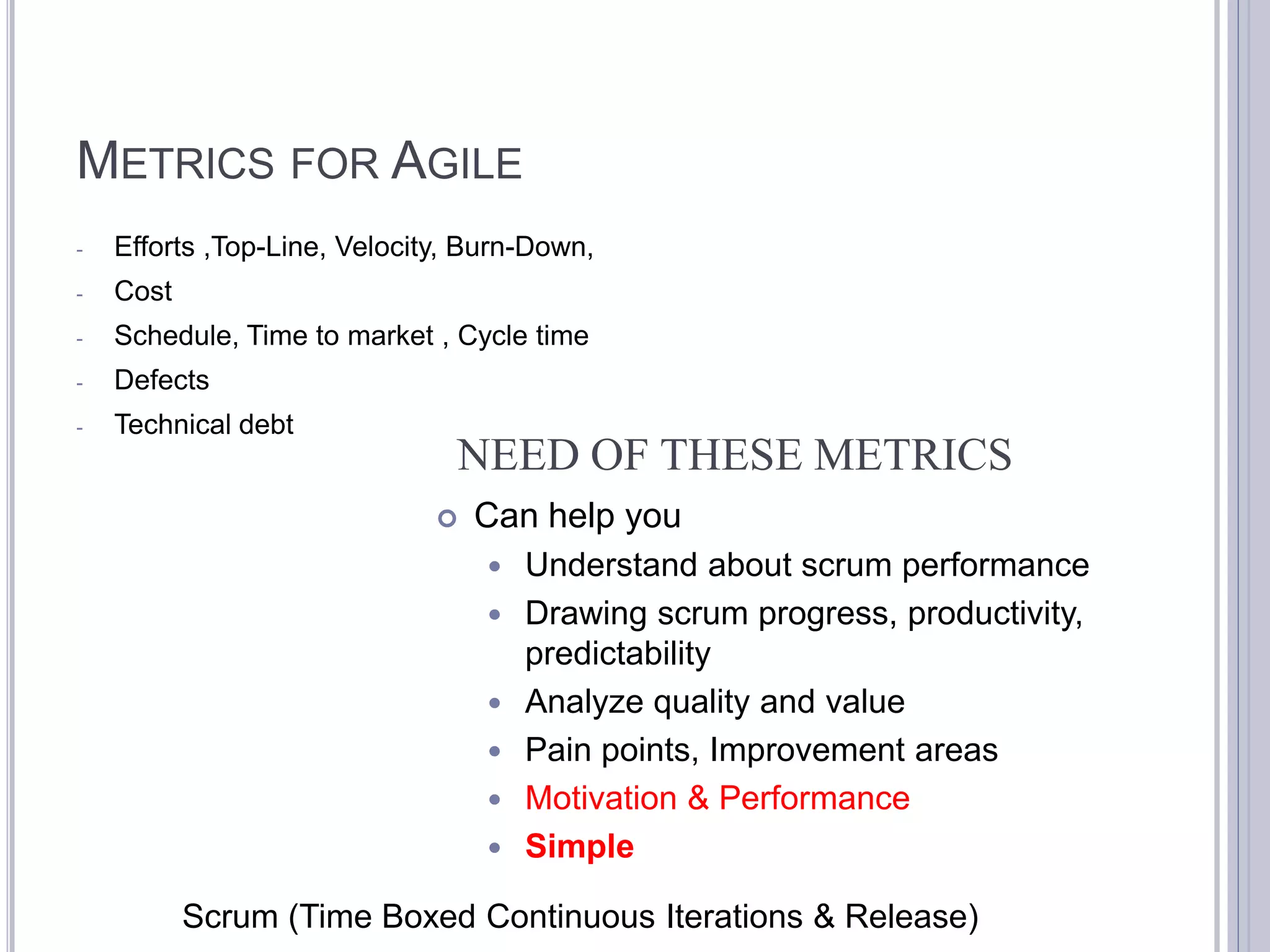
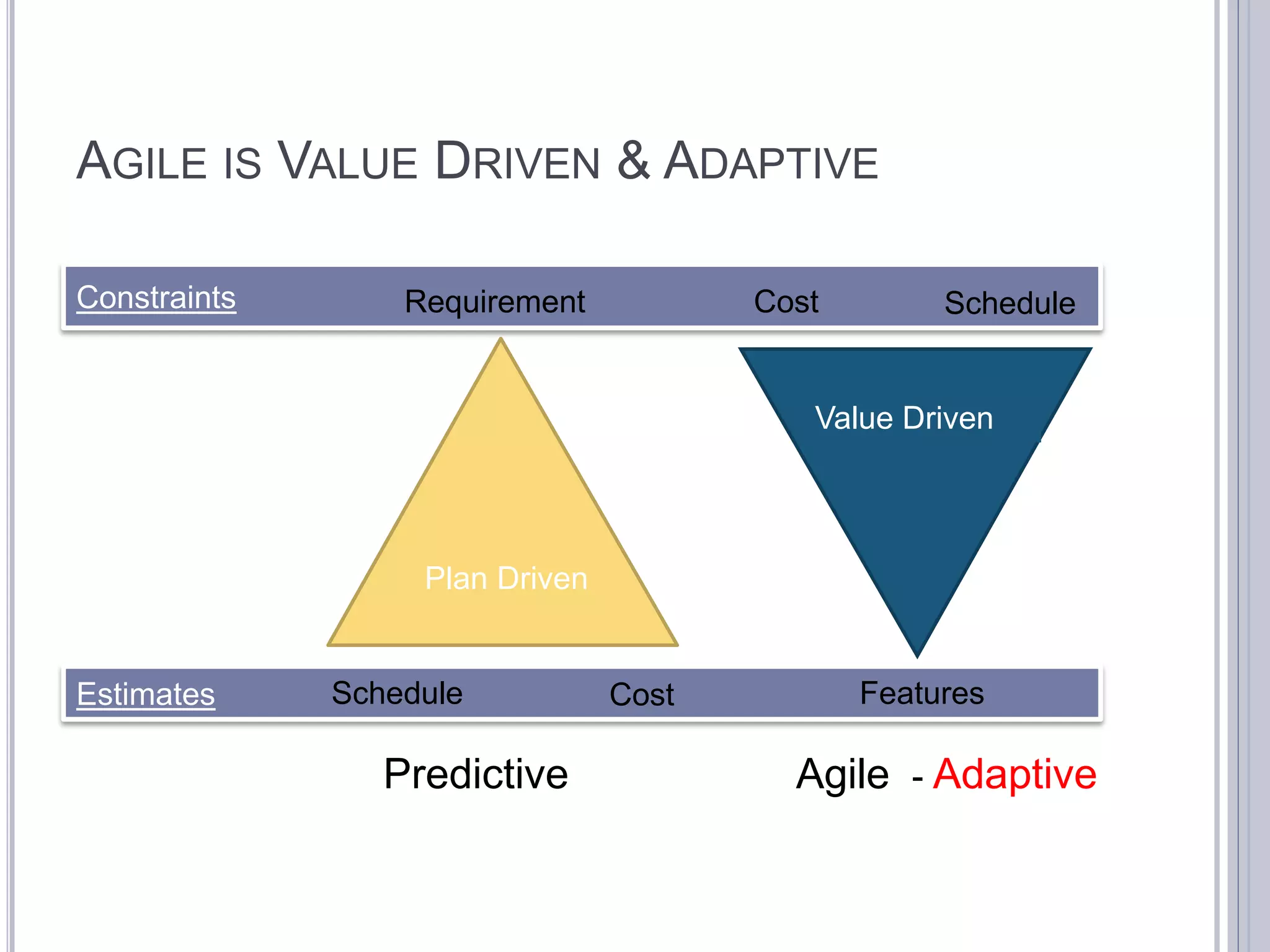
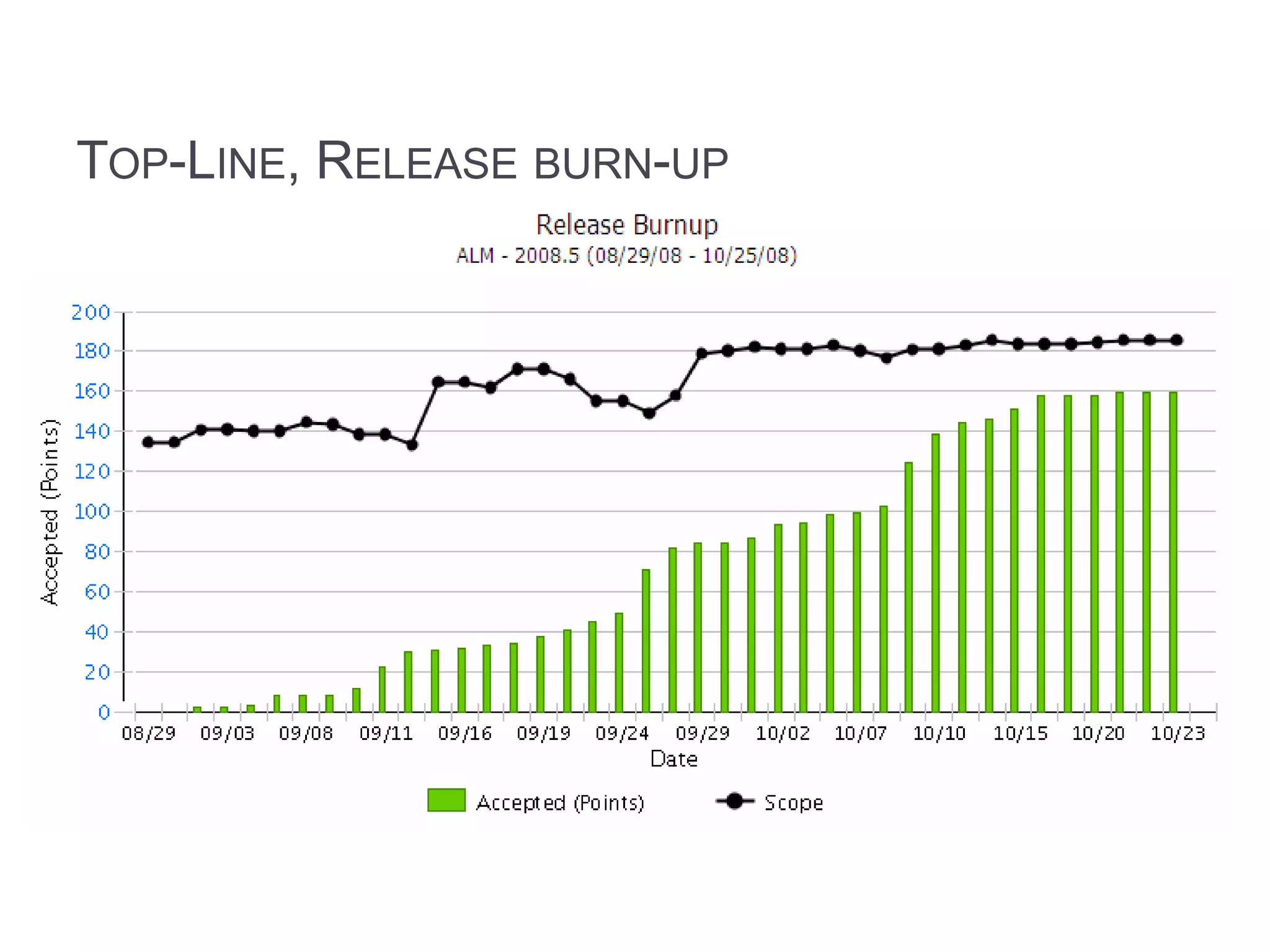
