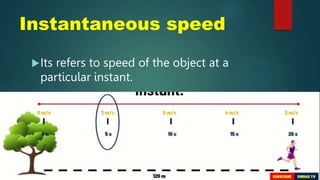
Speed is a scalar quantity that describes the distance traveled per unit of time. Common units include km/h, m/s, and mi/h. Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction. Average speed represents the total distance traveled divided by the total time, while instantaneous speed refers to the speed at a particular moment. Constant speed means the speed stays the same over the distance and time traveled. An example calculates a runner's average velocity from their change in position over a period of time.