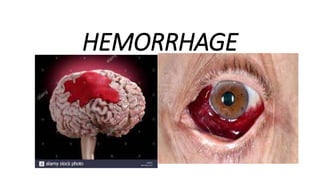
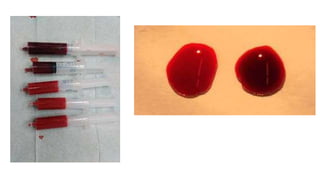
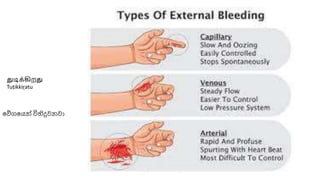
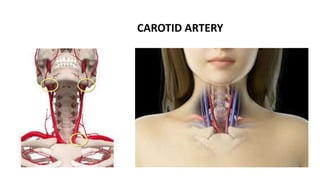
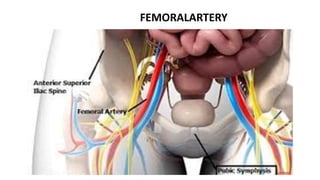
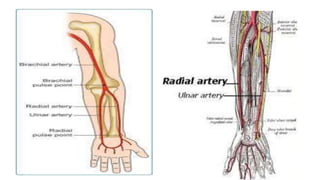
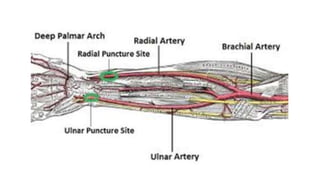
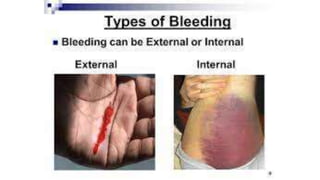
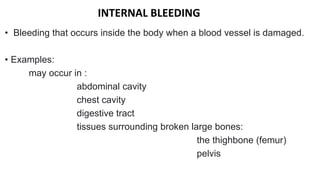
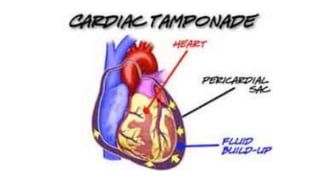
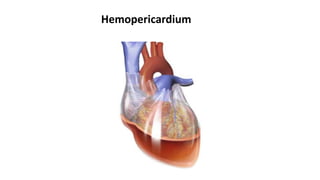
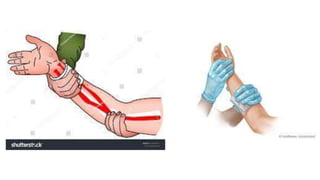
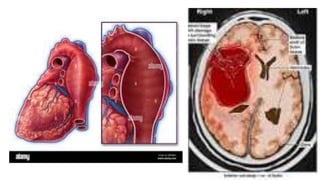
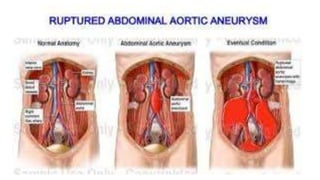
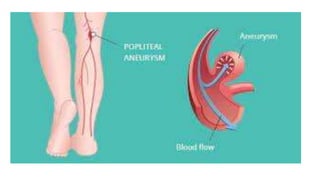
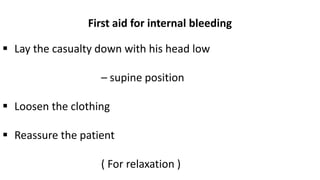
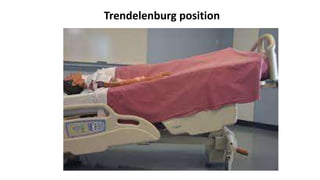
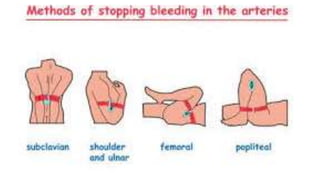
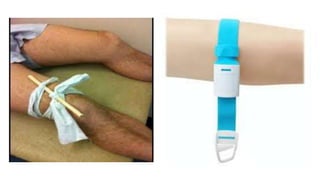
This document discusses measures for emergency situations focusing on hemorrhage (bleeding) and shock. It defines hemorrhage as the escape of blood from damaged blood vessels. There are three types of bleeding - arterial, venous, and capillary. Arterial bleeding is the most serious as it involves large pulsing blood vessels. Signs of internal bleeding include vomiting blood, coughing up blood, black tarry stools, and blood in urine. First aid for bleeding involves applying direct pressure, elevating the injured area, and seeking immediate medical attention for serious or uncontrolled bleeding. Shock is a life-threatening condition where blood flow to vital organs is reduced, which if not treated promptly can lead to organ failure and death.