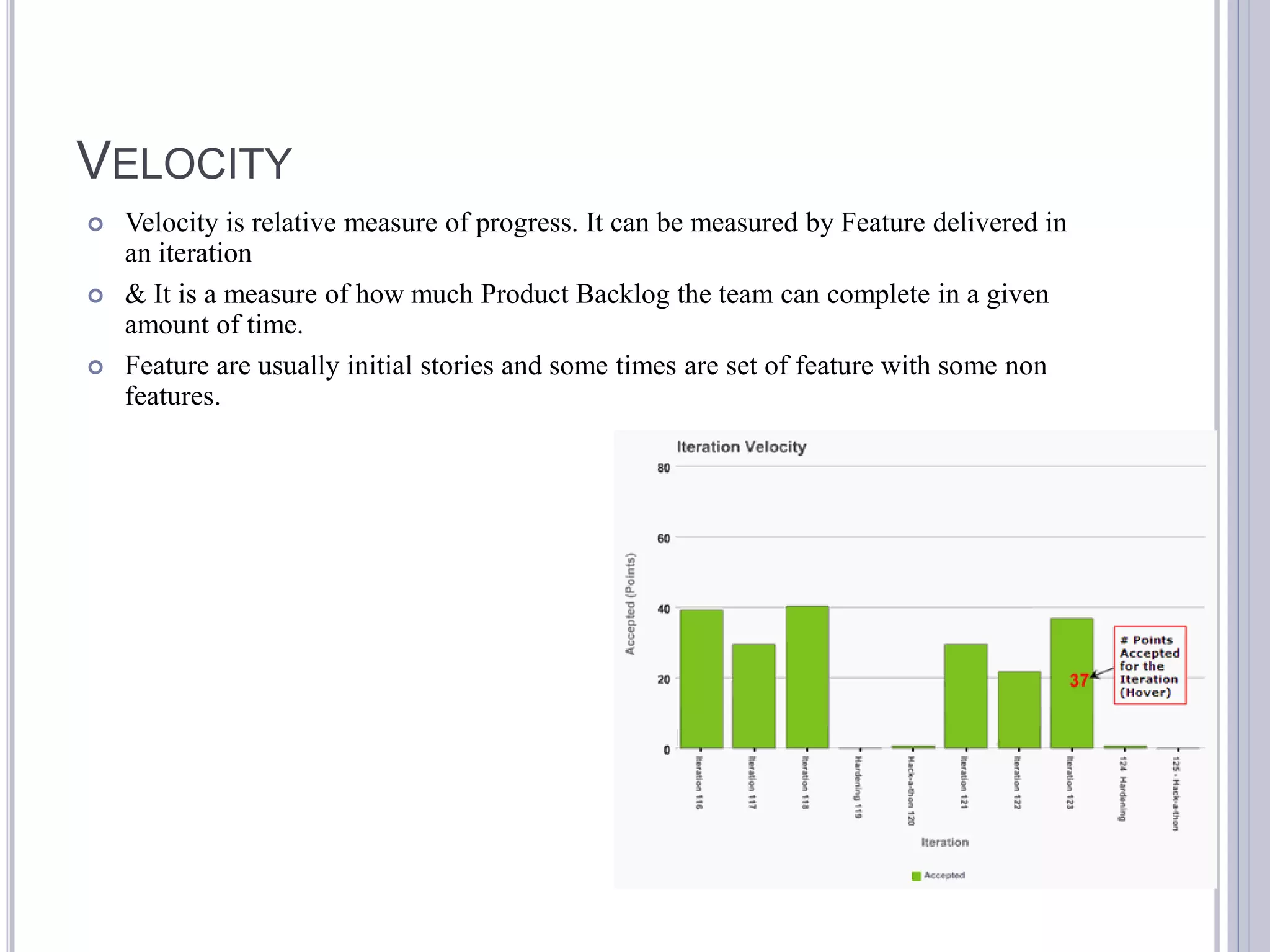
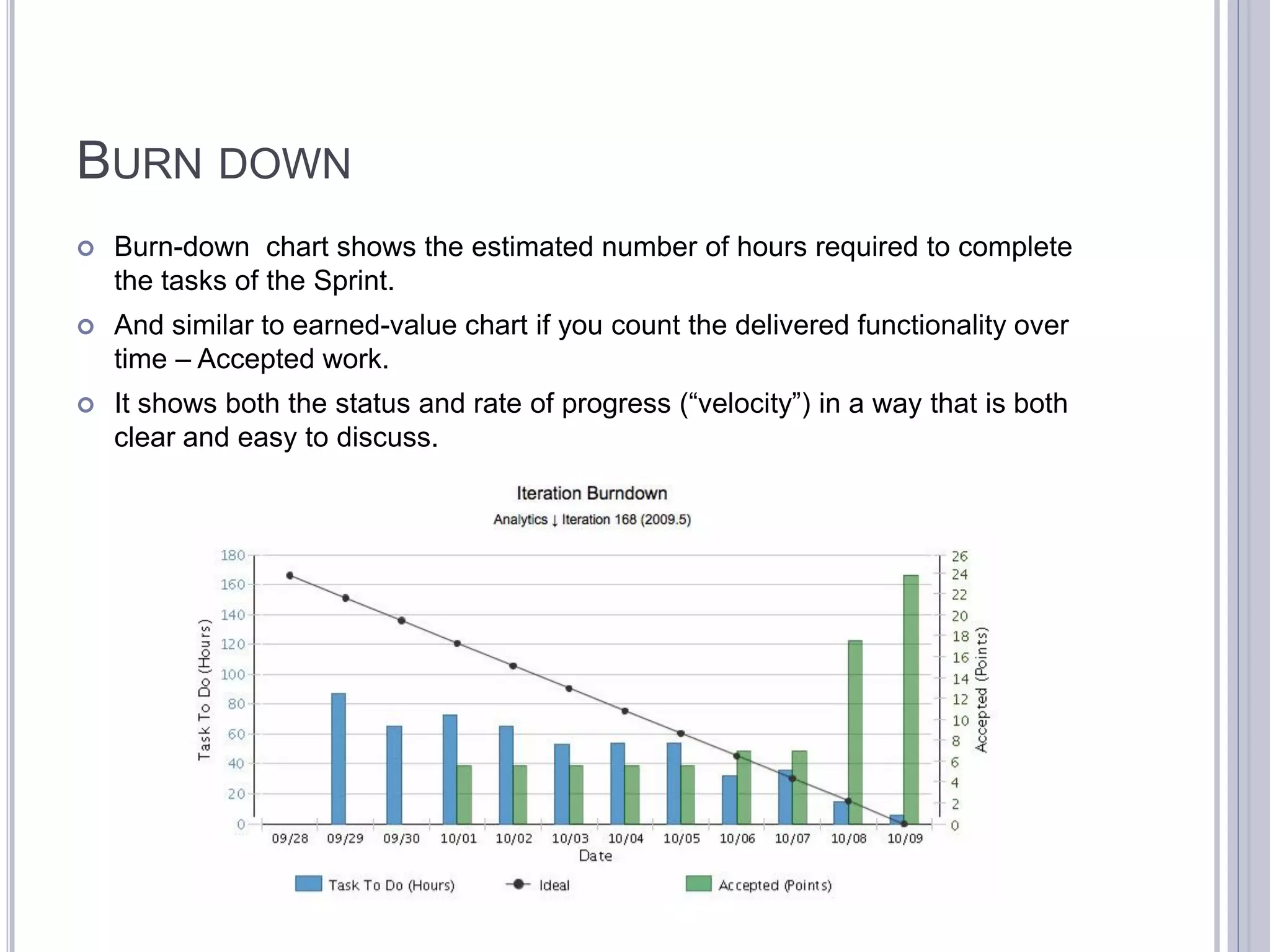
