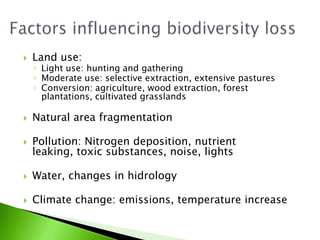
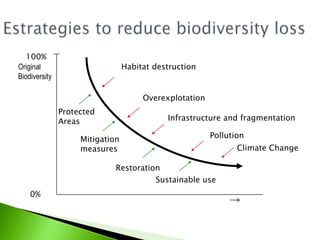
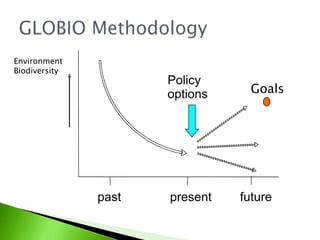
1) The document summarizes the GLOBIO methodology, which models mean species abundance (MSA) as an indicator to assess biodiversity loss due to human pressures like land use, infrastructure, climate change, and nitrogen deposition.
2) GLOBIO can evaluate current biodiversity state, identify trends, and evaluate policy options to support decision-making. It has been applied globally and for many countries and regions.
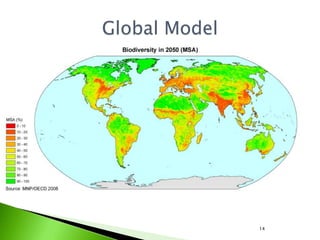
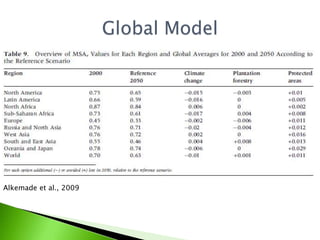
3) MSA is used as a single indicator, representing the average abundance of original species relative to an undisturbed state. GLOBIO aims to help identify causes of biodiversity loss and evaluate if targets will be attained under different policy scenarios.