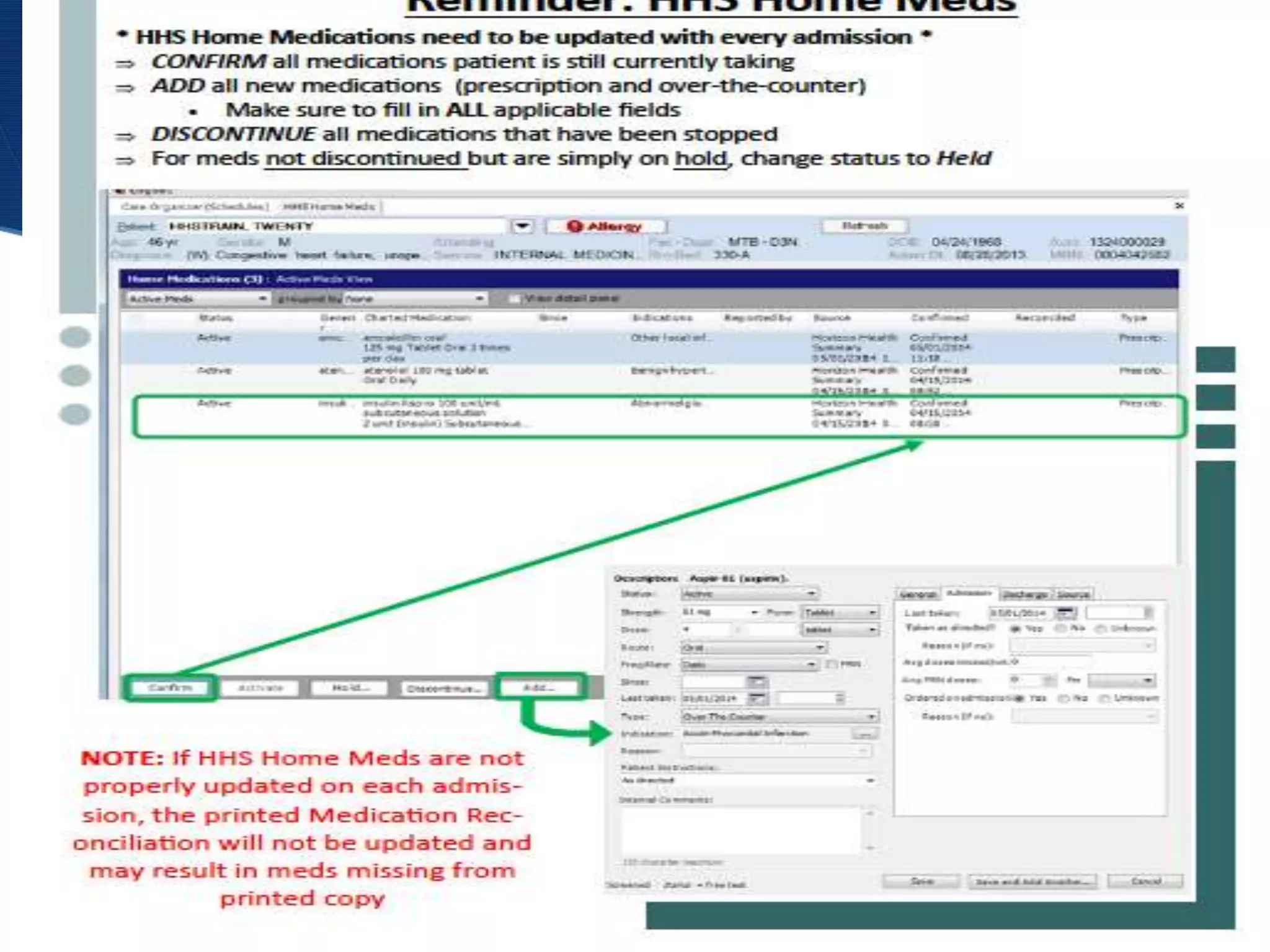
The document discusses medication reconciliation and errors. It notes that adverse drug events are common in hospitals and can result in harm or death. A study found over 50% of patients had at least one unintentional medication discrepancy upon admission. The challenges include a lack of standardized processes and clear ownership when patients transition between care settings. The document proposes interventions like education, standardized workflows, technology solutions, and policies to fully implement a medication reconciliation program across nursing, pharmacy, physicians, and patients to reduce errors and discrepancies.