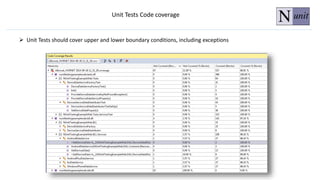
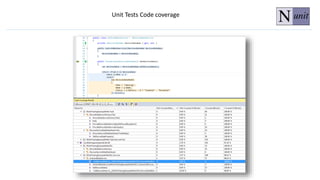
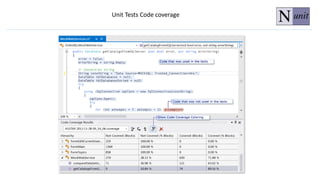
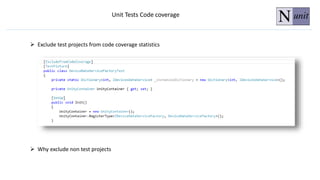
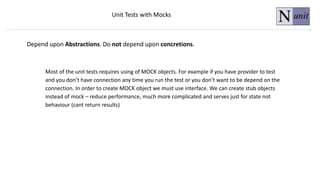
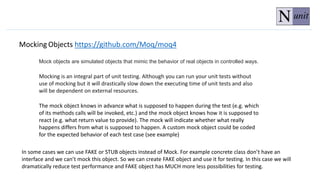
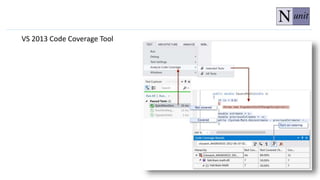
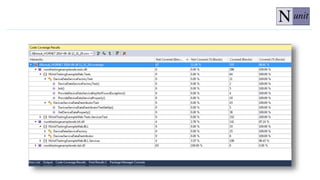
The document discusses unit testing principles and purposes. It states that unit testing is used to prove that classes work properly in isolation, catch bugs early, enforce high-quality code, and make refactoring safer. Unit testing encourages modular and loosely coupled code. However, it does not replace integration or system testing and not all code can be unit tested. The document also provides examples of when code should be refactored before writing unit tests.









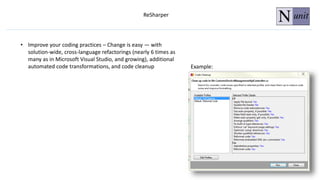

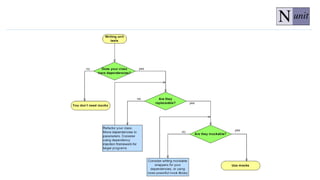
![Examples of when you should refactor the code before creating unit tests
Tested Method / Class (Unit) has more than one responsibility
Private Class / Methods.
(Possible with using reflection, but will significantly reduce the performance of
tests)
Method / Class don’t allow dependency injection,
for example tightly coupled instances [new
object();]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/214d312c-f9c3-4975-b2c1-cfff333d834d-170113161803/85/Unit-Testing-Full-19-320.jpg)