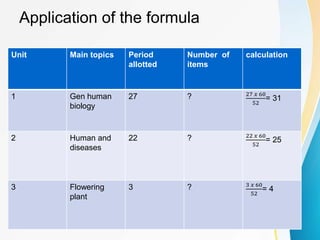
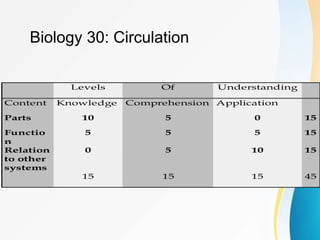
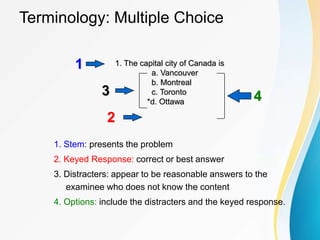
This document discusses measurement, assessment, evaluation, and testing in education. It provides definitions and concepts for these terms. Measurement involves determining attributes or dimensions of objects, while evaluation assigns value to measures. Assessment gathers evidence of student performance over time. Tests are standardized questions used to measure skills. The document focuses on tables of specifications for organizing test content, item selection, and item construction guidelines. These include writing clear, concise questions and avoiding trick questions.