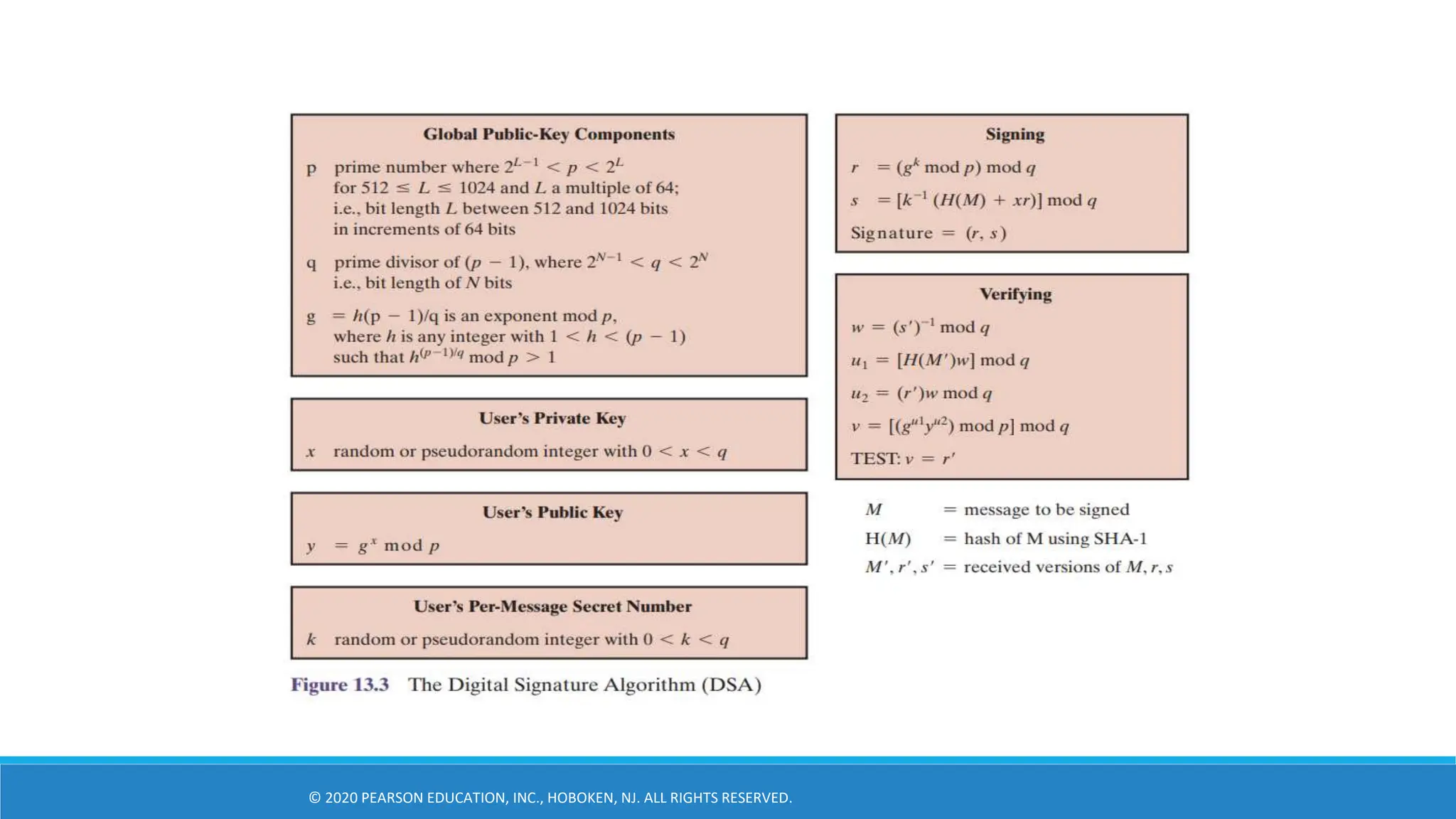
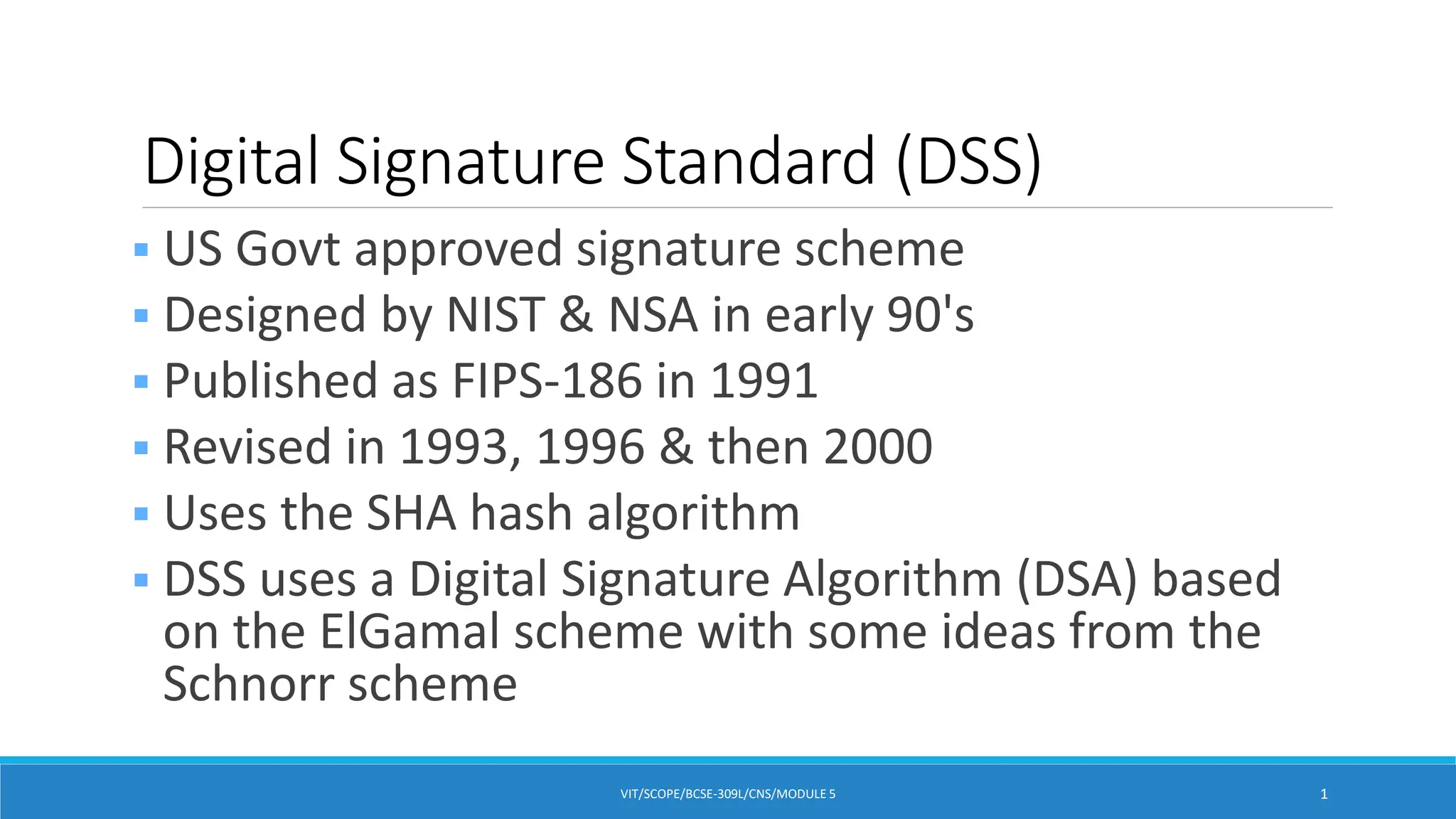
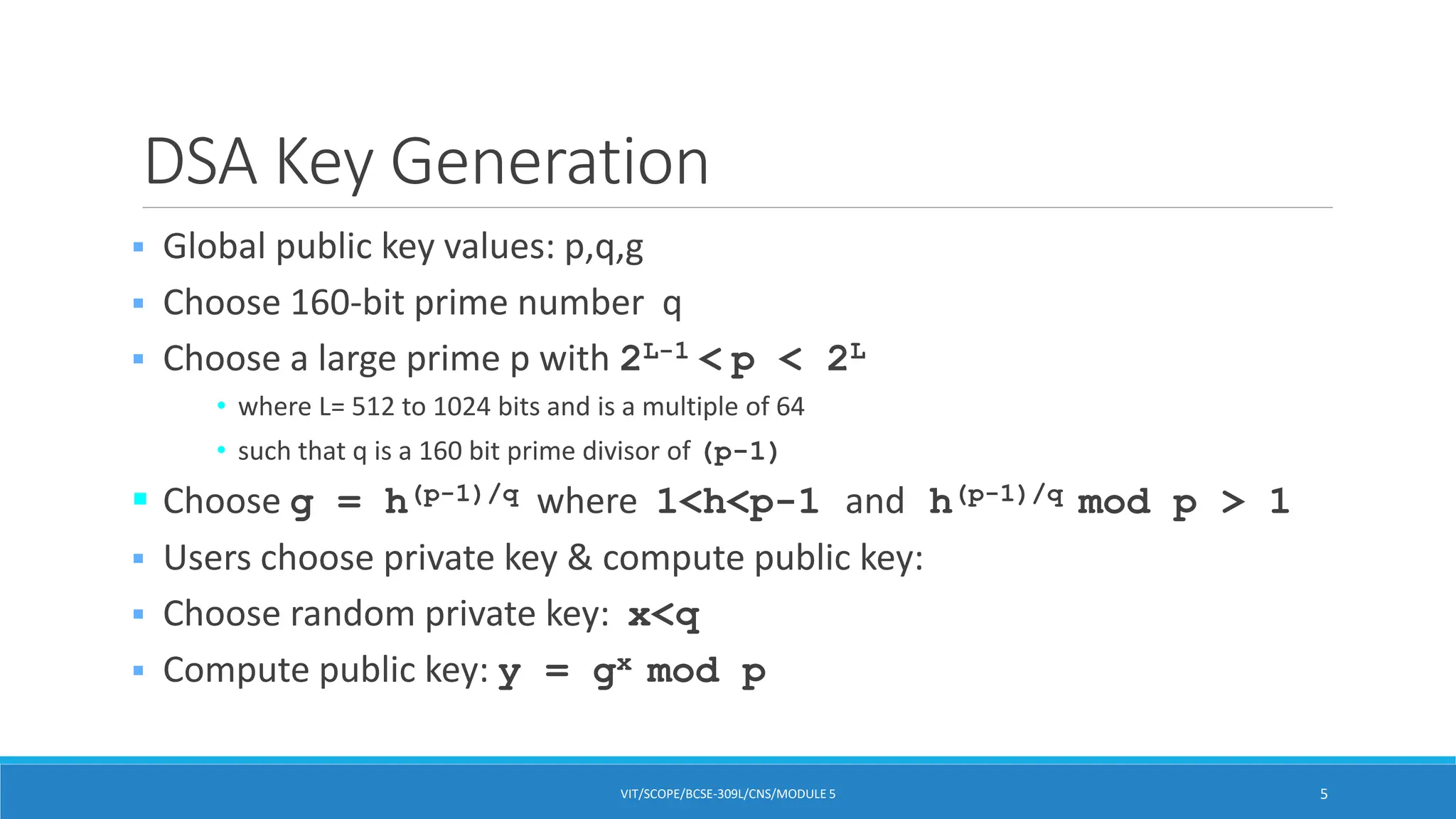
The Digital Signature Standard (DSS) was designed by NIST and NSA in the early 1990s to be a US government approved digital signature scheme. It uses the Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA) which creates 320-bit signatures with 512-1024 bit security, making it smaller and faster than RSA. DSA is based on the discrete logarithm problem and uses public and private keys to generate signatures for verification in a similar way to the ElGamal and Schnorr signature schemes.
