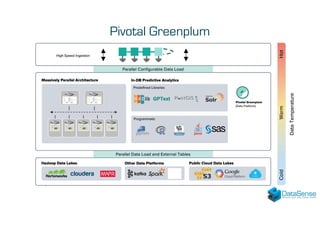
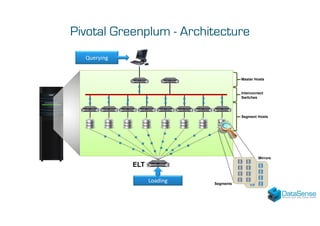
The document discusses Data Vault 2.0, a data modeling technique for integrating historical data from multiple sources. It then summarizes Pivotal Greenplum, an open source massively parallel processing database, and provides examples of reference cases using these technologies for data integration and analytics projects.