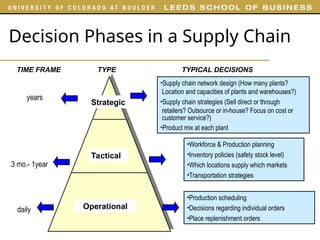
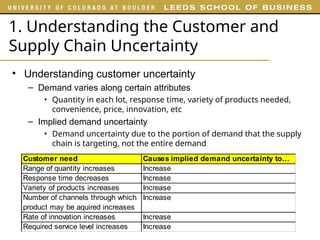
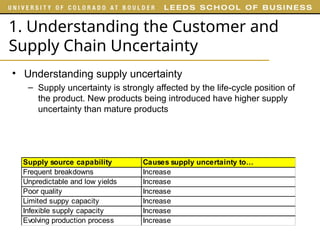
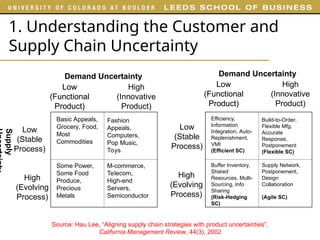
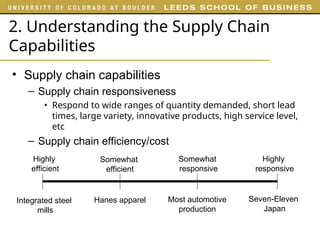
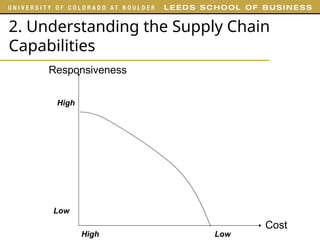
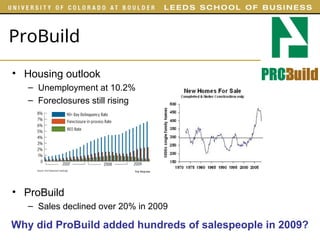
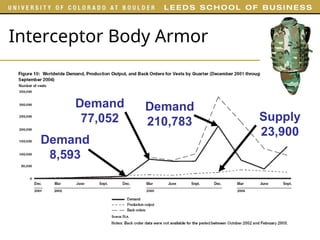
The document outlines various examples and concepts related to supply chain management, including specific case studies such as Crocs and Netflix. It discusses key decision phases in supply chain management, emphasizing the importance of aligning supply chain strategy with competitive strategy to meet customer needs effectively. Additionally, it covers challenges faced by companies like ProBuild and the impact of market conditions on supplier operations.








![Compound
Italy
Florida*
China
Mexico*
Mold
Canada*
Bosnia
China
Mexico*
Brazil*
Assemble
Denver 3rd
party
distributor
Package &
Label
Denver
Color
Pellets
Size & Style
blanks
Small
retailer
Large
Retailer
Europe
Warehouse
/ distribute
Denver
Style &
size
molds
Bosnia
China
Mexico*
Brazil*
Bosnia
China
Mexico*
Brazil*
Bosnia
China
Mexico*
Brazil*
Labeled,
packaged
Croc
Complete
Croc
Large
Retailer
Asia
Large
Retailer
South
America
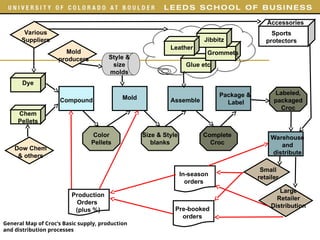
Croc’s Global Production strategy
[2]
[1]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[1] Maintain Florida plant for “Made in USA label
[2] Take advantage of tariffs, e.g., Canada to Isreal
[3] Maintain higher service component of warehousing and labeling for small retailers
[4] Minimize geographic transport by producing in region, including warehousing
[5] Move style and size molds between facilities to maximize production
[6] Use China for large volume, long-term orders from pre-season orders
[6]
*Owned by Crocs vs. outsourced](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/maximizingscmsurplus-250130102701-b6941d17/85/Maximising-Supply-Chain-Management-surplus-ppt-15-320.jpg)