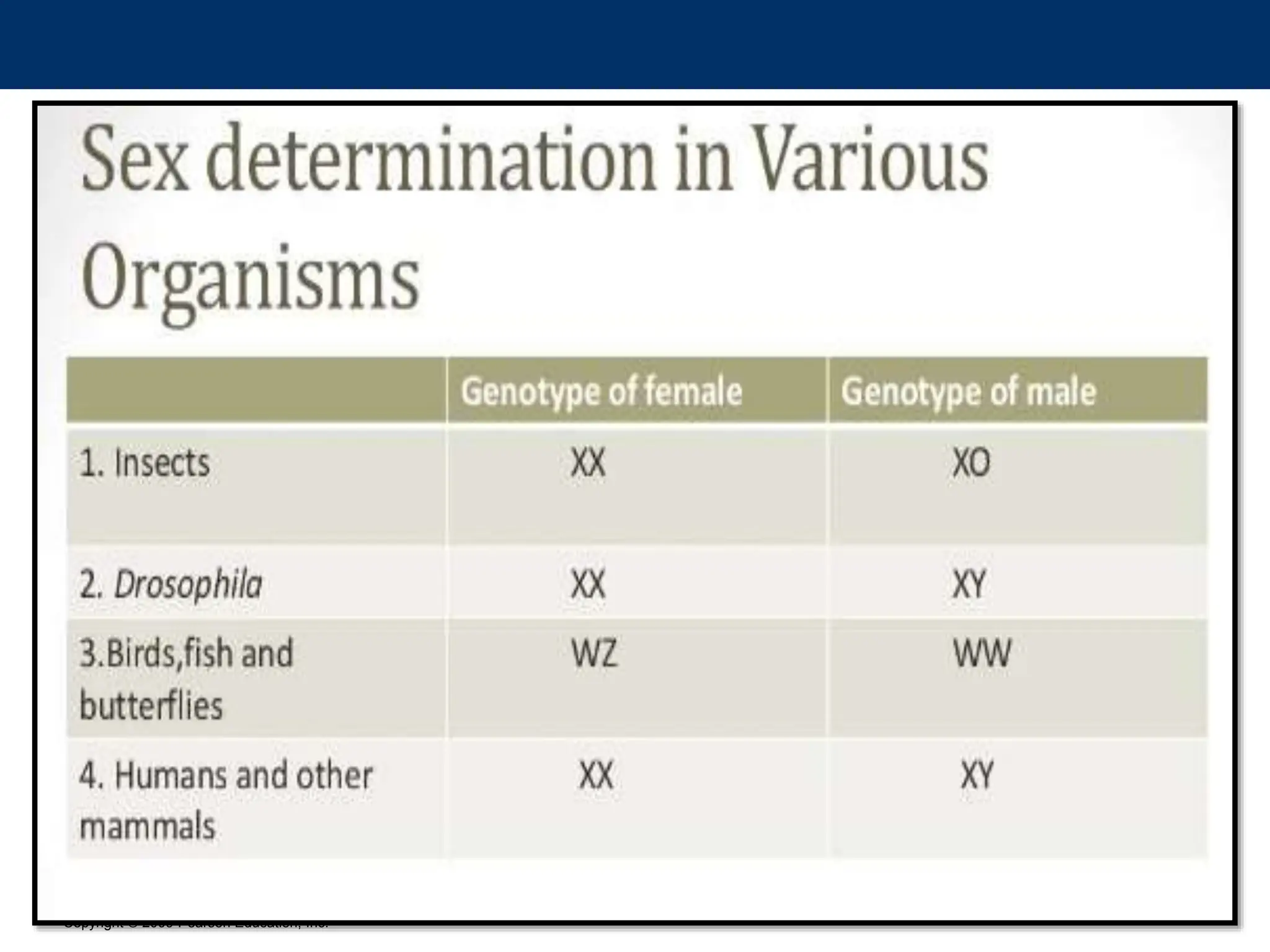
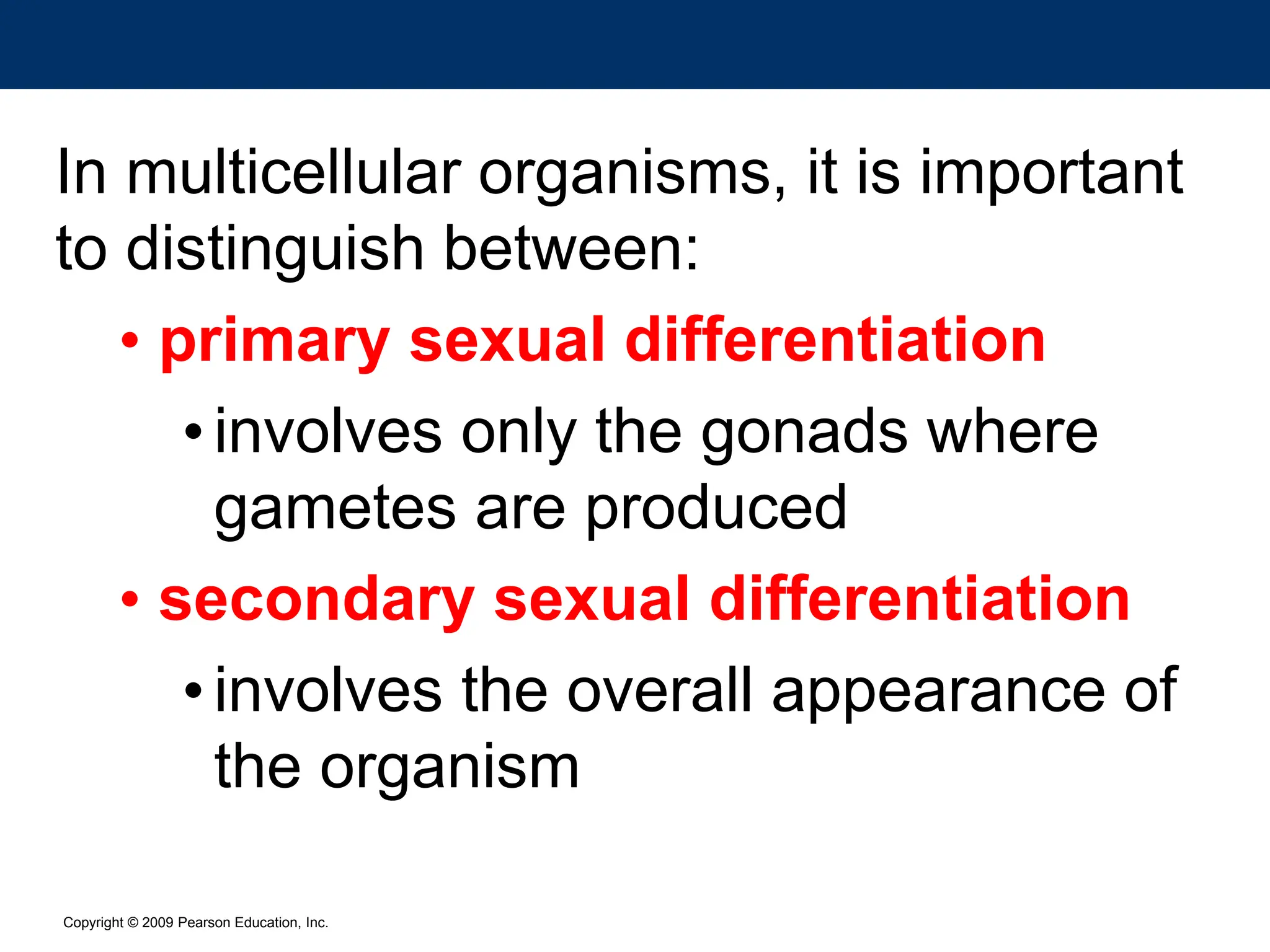
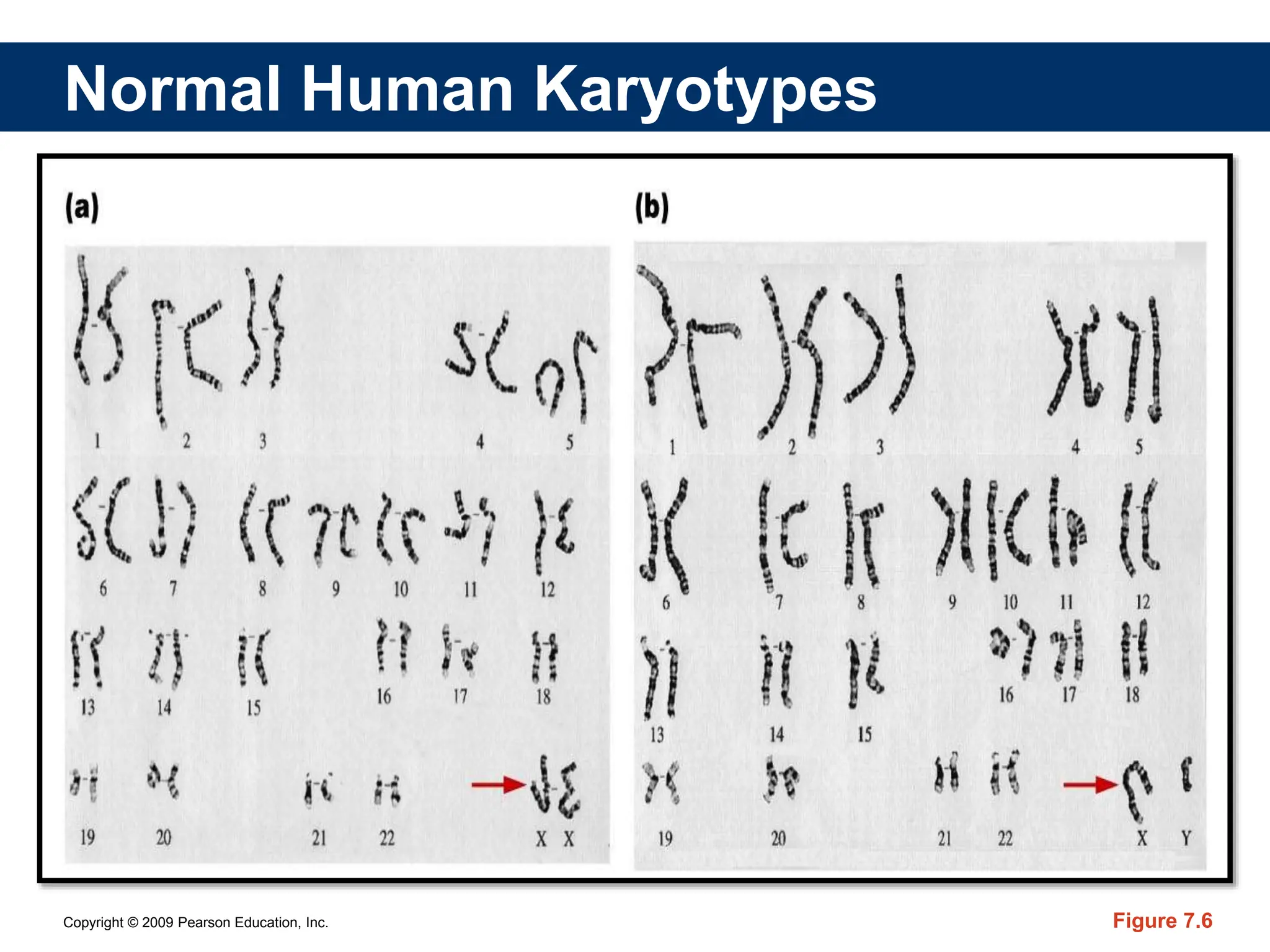
