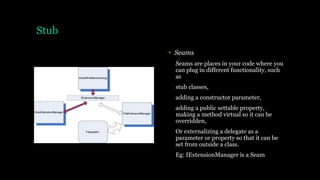
Unit testing involves testing individual units or components of an application to verify that each unit performs as expected. A unit test automates the invocation of a unit of work and checks the expected outcome without relying on other units. Good unit tests are automated, repeatable, easy to implement, run quickly and consistently, and isolate the unit from its dependencies. Integration testing differs in that it involves testing units using real dependencies rather than isolated fakes or stubs. Test-driven development involves writing tests before code so that tests fail initially and then pass after the code is implemented. Unit testing frameworks like NUnit provide attributes to mark tests, expected exceptions, setup and teardown methods, and assertions to validate outcomes.








![NUnit attributes
[TestFixture]
public class LogAnalyzerTests
{
[Test]
public void
IsValidFileName_BadExtension_ReturnsFalse()
{
LogAnalyzer analyzer = new LogAnalyzer();
bool result =
analyzer.IsValidLogFileName("filewithbadextension
.foo");
Assert.False(result);
}
}
A unit test usually
comprises three main
actions
1. Arrange objects,
creating and setting
them up as necessary
2. Act on an object
3. Assert that something is
as expected](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unittesting-170930083241/85/Unit-testing-10-320.jpg)



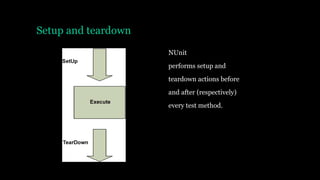
![Setup and teardown
[TestFixtureSetUp] and
[TestFixtureTearDown] allow setting up
state
once before all the tests in a specific class
run and once after all the tests have been
run (once per test fixture)
You almost never, ever use TearDown or
TestFixture methods in unit test projects
If you do, you’re very likely writing an
integration test, where you’re touching the
filesystem or a database, and you need to clean
up the disk or the DB after the tests.
Use it only to “reset” the state of a static variable
or singleton in memory
between tests](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unittesting-170930083241/85/Unit-testing-15-320.jpg)
![Checking for expected exceptions
public class LogAnalyzer
{
public bool IsValidLogFileName(string
fileName)
{
…
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(fileName))
{
throw new ArgumentException(
"filename has to be provided");
}
…
}
}
[Test]
[ExpectedException(typeof(ArgumentException),
ExpectedMessage ="filename has to be
provided")]
public void
IsValidFileName_EmptyFileName_ThrowsException
()
{
m_analyzer.IsValidLogFileName(string.Empty);
}
private LogAnalyzer MakeAnalyzer()
{
return new LogAnalyzer();
}
Factory Method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unittesting-170930083241/85/Unit-testing-16-320.jpg)

![Ignoring tests
[Test]
[Ignore("there is a problem with this
test")]
public void
IsValidFileName_ValidFile_ReturnsTrue()
{
/// ...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unittesting-170930083241/85/Unit-testing-18-320.jpg)