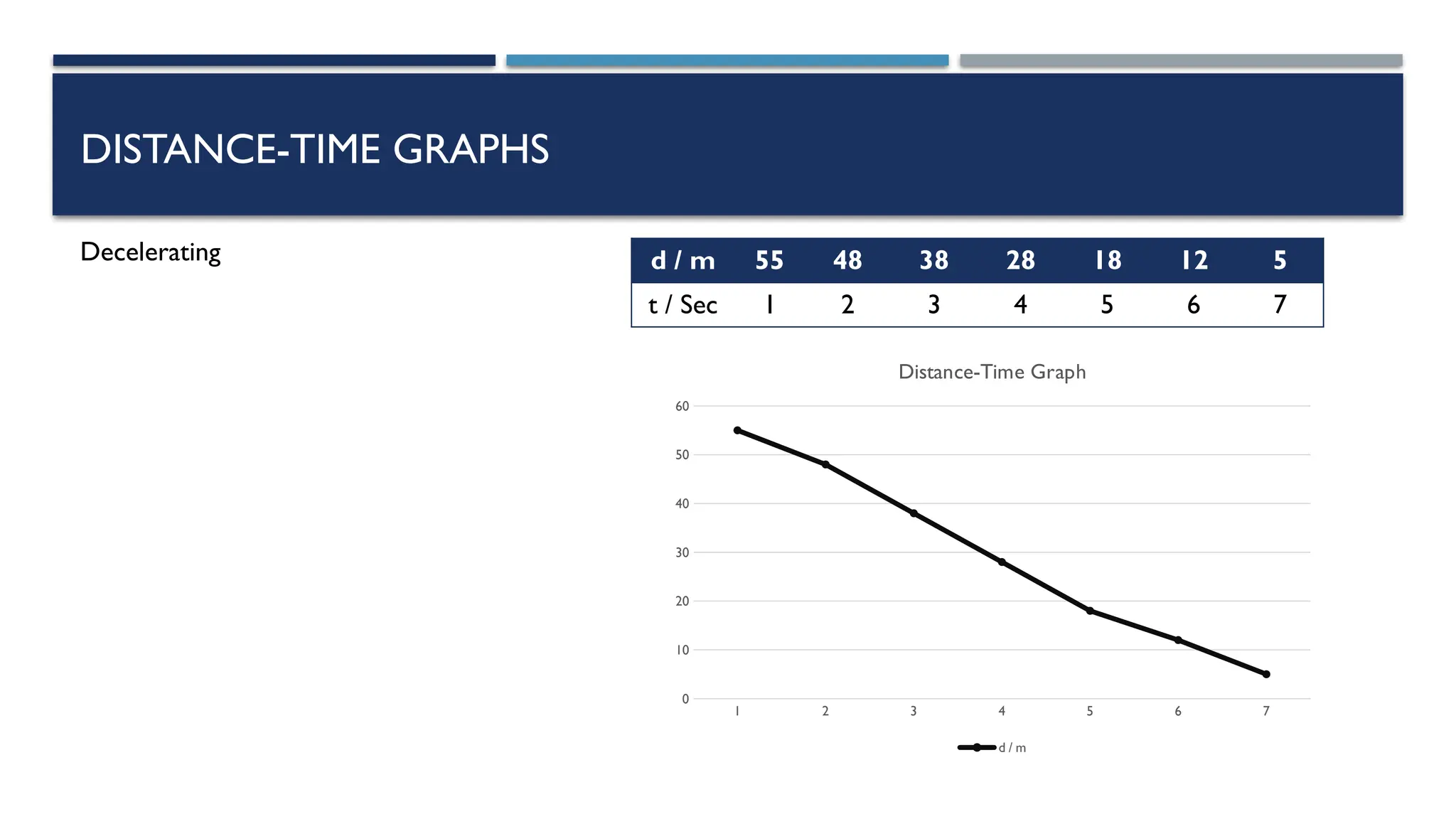
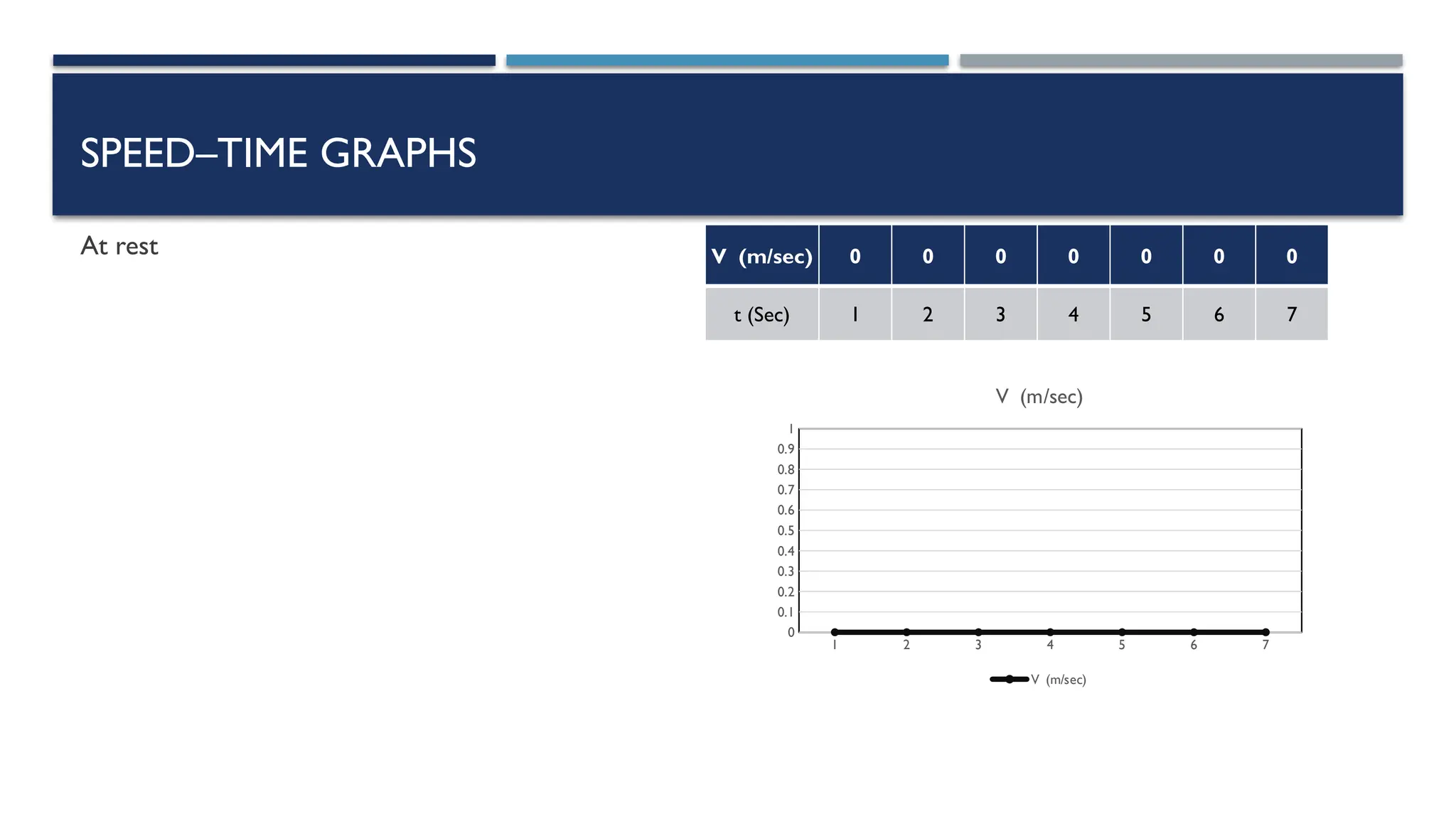