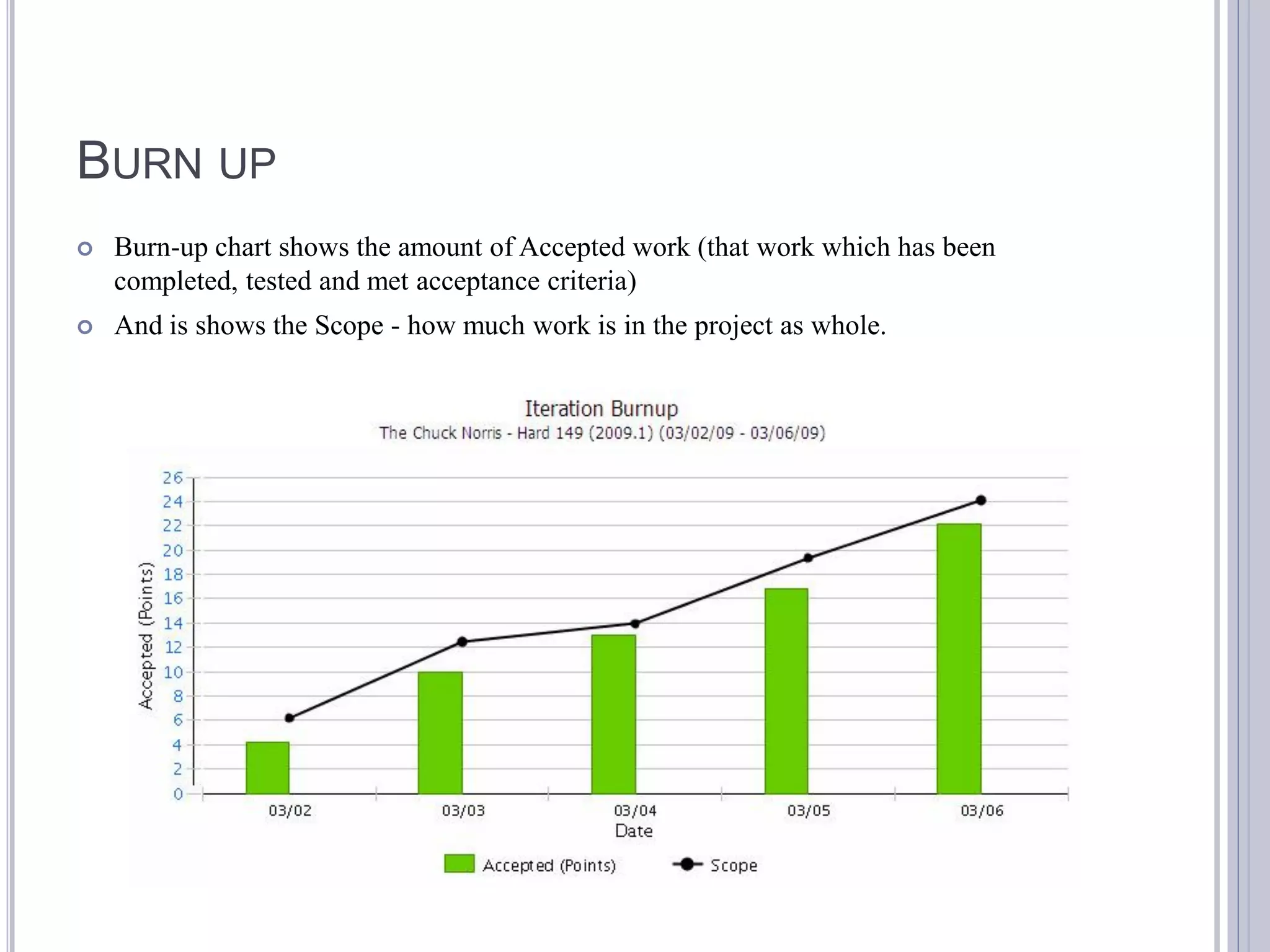
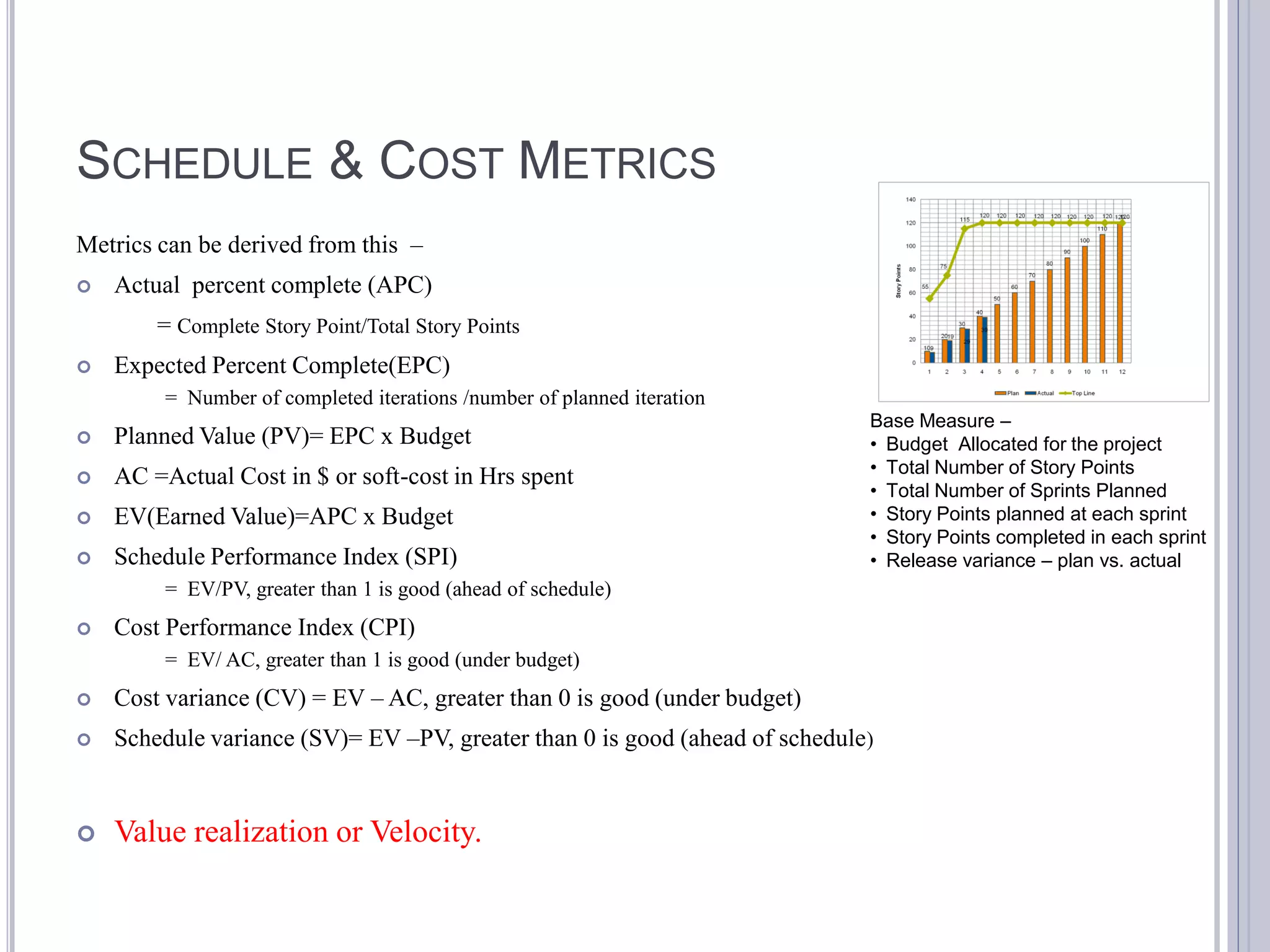
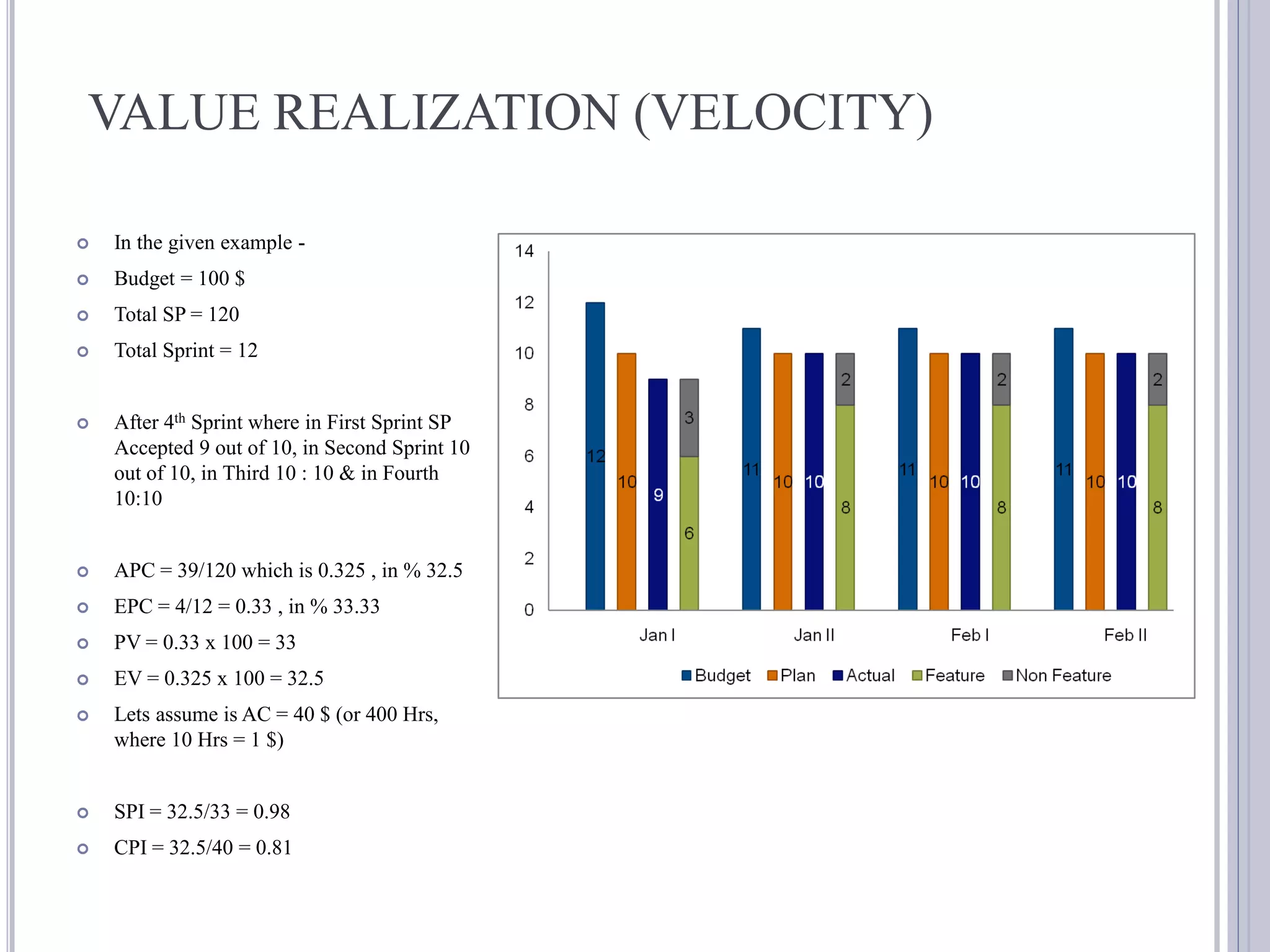
