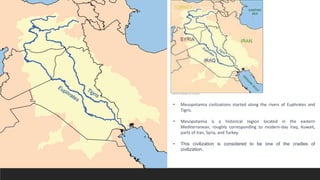
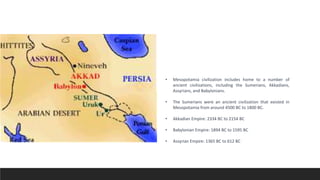
Mesopotamia was the site of early civilizations along the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. This region, located in modern Iraq, saw the rise of Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian, and Assyrian empires between 4500 BC and 600 BC. The Sumerians developed advanced technologies like the wheel, plow, and writing system. They lived in city-states with complex social hierarchies and religious beliefs. The city of Ur was a major cultural and economic center, with monumental structures like its large ziggurat dedicated to the moon god. Mesopotamian civilizations laid the foundations for future societies in their development of urban planning, mathematics, and complex social