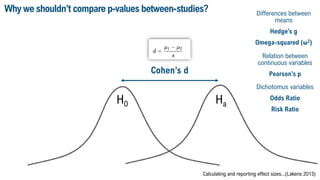
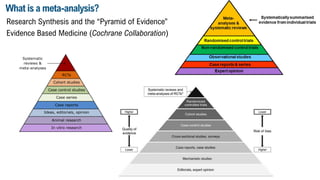
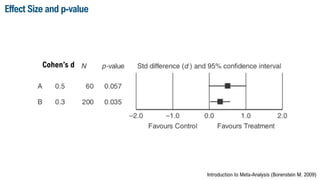
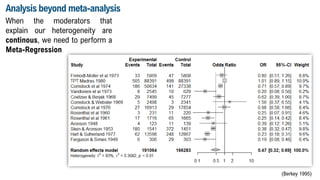
This document discusses meta-analysis and research synthesis. It begins by explaining the differences between narrative and systematic literature reviews. It then discusses effect sizes and how they are used to quantitatively assess the magnitude of effects across studies, rather than just determining whether an effect exists. The document defines meta-analysis as a statistical tool that combines the results of multiple studies, usually from a systematic review, to produce a summary effect size. Examples of applications and techniques for analysis beyond just the summary effect size are provided, including investigating heterogeneity and performing subgroup and meta-regression analyses. Steps for conducting a meta-analysis are outlined at the end.



![Comparing Between Studies: Towards Quantitative Assesment
”4 studies including data from 340
patients evaluated the effect of [...]
Study A, B and C found significant
diferences between control and
patients [...] D failed to found
significant effect.” or “75% of
studies found diferences”
Other relevant information
about the studies
Study A: p=0.011*
Study B: p<0.001**
Study C: p=0.006*
Study D: p=0.087
Systematic
Review of
Literature
Excluded
studies
Research
Question
Effect of neuropathic
pain on anxiety](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/metaanalysis2022-220726071016-d1dea6a7/85/Meta-Analysis-and-Research-Synthesis-4-320.jpg)