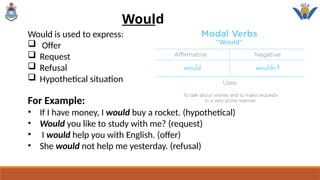
The document discusses modal verbs in English, defining them as auxiliary verbs that modify main verbs to express specific meanings such as ability, possibility, advice, and obligation. It categorizes various modal verbs like can, could, shall, should, will, may, might, would, and must, along with their uses and examples in different contexts. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of understanding modal verbs for effective communication and expression in the English language.