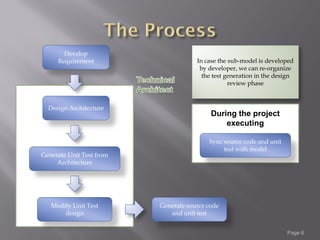
The document discusses unit testing tools that can be integrated with Enterprise Architect modeling software. It describes how JUnit, Cobertura, Emma, and Testdox can be used for Java unit testing and code coverage, and how NUnit, NCover, and Troy can be used for .NET unit testing and code coverage. The document proposes generating unit tests from architecture models in Enterprise Architect to enforce a test-first development approach and ensure tests match requirements and design specifications. Some challenges with the approach are also outlined.