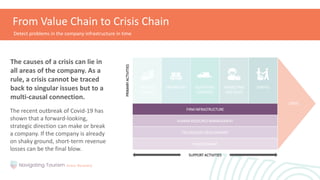
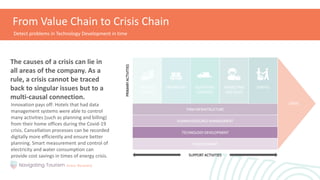
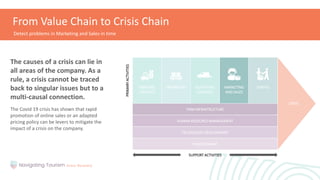
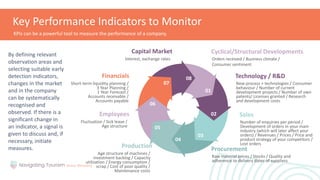
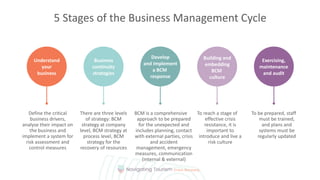
This module provides an overview of precaution and crisis avoidance strategies. It covers the following key points in 5 sections:
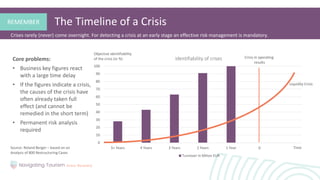
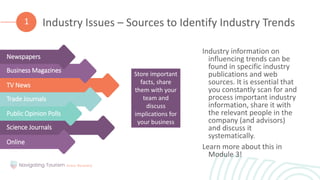
1. Understanding risk factors and early warning signs that can lead to a crisis in order to prevent issues.
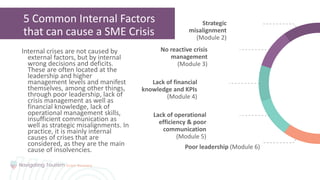
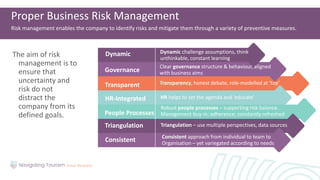
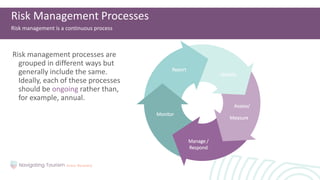
2. Learning the importance of business risk management for identifying and mitigating risks through preventative measures.
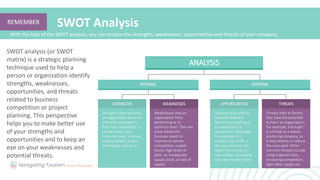
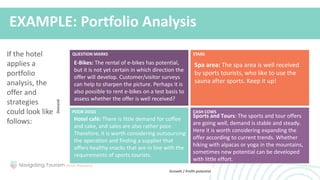
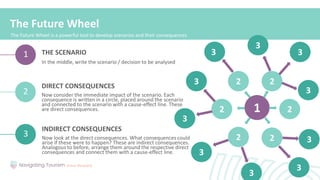
3. Knowing various tools for developing an effective strategy, such as SWOT analysis and portfolio analysis, to apply strategic planning.
4. Recognizing potential crisis risk factors within a company so they can be evaluated early.
5. Understanding the principles of business continuity management to maintain operations during a disruption.
After completing this module, the reader will gain insight