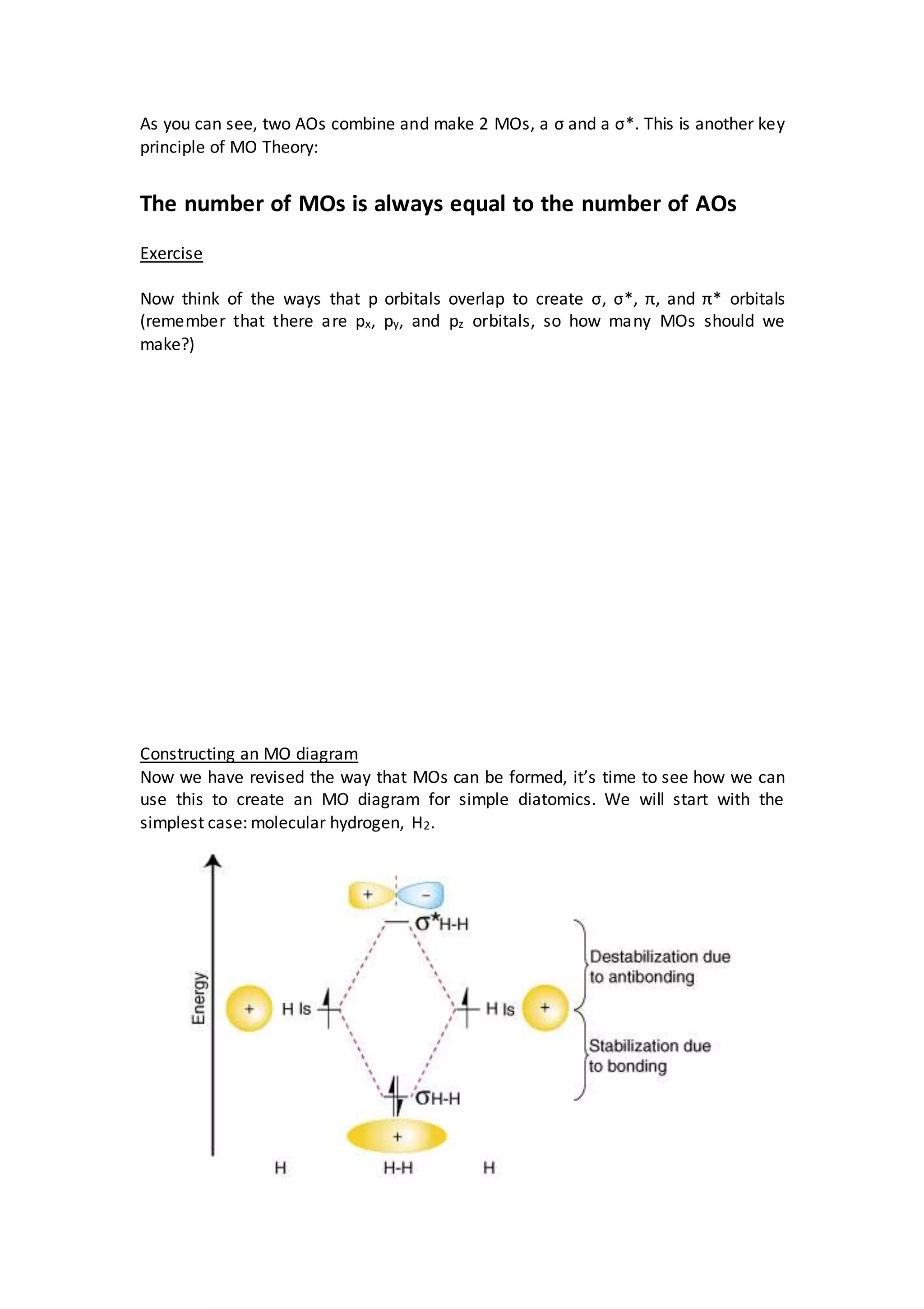
This document discusses molecular orbital theory and how it can be used to calculate bond order in diatomic molecules. It explains that atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals, with the number of molecular orbitals always equal to the number of atomic orbitals. The key types of molecular orbitals - sigma, sigma star, pi, and pi star - are formed from the overlap of s and p orbitals. As an example, it shows the molecular orbital diagram for H2, where the 1s atomic orbitals form a bonding and antibonding sigma molecular orbital. The bond order is calculated to be 1.