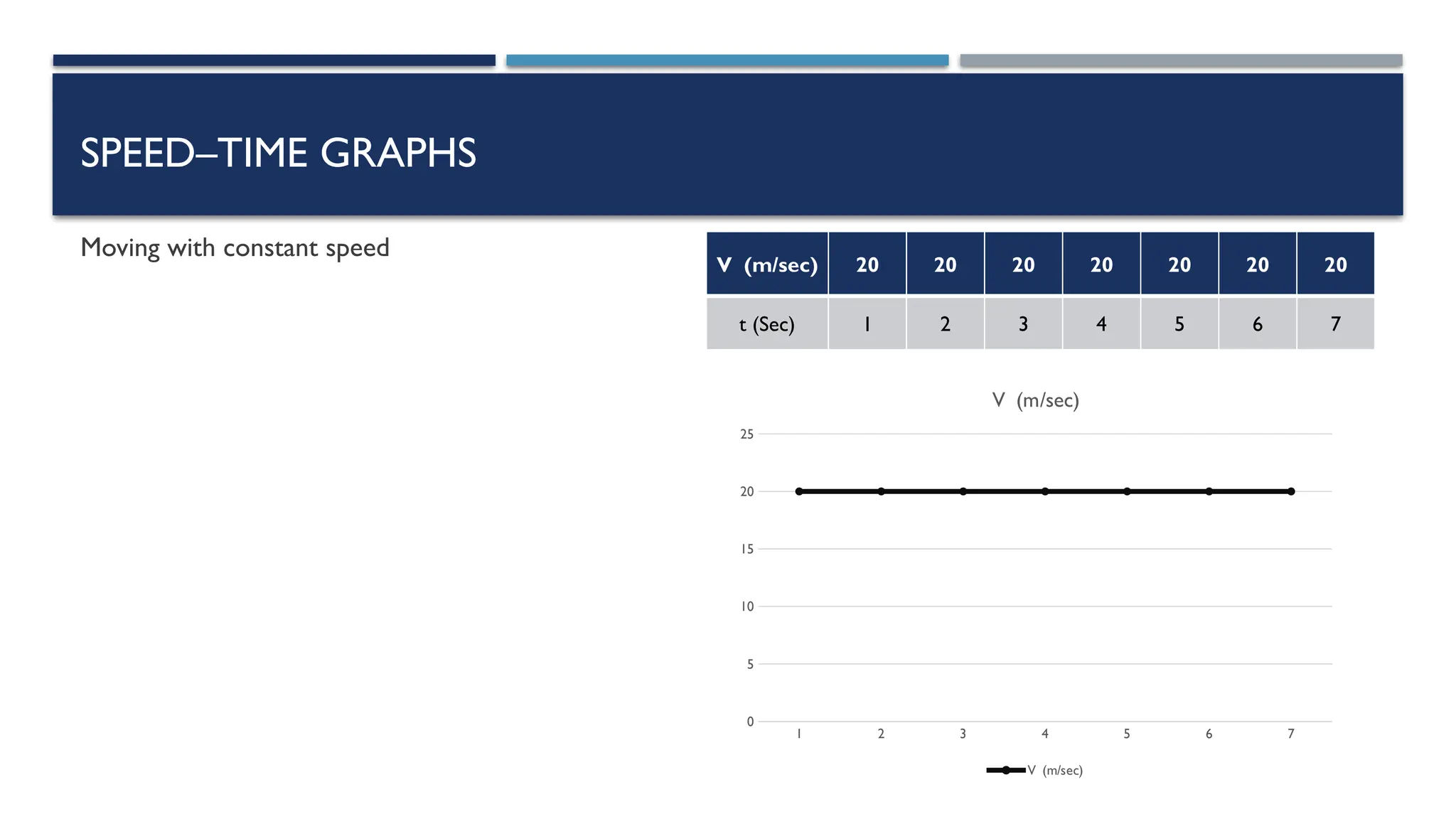
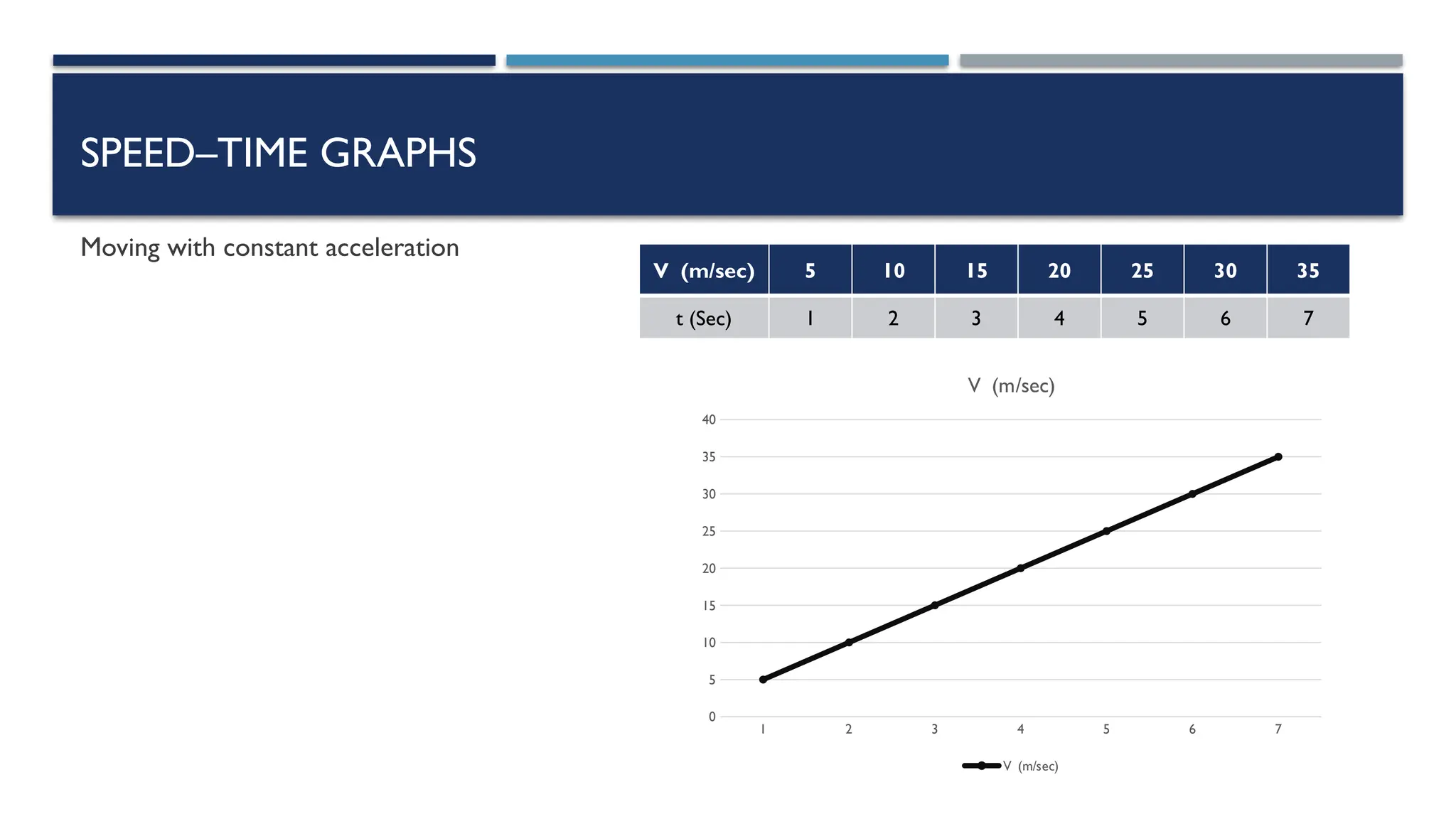
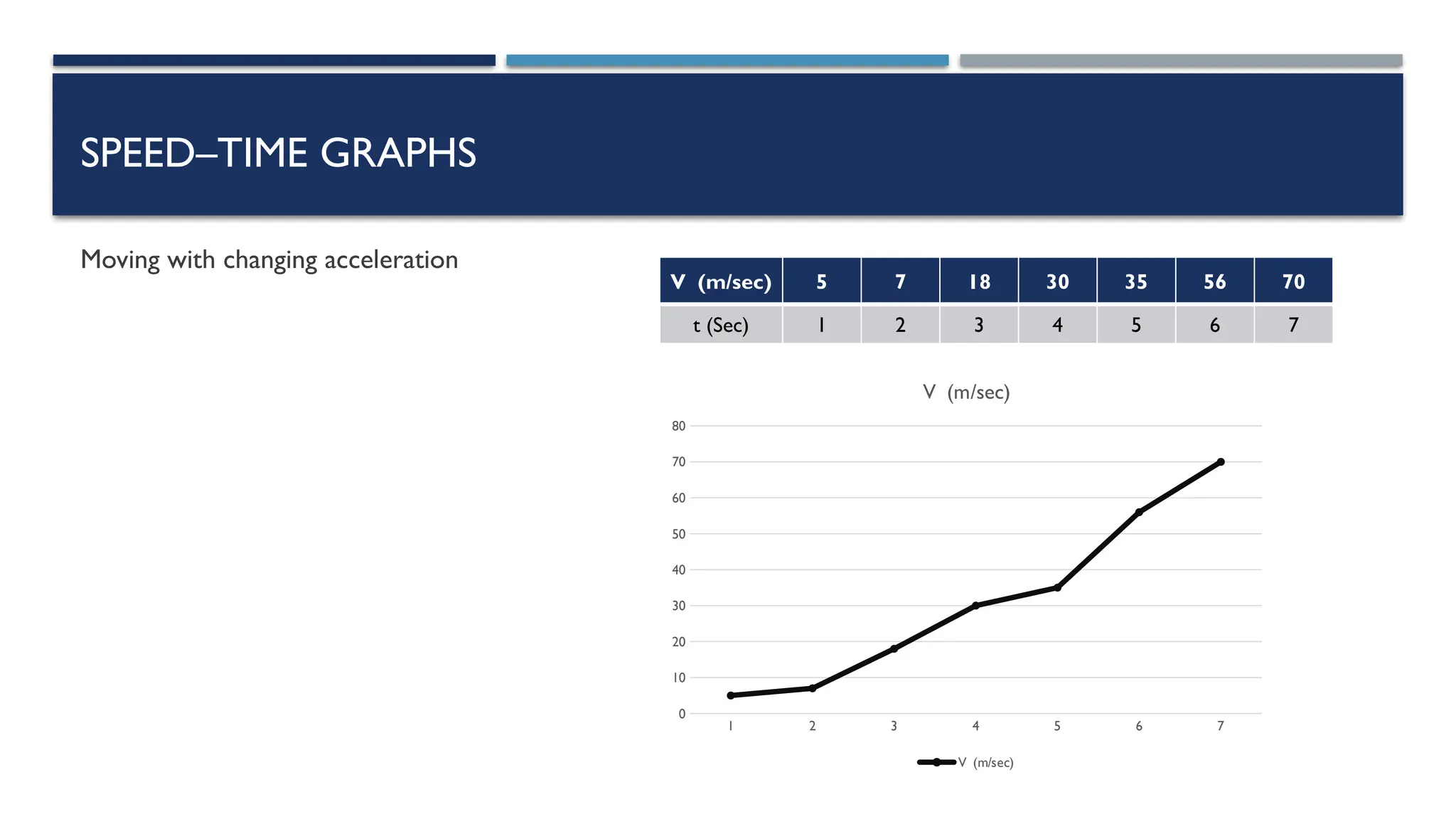
