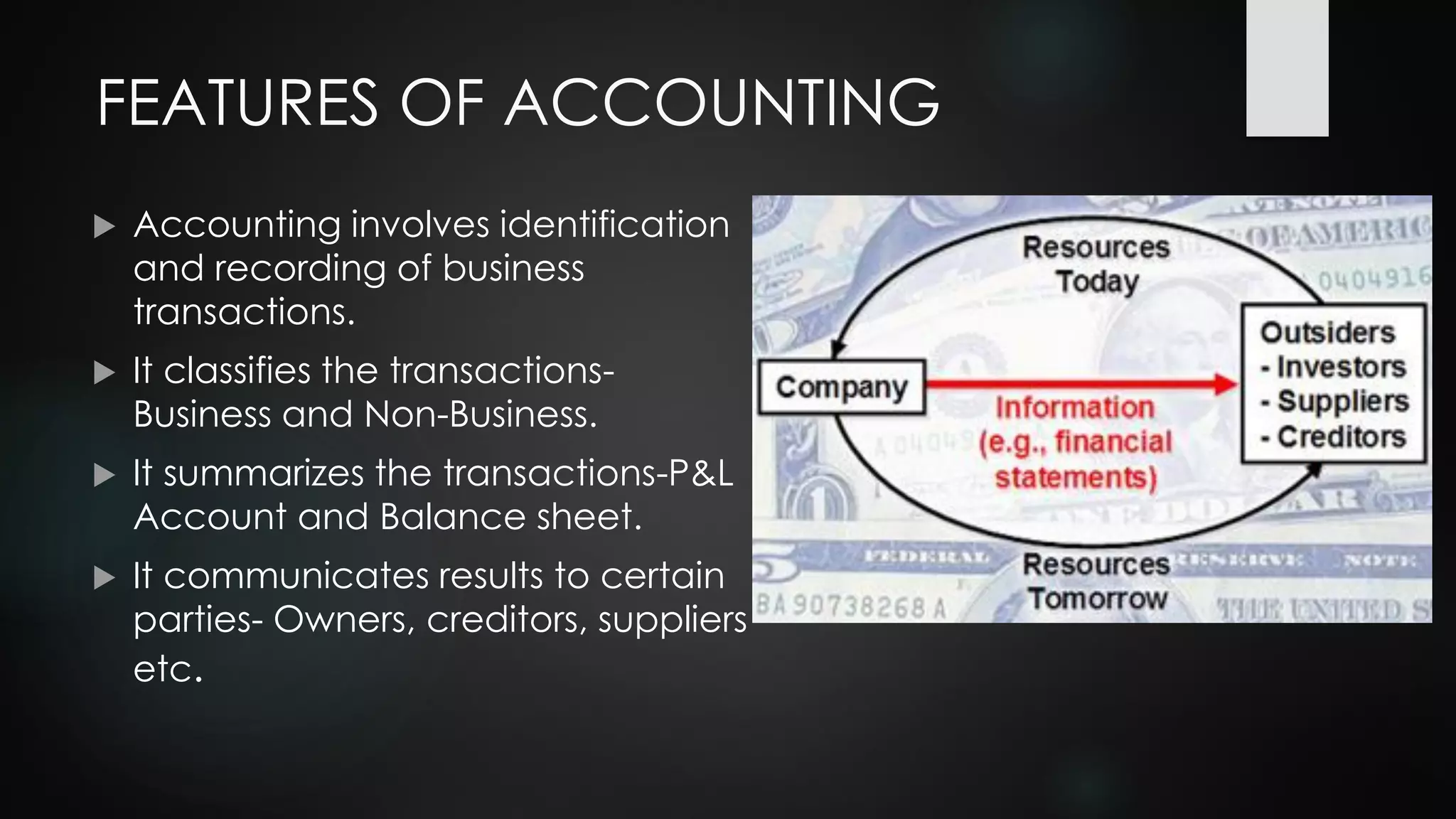
The document discusses accounting theory and standards. It defines accounting and outlines its nature, objectives and functions. It describes accounting principles, concepts and conventions under GAAP. It then explains the importance of accounting standards and how standards are set in India, with the Accounting Standards Board (ASB) under ICAI harmonizing policies and practices by developing standards through study groups and drafting processes.