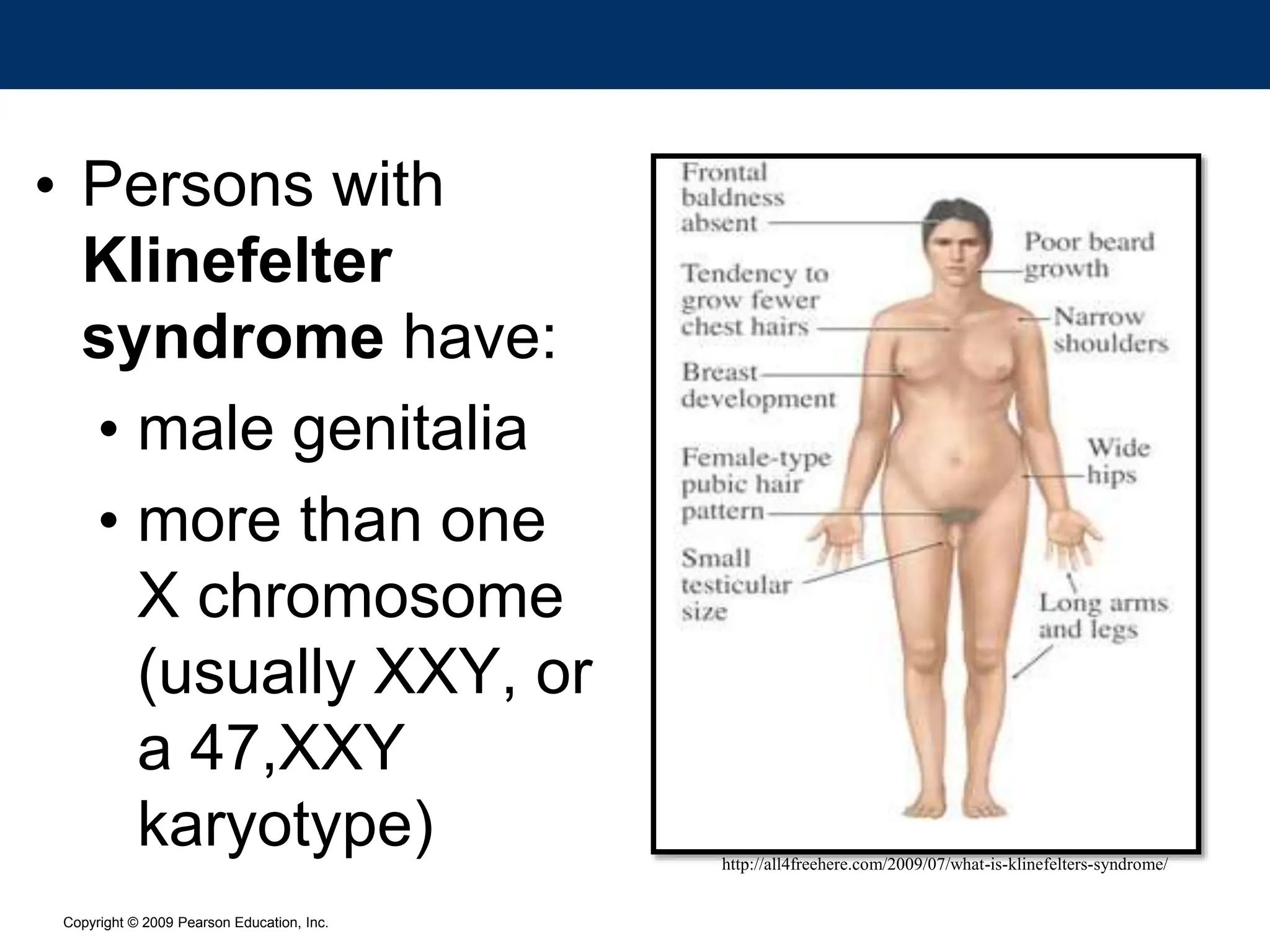
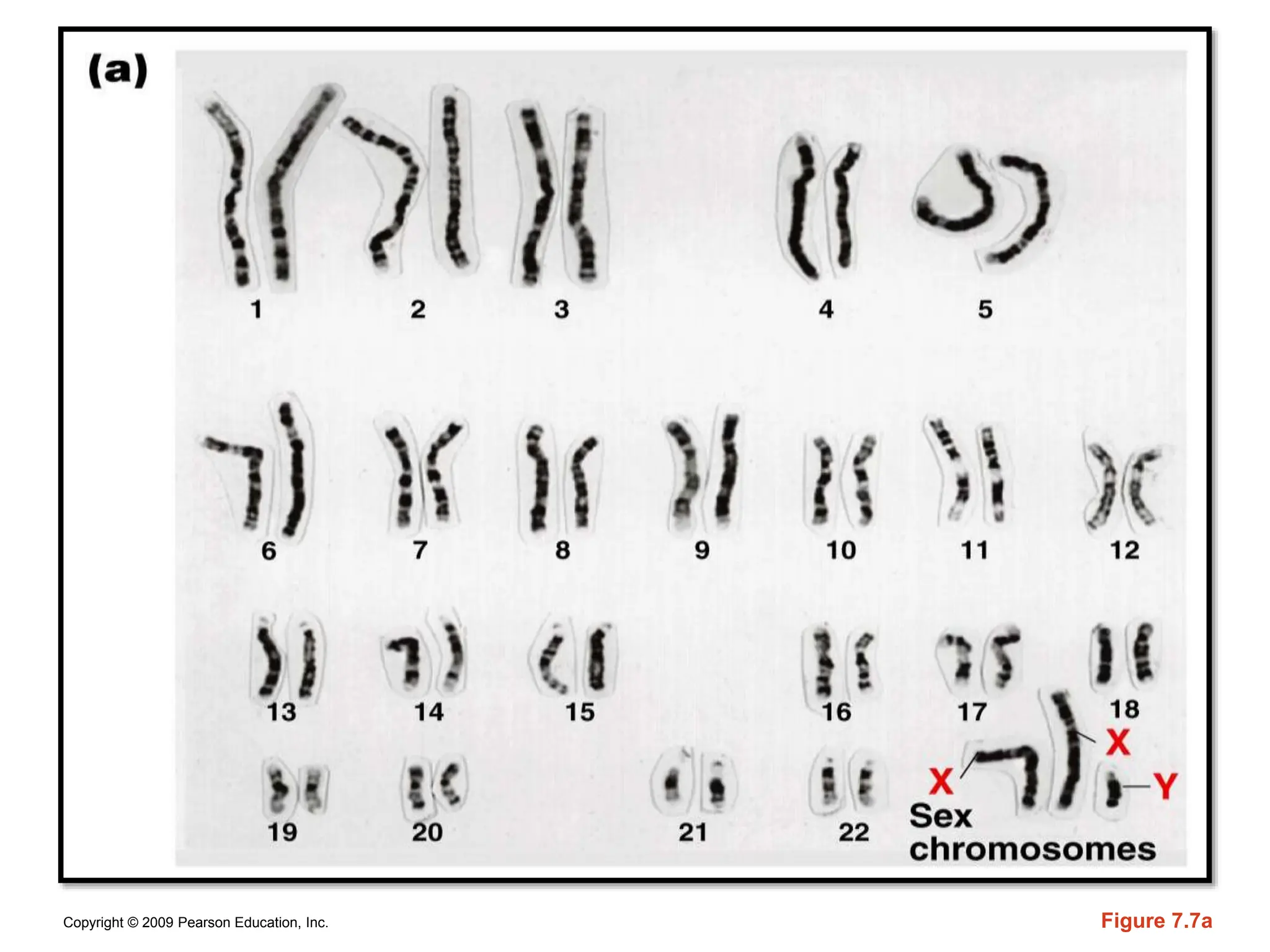
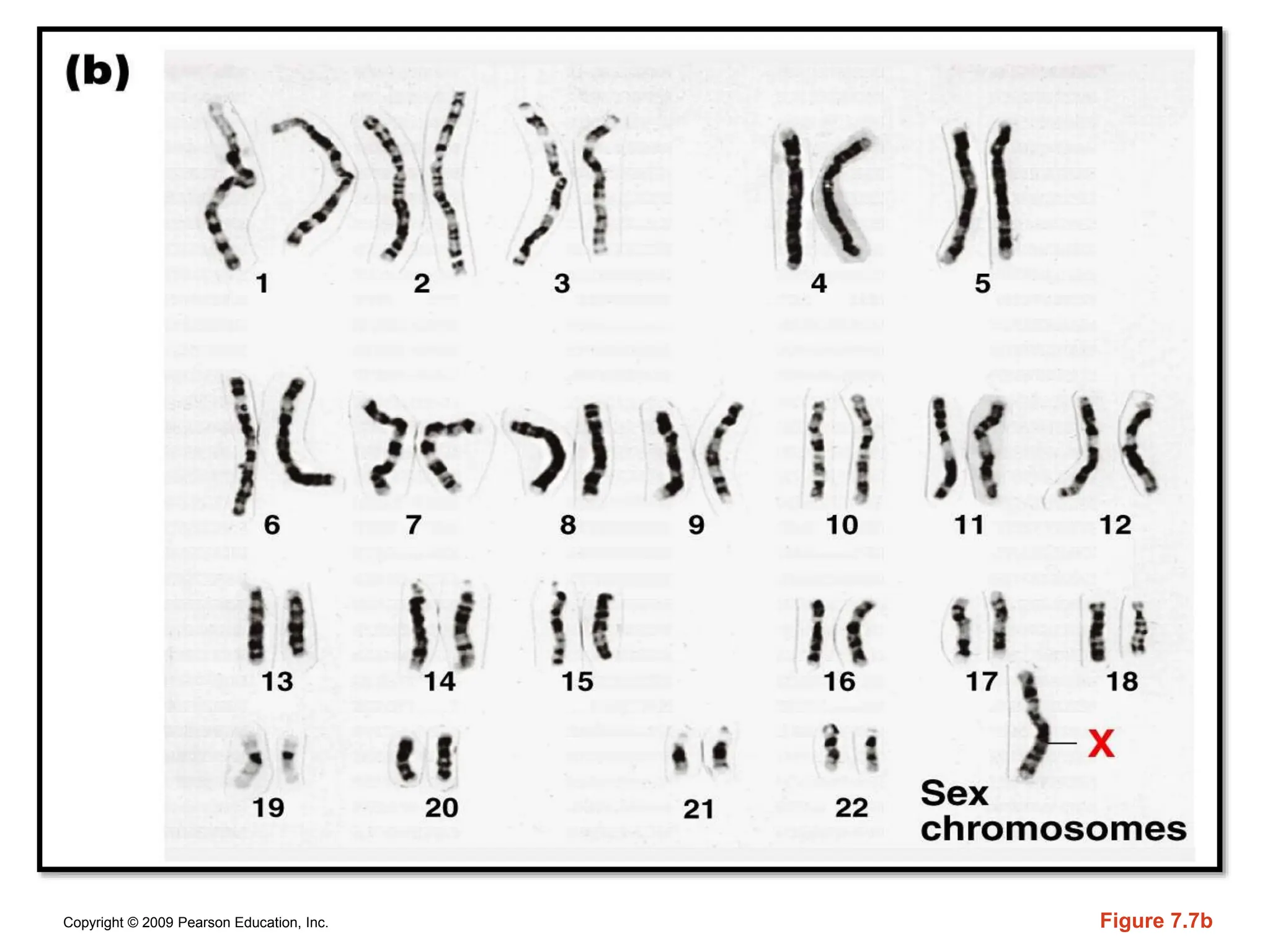
