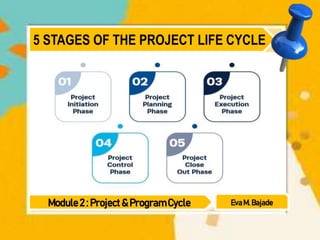
A program cycle is a series of steps that repeats until completion, providing a strategic and evidence-based approach to planning, implementing, assessing, and adapting programs. It follows four main phases: initiation, planning, execution, and closure. Similarly, a project life cycle involves initiation, planning, execution, control, and closeout phases to deliver projects on time and to satisfaction. Both aim to structure the management process but a program cycle focuses more on organizational results and value.