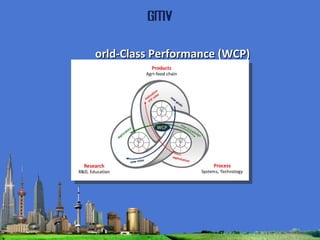
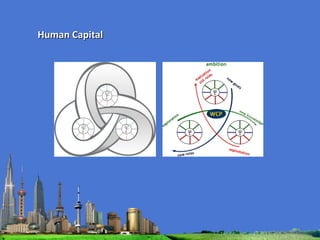
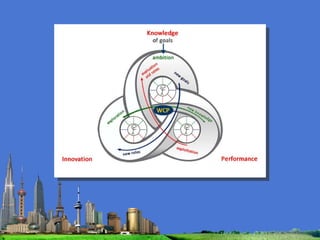
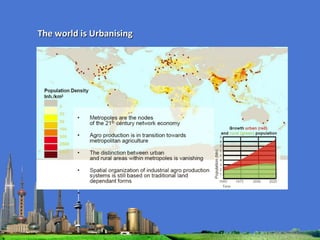
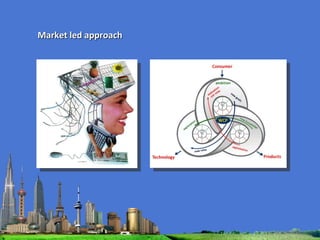
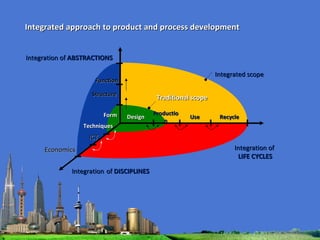
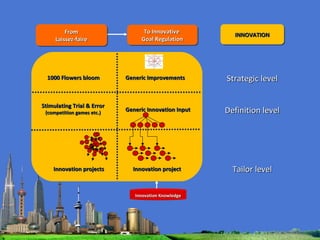
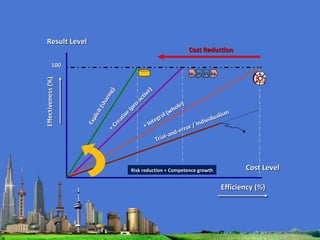
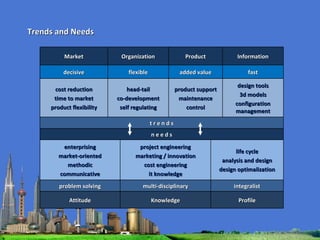
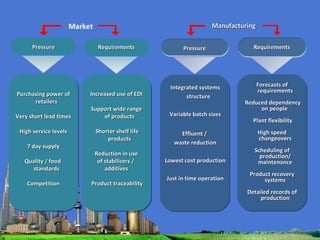
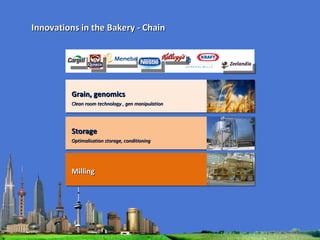
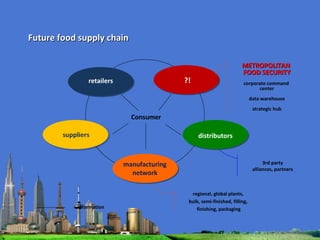
The document outlines the agenda for the MFS Conference in New Delhi, India, which will cover introductions, performances in food processing technology and products, ambitions with a market-led approach, and innovations in cooperation, research, and education. Key topics that will be discussed include the Netherlands as a leader in the global agri-food industry, world-class performance initiatives, challenges and opportunities in the Indian food system, and a vision for long-term metropolitan food security in India through sustainable and innovative food production.