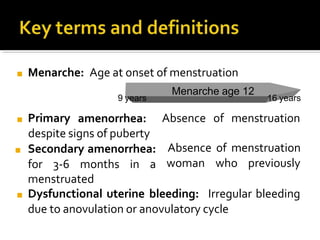
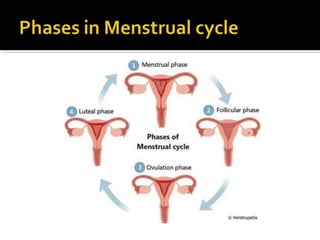
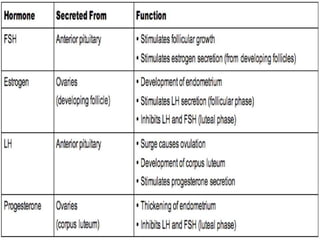
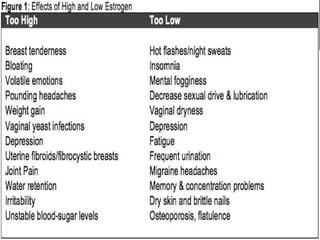
The three main hormones involved in the female menstrual cycle are estrogen, progesterone, and luteinizing hormone (LH). Estrogen causes the thickening of the uterine lining and development of female secondary sex characteristics. Progesterone maintains the thickened uterine lining to prepare for potential implantation. If implantation does not occur, decreasing progesterone levels cause the uterine lining to shed through menstruation. LH surges near ovulation to trigger the release of a mature egg. Together, these hormones regulate the monthly changes in a woman's reproductive system through menarche, menstruation, and menopause.