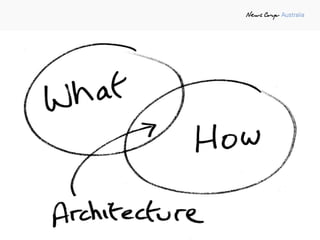
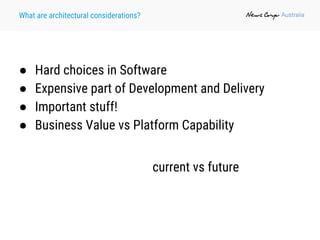
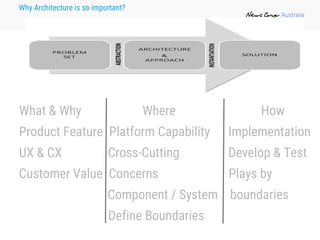
The document outlines the importance of software architecture, defining it as the fundamental organization of a system and emphasizing its role in delivering business value through robust and flexible applications. It covers various architectural and design patterns, the relationship between software architecture and design, and the principles guiding agile architecture development. The document concludes with the notion that software architecture is a shared responsibility and a living document that adapts to changing needs.