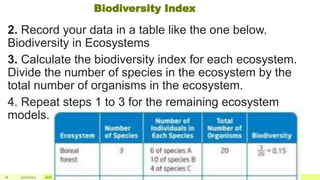
The document discusses the concept of biodiversity, emphasizing its importance and the need to protect it from diminishment. It outlines methods for measuring biodiversity, such as canopy fogging, quadrat sampling, and transect sampling, and highlights biodiversity hotspots. Additionally, it explains the biodiversity index and how it can be calculated to assess the health of ecosystems.