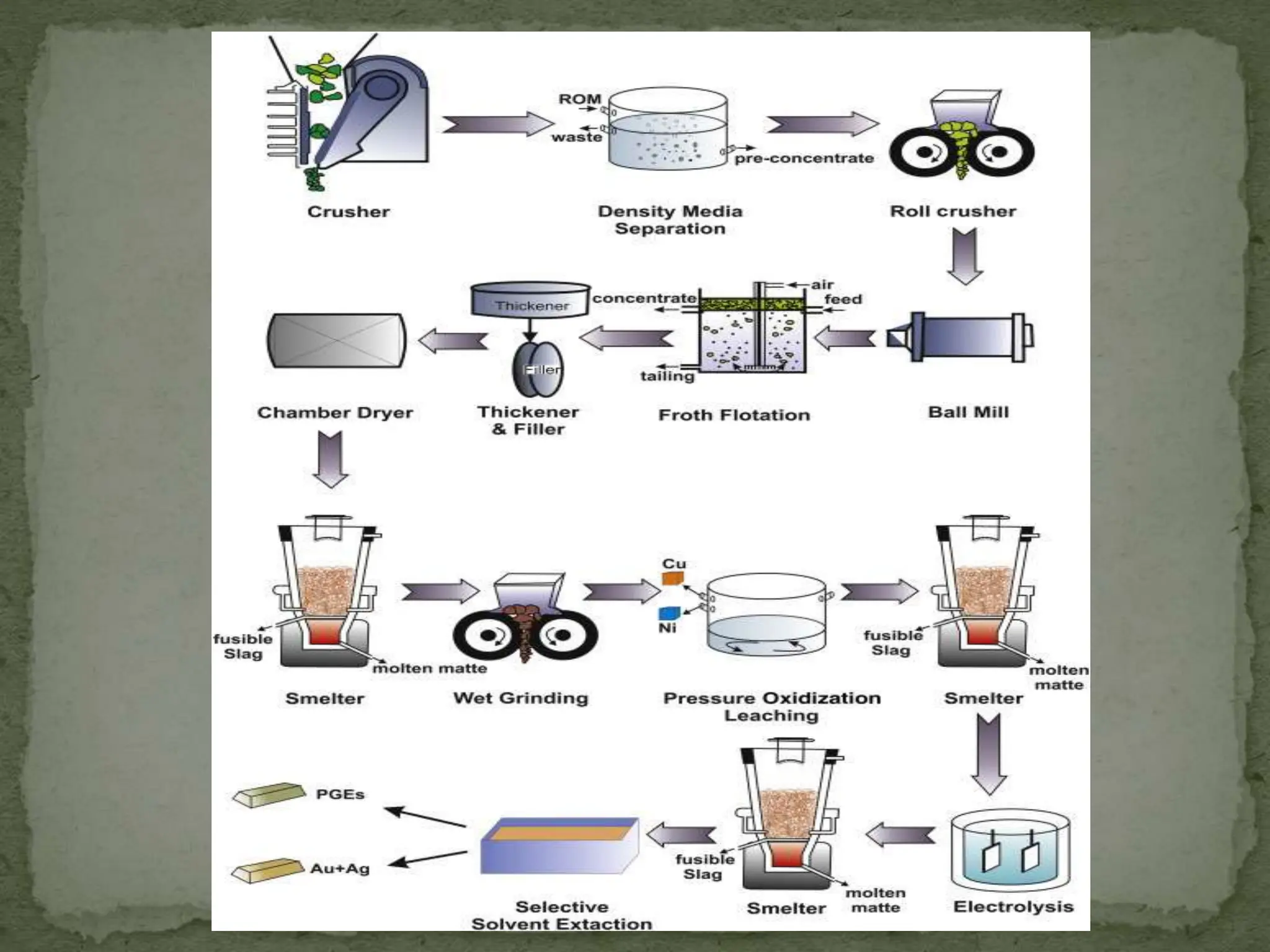
The document is a presentation on mineral processing technology. It discusses how metals are found naturally, the main components of mineral processing which include crushing, grinding, sizing, classification, concentration and dewatering. It also discusses the advantages, such as making mineral resources profitable and increasing mining production. However, it notes disadvantages such as destruction of land from subsidence and impact on the biological environment. In conclusion, it emphasizes the importance of ore microscopy in mineral technology to allow for the economic extraction of metals from lower grade ores through efficient beneficiation.