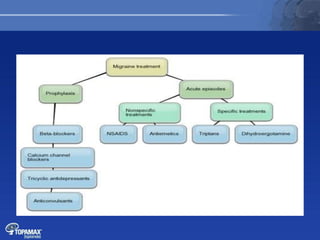
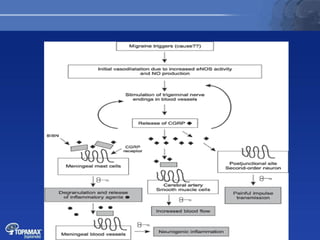
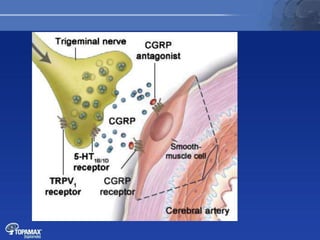
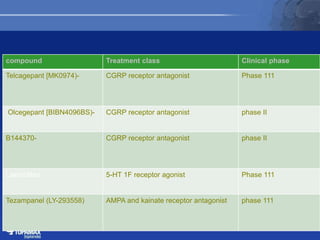
The document discusses the pathophysiology of migraines. It outlines three main theories: [1] the vascular theory which attributes migraines to vasodilation, [2] the neurogenic theory which points to neuronal events like cortical spreading depression, and [3] a combined neurovascular theory. Newer research highlights the role of CGRP, which is involved in trigeminal pain processing and vasodilation. CGRP antagonists and monoclonal antibodies show promise as preventive migraine treatments.