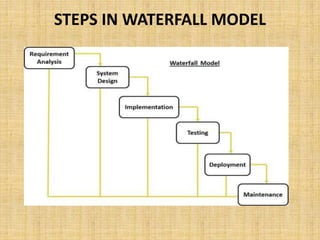
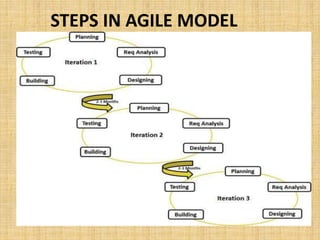
The document discusses two common project management methodologies: the waterfall model and the agile model. The waterfall model is a traditional, linear approach where each phase must be completed sequentially before moving to the next. In contrast, the agile model is an iterative approach that values adaptability and customer feedback, with developers working in short sprints and requirements evolving throughout the project. The document compares the two methods, noting waterfall is best for smaller, well-defined projects while agile handles more unpredictable projects through a flexible adaptive approach.