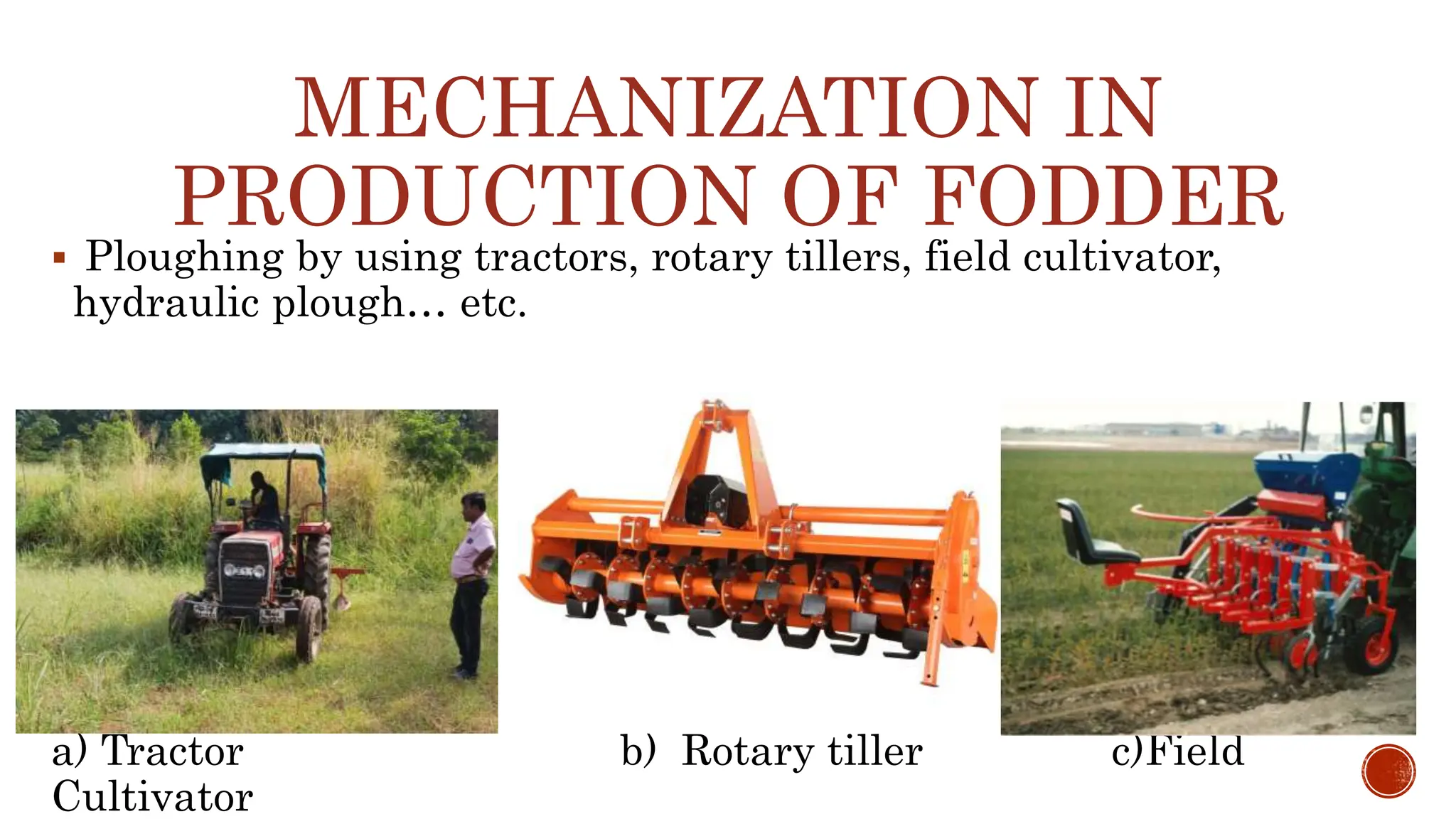
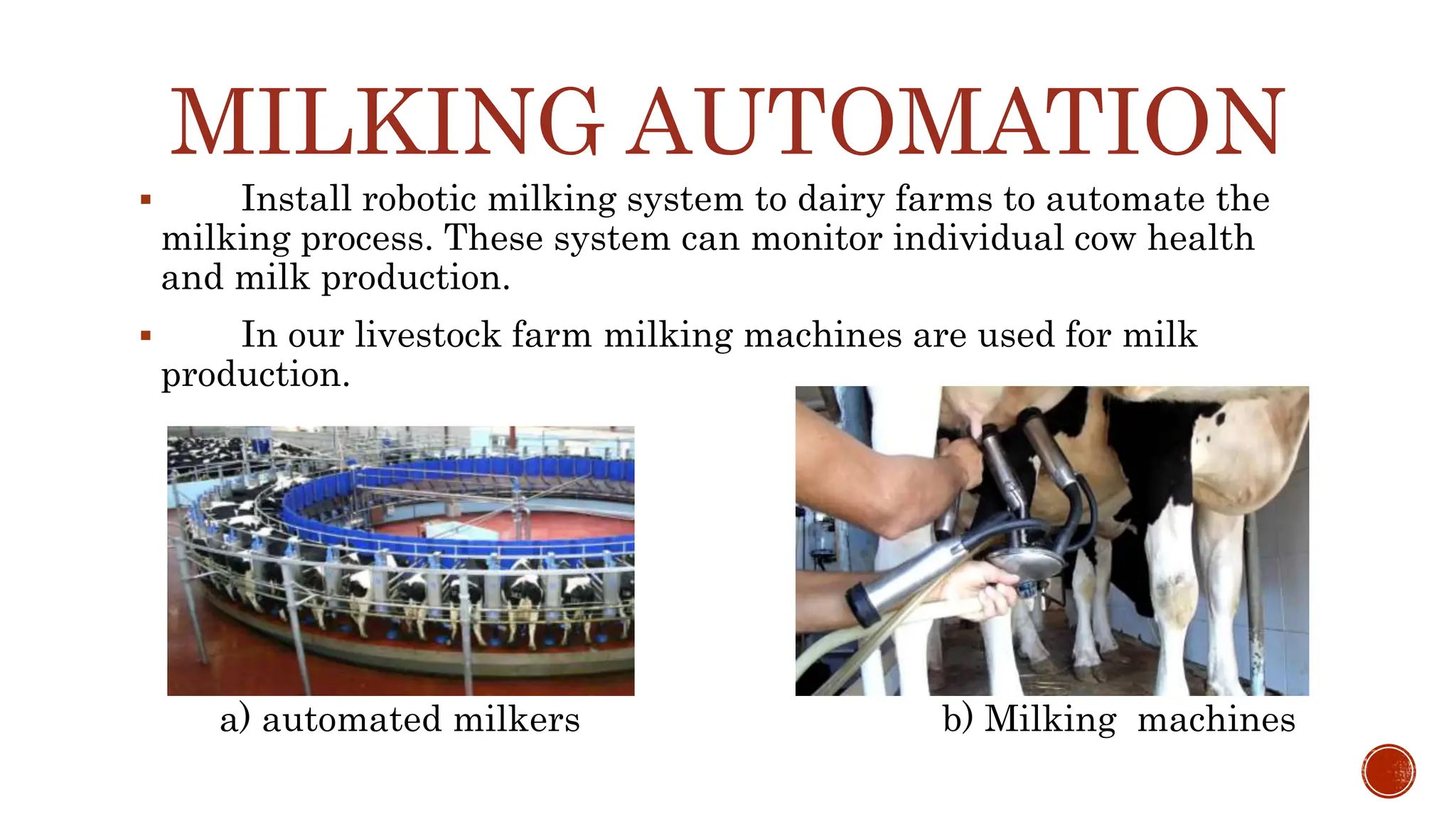
Mechanization of livestock replaces traditional human methods with machines to improve efficiency. It can automate feeding, milking, manure management, monitoring, fencing, data collection, and more. Proper implementation requires considering a farm's individual needs and gradually introducing affordable technologies to save labor and costs while ensuring animal welfare. Overall, livestock mechanization aims to enhance production and management.