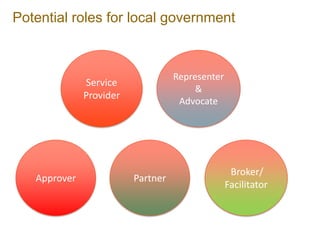
This document discusses international best practices for the role of local governments in multi-stakeholder collaboration for socially responsible mining and sustainable community development. It outlines how mining can impact and provide opportunities for local communities. The roles local governments could play are discussed, including as a service provider, advocate, approver, and partner. However, many local governments have limited capacity and capabilities to effectively participate. Suggestions are provided to strengthen local governments' involvement, such as requiring company consultation, education, training, and technical support. An example from Australia shows how one local council and mining company collaborated on economic diversification planning.