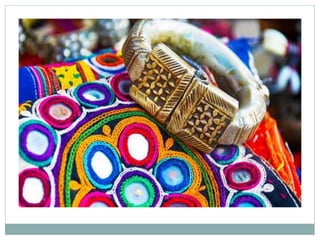
Mirror work originated in 13th century Persia and was brought to India during the Mughal era by traders and travelers. It involves decorating fabric with small pieces of mirror or mica in various shapes and sizes using stitches. There are three main types: hand blown glass shisha, machine cut glass shisha, and shisha embroidery. In traditional Rajasthani clothing, mirror work embroidery is used to represent the landscapes of India and ward off evil spirits according to Islamic beliefs. Each Indian state has developed its own unique styles of mirror work featuring motifs, colors, and shapes inspired by nature.