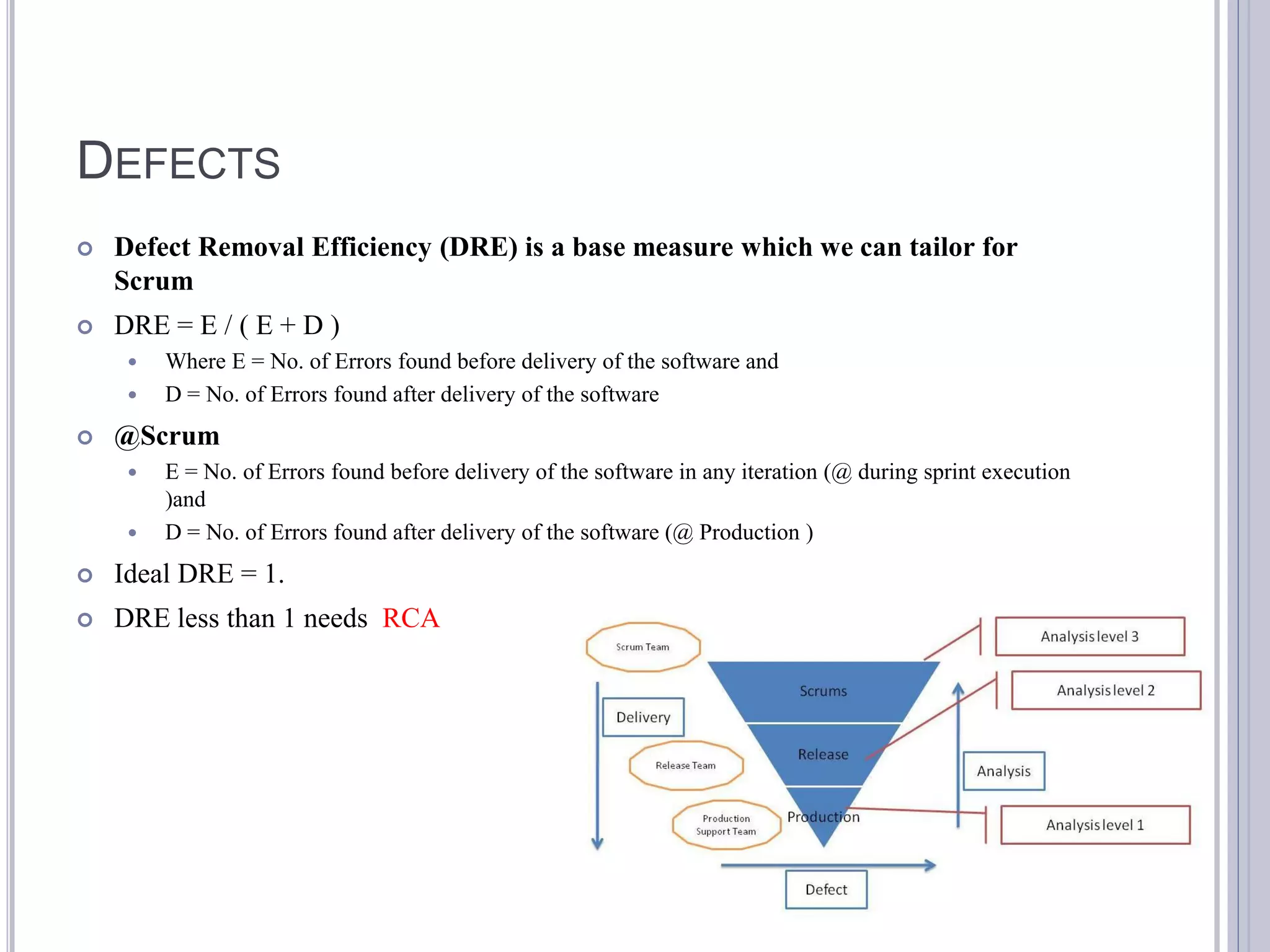
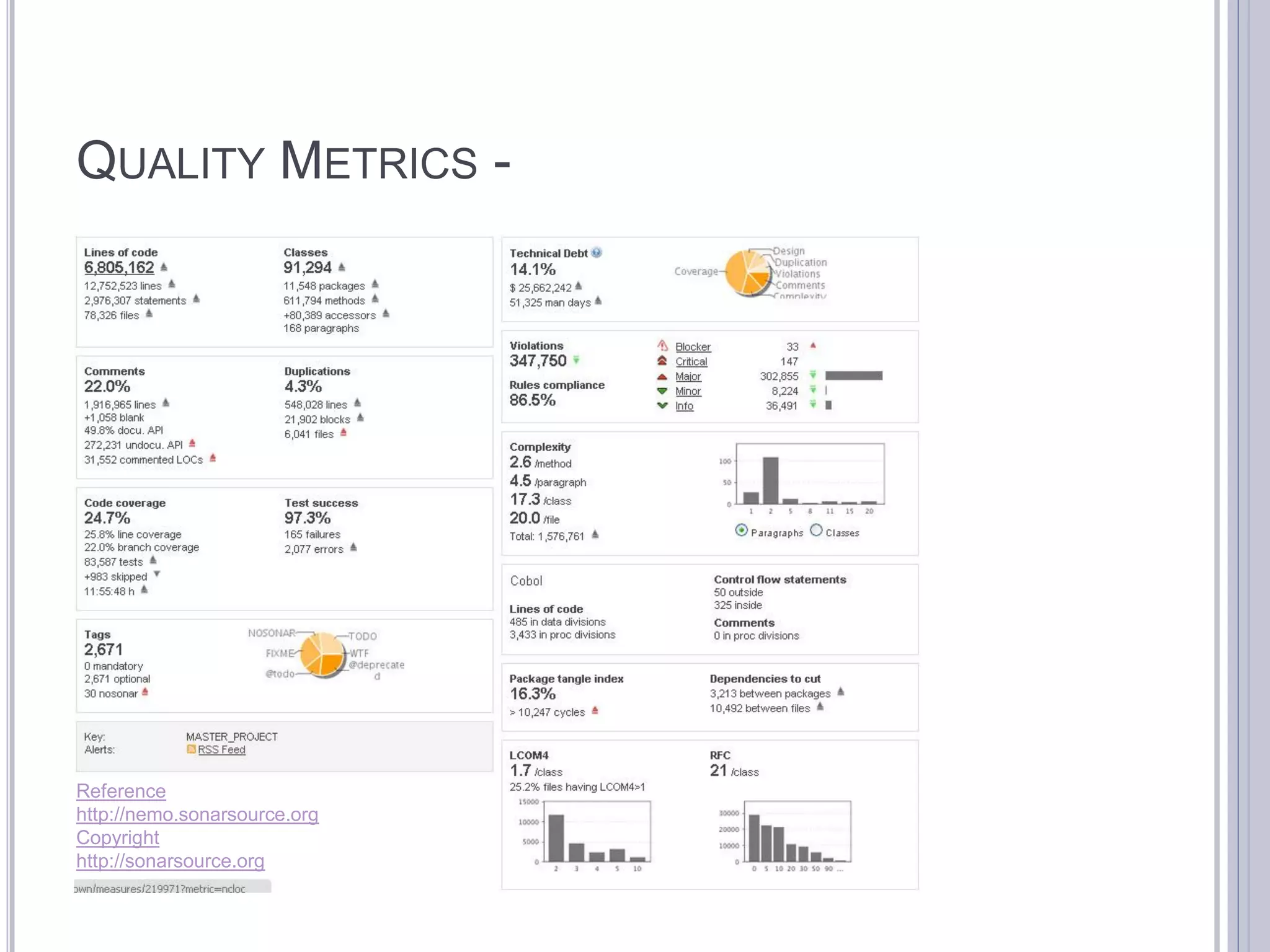
This document discusses metrics for agile projects including effort, defects, schedule, cost, size, velocity, burn down, burn up, technical debt, and quality. It defines these terms and explains how to calculate metrics like actual percent complete, expected percent complete, planned value, earned value, schedule performance index, and cost performance index to measure project performance. Defect removal efficiency is also discussed as a quality metric.