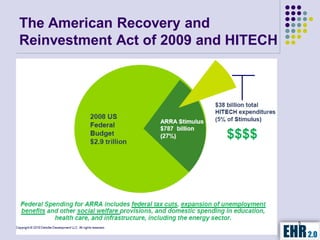
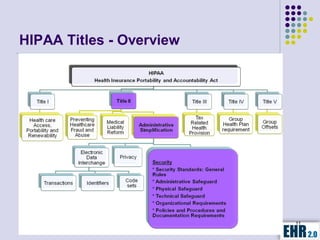
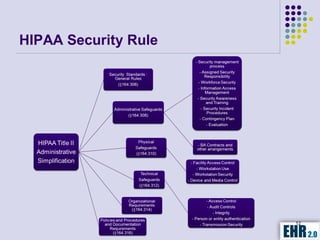
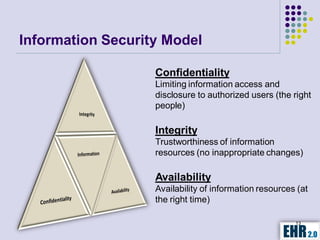
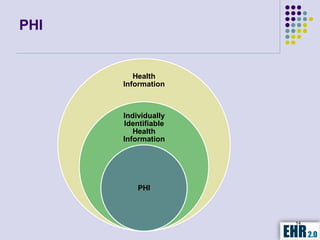
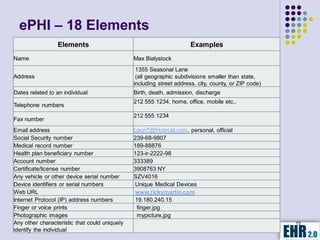
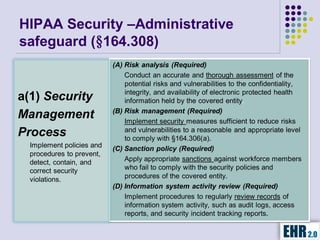
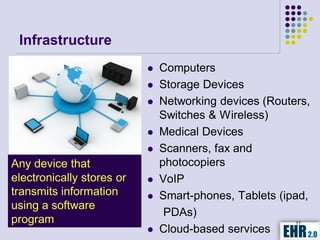
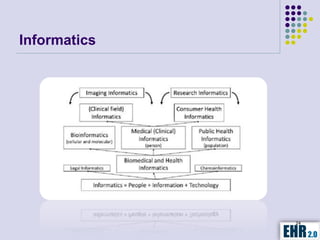
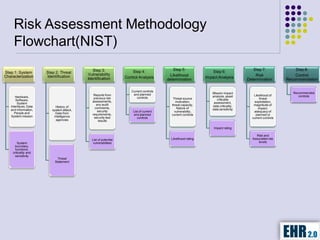
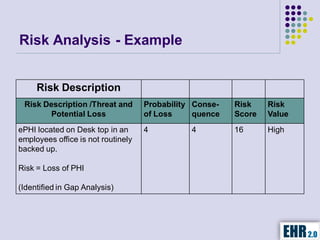
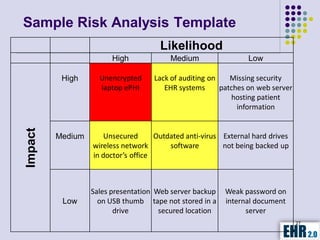
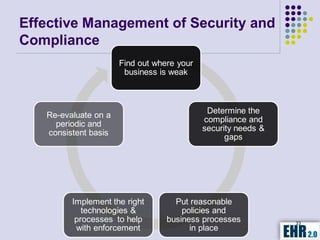
The document outlines the mission of EHR 2.0 to assist healthcare organizations in securing IT systems and complying with HIPAA/HITECH regulations through education, consulting, and tools. It details the importance of conducting meaningful use risk analysis as part of compliance with federal requirements and the implications of the HITECH Act on HIPAA regulations. Additionally, it highlights key elements, assessment methodologies, security measures, and best practices to enhance data protection and compliance in healthcare IT.