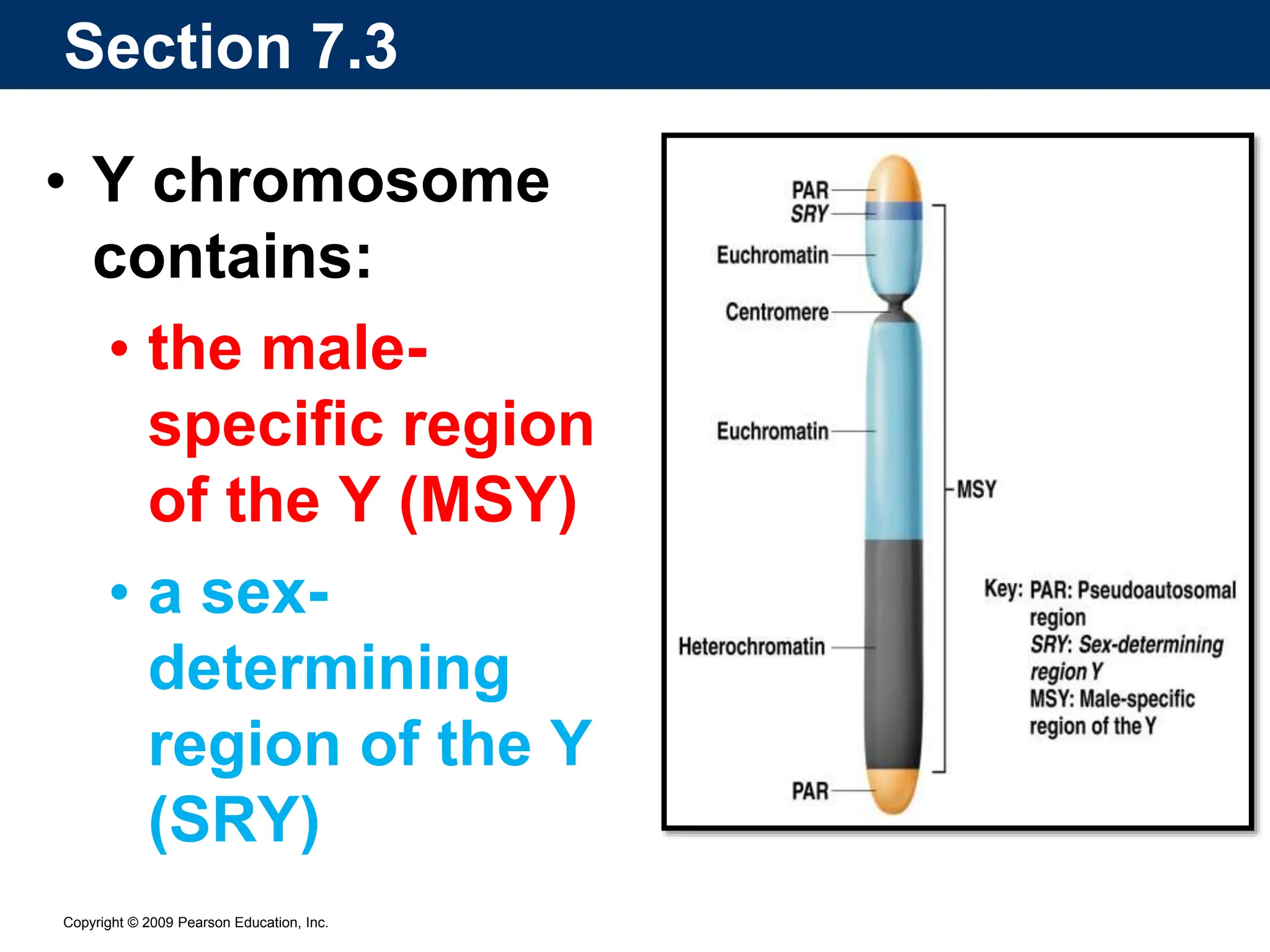
The document discusses sex determination in multicellular organisms, highlighting primary and secondary sexual differentiation and the role of sex chromosomes, specifically the X and Y chromosomes in humans. It explains conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome and Turner syndrome, which result from atypical chromosome patterns affecting sexual development. The document emphasizes that males have one X and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes, detailing the genetic implications of these differences.