![© 2020 PEARSON EDUCATION, INC., HOBOKEN, NJ. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
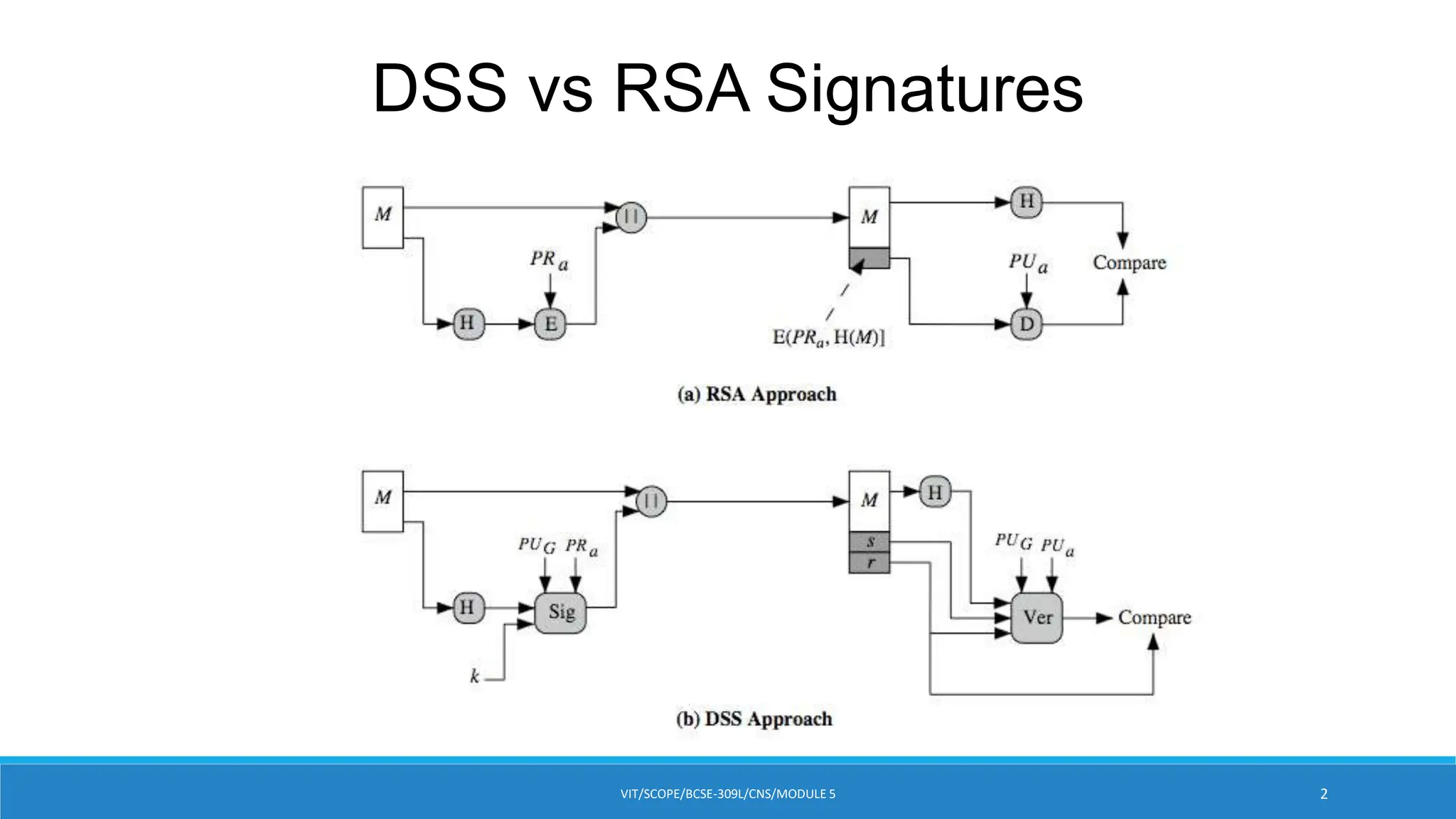
Figure 13.2 Two Approaches to Digital Signatures
M
H
| |
PR a
(a) RSA Approach
M
E(PRa, H(M)]
E D
H
Compare
PUa
M
H
| |
PR a
PUG
M
Sig Ver
H
Compare
k
s
r
PUa
PUG
(b) DSA Approach](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module5-dss-240417042850-b7483500/75/Module-5-DSS-pptx-crypto-currency-notes-incoming-3-2048.jpg)
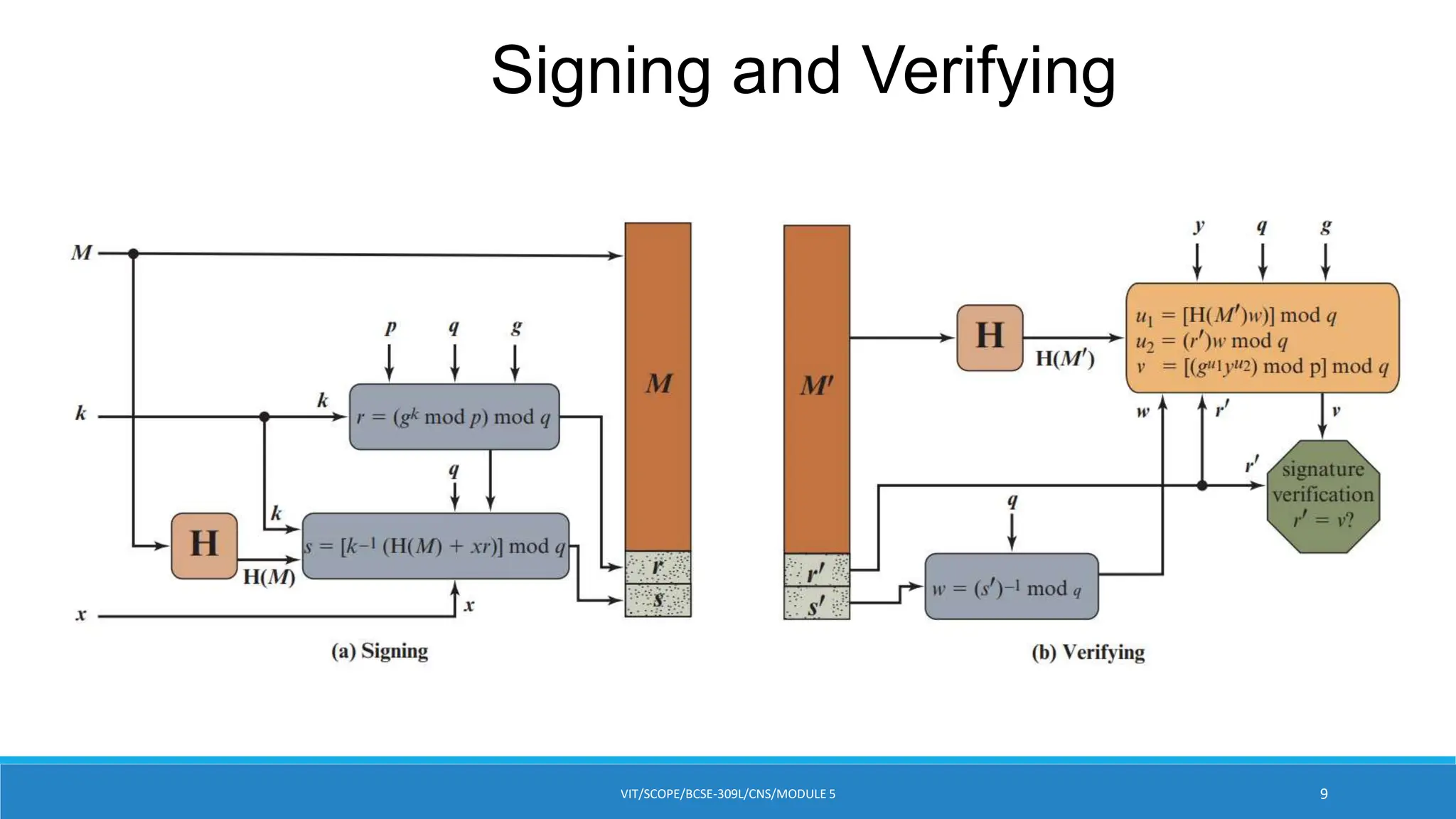
![DSA Signature Creation
To sign a message M the sender:
Generates a random signature key k, k<q
o k must be random, be destroyed after use, and never be reused.
Then computes signature pair:
r = (gk mod p)mod q
s = [k-1(H(M)+ xr)] mod q
Sends signature (r,s) with message M
VIT/SCOPE/BCSE-309L/CNS/MODULE 5 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module5-dss-240417042850-b7483500/75/Module-5-DSS-pptx-crypto-currency-notes-incoming-6-2048.jpg)
![DSA Signature Verification
Having received M & signature (r,s)
To verify a signature, recipient computes:
◦ w = s-1 mod q
◦ u1= [H(M)w ]mod q
◦ u2= (rw)mod q
◦ v = [(gu1 yu2)mod p ]mod q
If v=r then signature is verified
VIT/SCOPE/BCSE-309L/CNS/MODULE 5 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module5-dss-240417042850-b7483500/75/Module-5-DSS-pptx-crypto-currency-notes-incoming-7-2048.jpg)