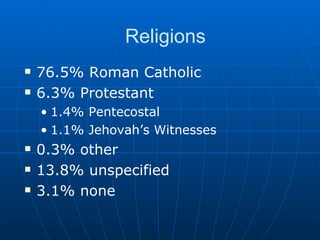
The document provides demographic and economic information about Mexico:
- Mexico has a population of around 108 million people, with one-third under 15 years old and 7% over 60. Life expectancy is 70-76 years.
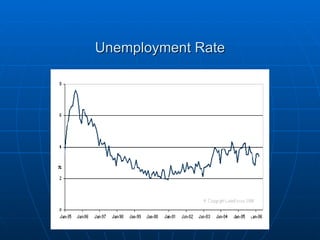
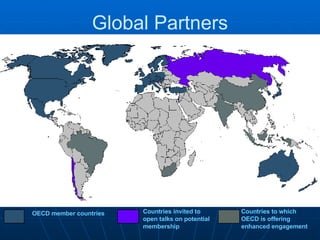
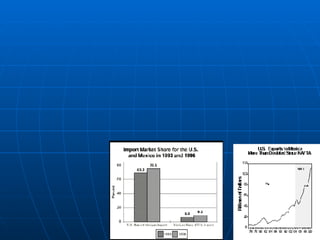
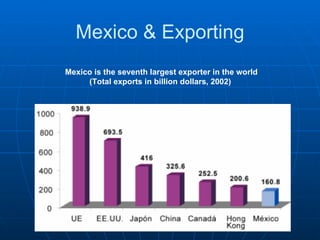
- The workforce is distributed between agriculture (4%), industry (26%), and services (70%). Exports are mainly to the US while imports come from the US, Canada, Germany and Japan.
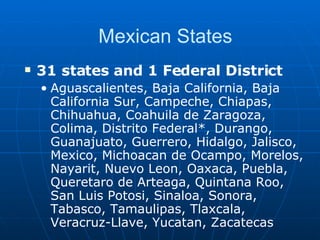
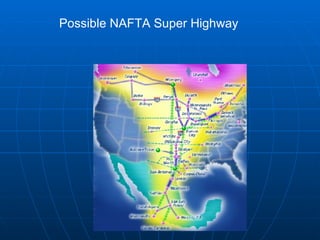
- Geographically, Mexico borders the US to the north and Guatemala/Belize to the south. It covers an area around twice the size of Texas with natural resources including petroleum, metals, and natural gas.