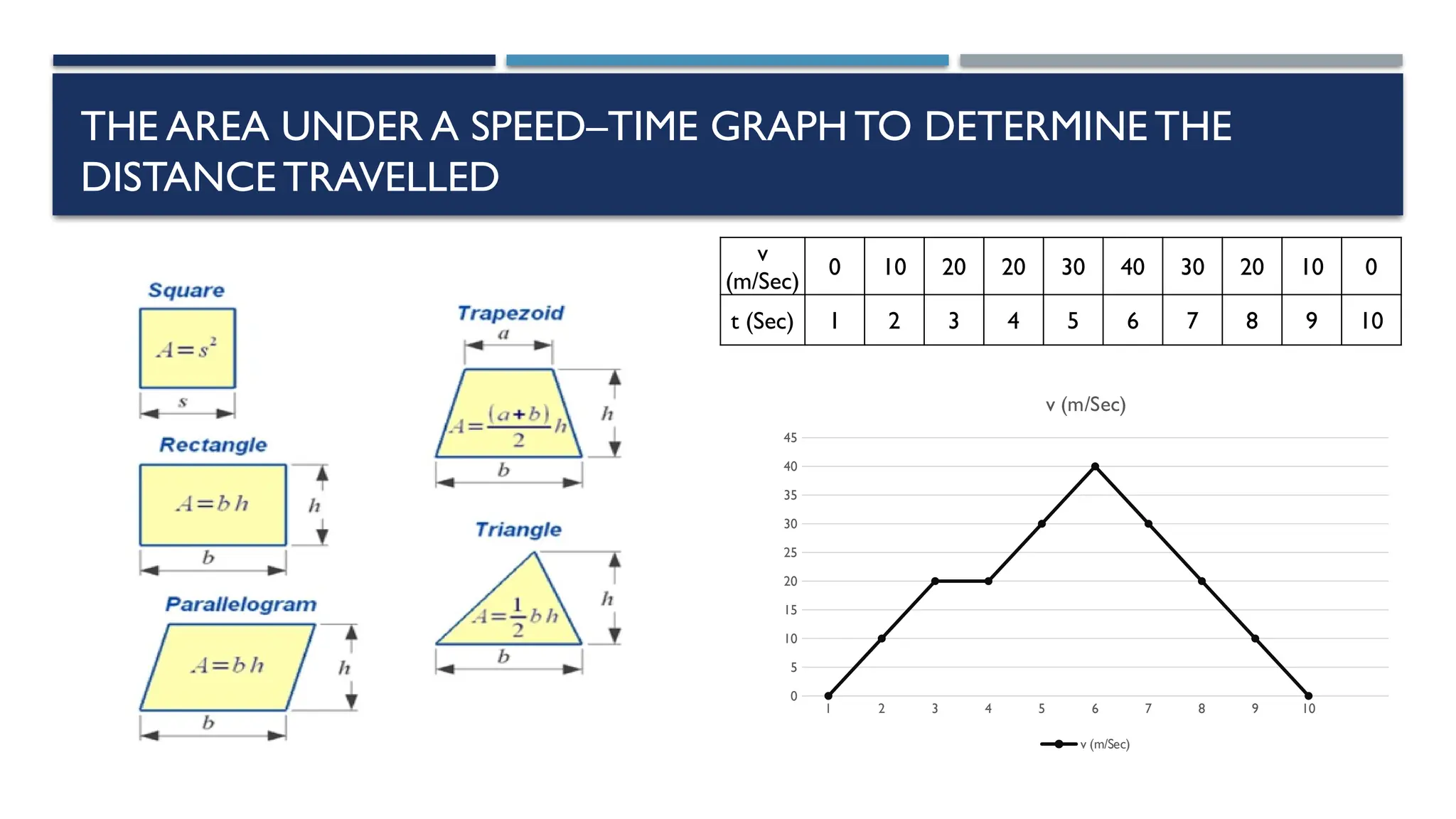
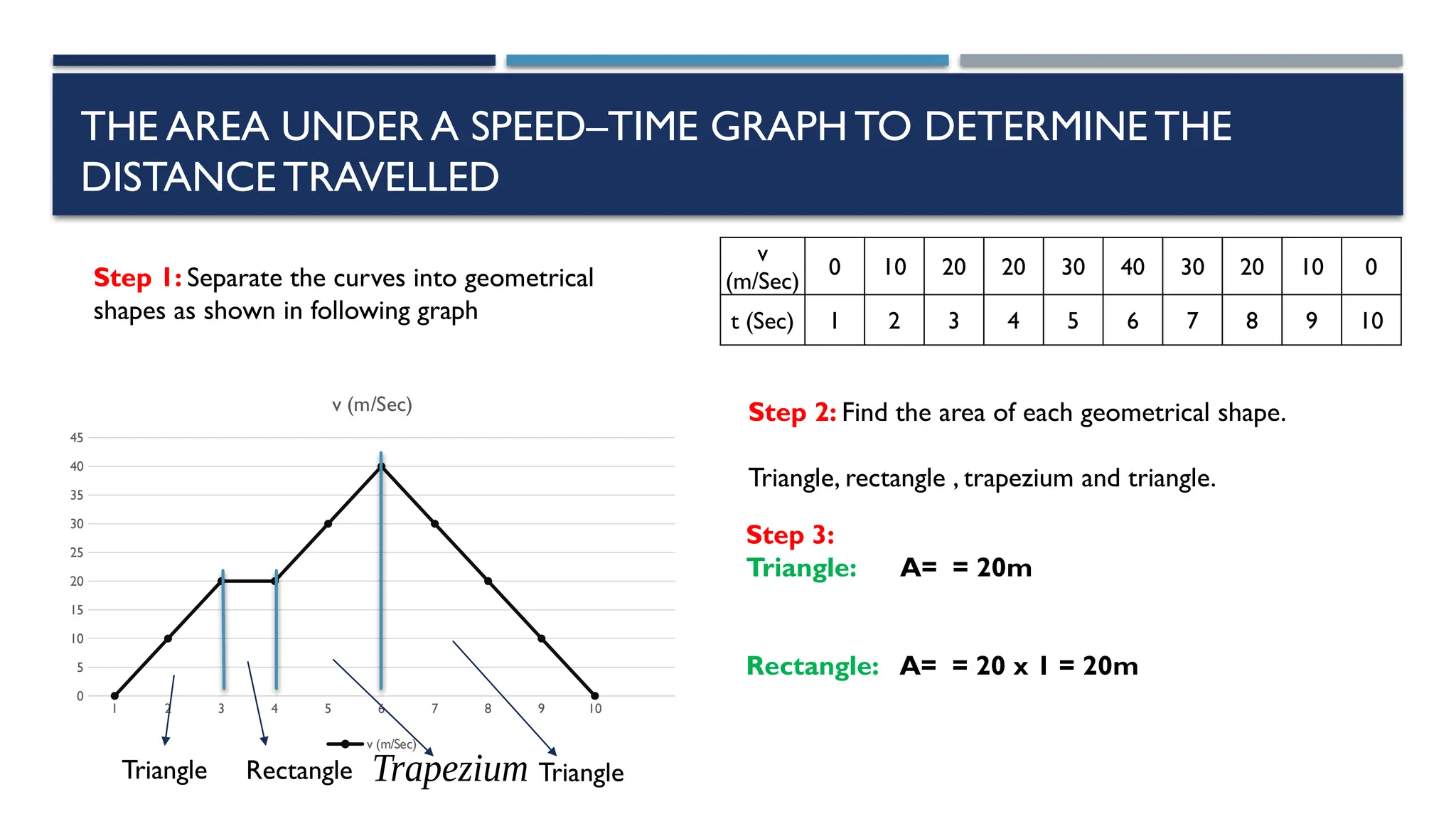
