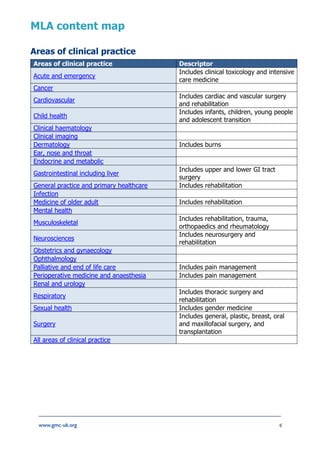
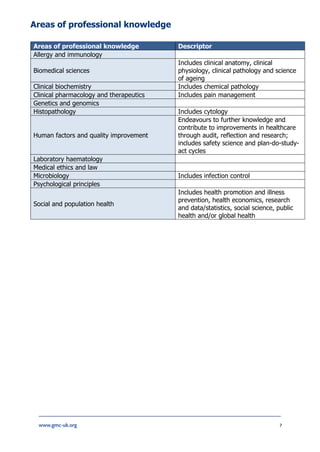
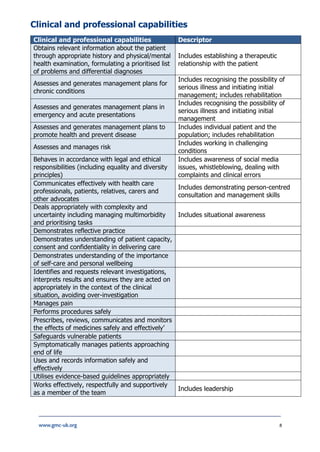
The document provides information about the Medical Licensing Assessment (MLA) content map, which outlines the core knowledge, skills, and behaviors needed for medical practice in the UK. The content map is organized into six domains: areas of clinical practice, areas of professional knowledge, clinical and professional capabilities, practical skills and procedures, patient presentations, and conditions. It serves to guide the development of the MLA's applied knowledge test and clinical skills assessment in ensuring candidates have met the common threshold for safe practice in the UK. The content was determined based on the GMC's Outcomes for Graduates and Generic Professional Capabilities Framework.