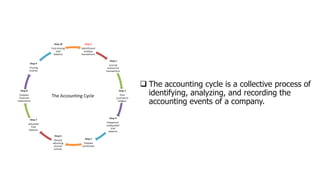
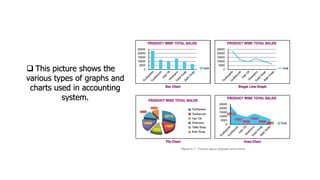
Accounting is defined as the process of identifying, measuring, and communicating economic information to allow for informed judgments and decisions. It involves recording financial transactions, classifying them, and communicating the results. The key aspects are identifying and measuring economic events and communicating that information to interested users. Accounting provides important data for control of assets and liabilities, ascertainment of financial affairs, and identification and recording of transactions. It aims to be reliable, relevant, understandable, and comparable. Computerized accounting systems now process accounting information digitally for improved accuracy and accessibility.























![ INFLATION ACCOUNTING:
Two methods are used:
(A)CURRENT PURCHASING POWER [CPP]:
Monetary and non-monetary
items are separated.
(B)CURRENT COST ACCOUNTING [CCA] :
Values assets at fair market
value rather than historical cost.
Process and practice of
adjusting financial
statements according to
its price indexes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20210219-snehasraj-commerce-comprehension-230608093937-7749361a/85/Comprehensive-study-of-accounting-26-320.jpg)

![ GENERALLY ACCEPTED ACCOUNTING
PRINCIPLES [GAAP]:
(GAAP) refer to a common set of accounting principles, standards, and
procedures issued by the Financial Accounting Standard Board(FASB).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20210219-snehasraj-commerce-comprehension-230608093937-7749361a/85/Comprehensive-study-of-accounting-28-320.jpg)