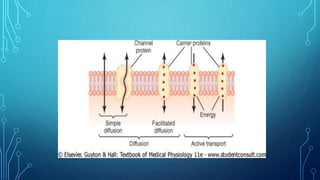
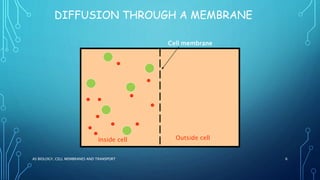
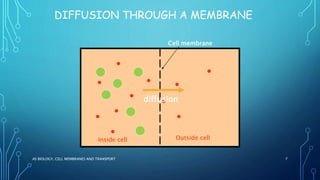
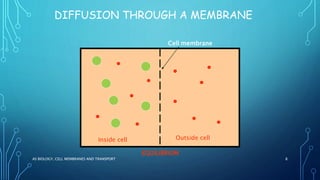
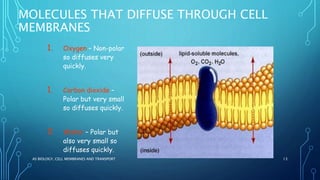
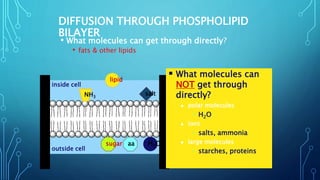
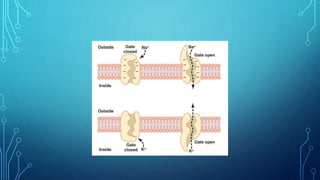
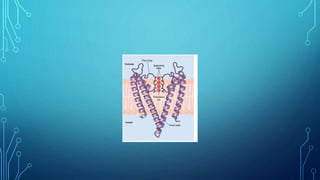
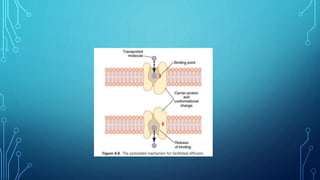
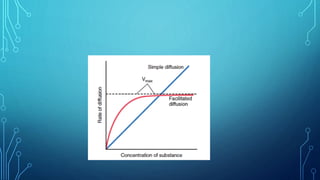
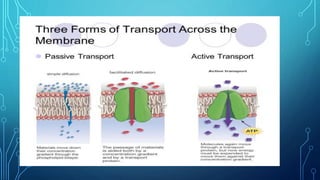
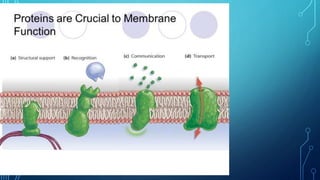
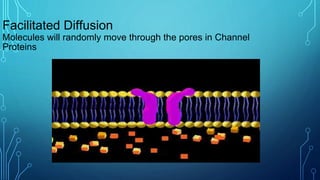
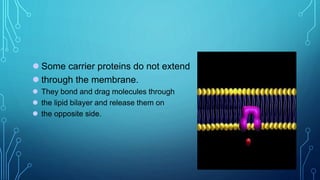
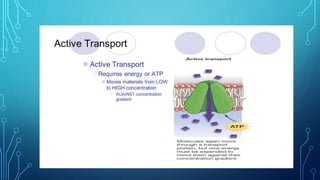
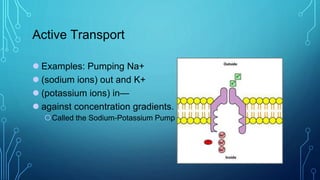
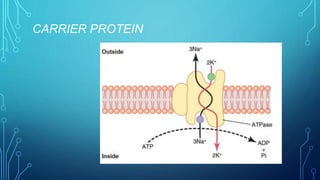
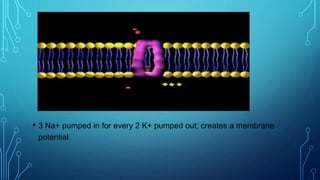
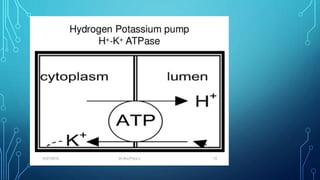
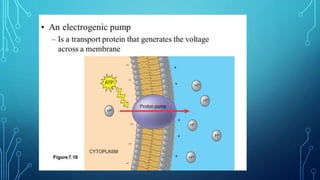
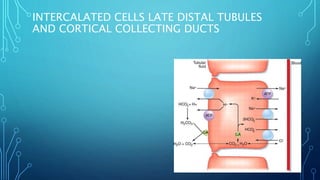
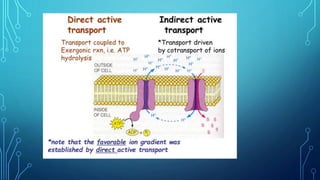
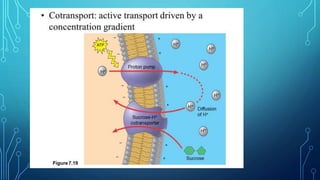