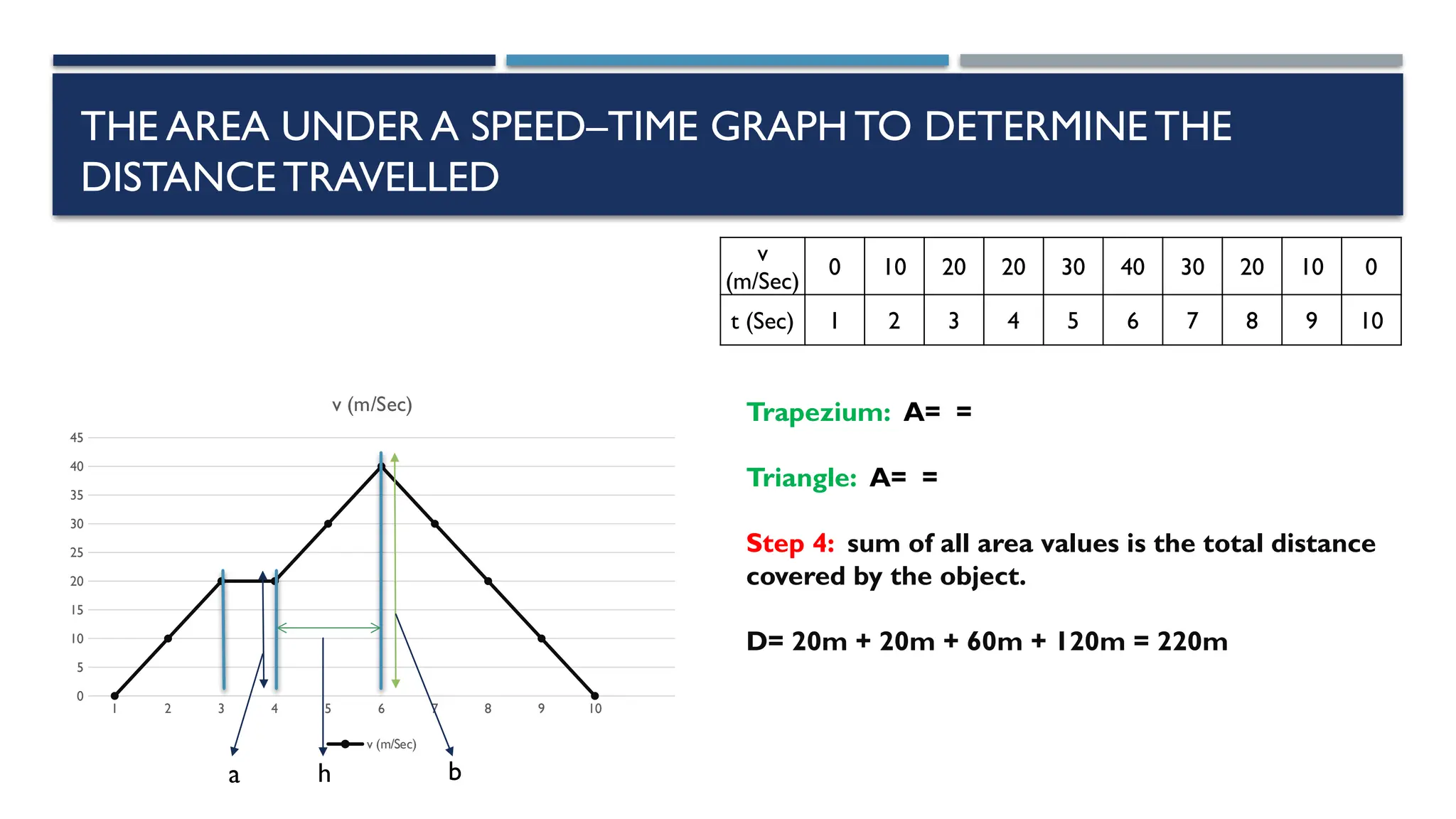
The document outlines key physics concepts related to motion, including how to interpret distance-time and speed-time graphs to determine an object's status (at rest, moving with constant speed, accelerating, or decelerating). It discusses the acceleration due to gravity (g) as approximately 9.8 m/s² near Earth's surface and factors affecting it, such as altitude and depth. Additionally, it explains how to calculate speed and distance traveled using the area under a speed-time graph.