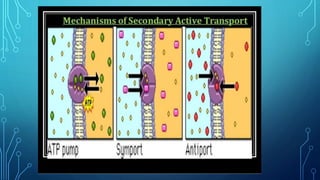
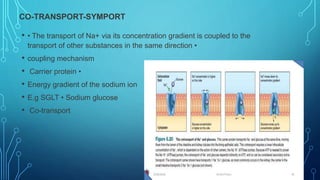
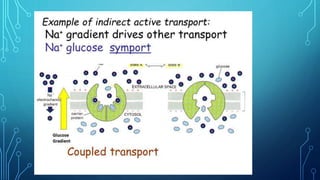
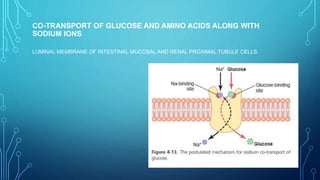
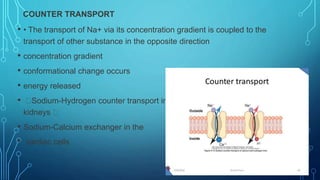
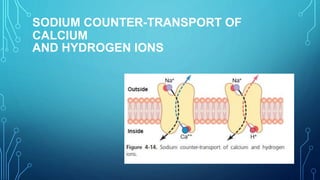
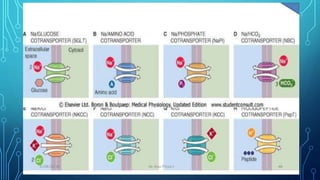
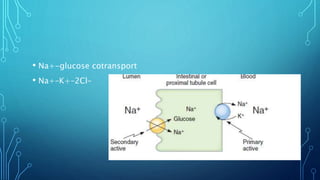
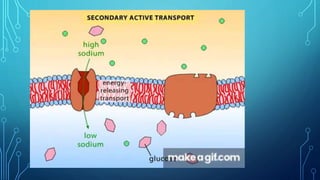
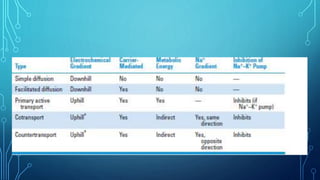
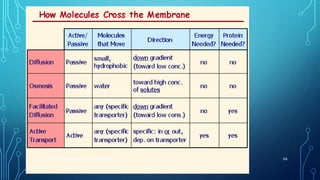
Transport across the cell membrane can occur through diffusion, facilitated diffusion, or active transport. Diffusion is the passive movement of molecules down their concentration gradient through the lipid bilayer or protein channels. Facilitated diffusion uses carrier proteins to transport molecules down their concentration gradient. Active transport moves molecules against their gradient and requires ATP. The sodium-potassium pump is an example of primary active transport that pumps sodium out and potassium into cells.