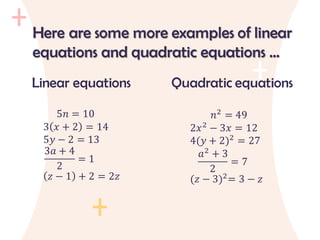
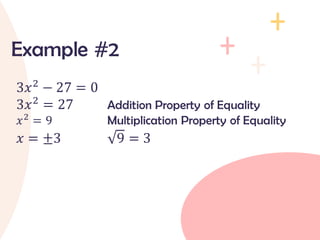
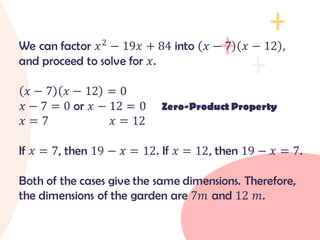
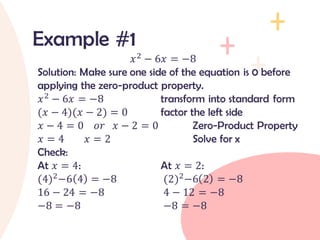
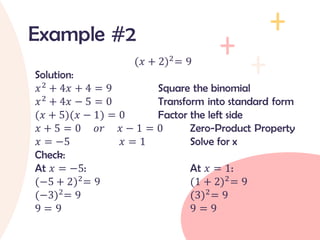
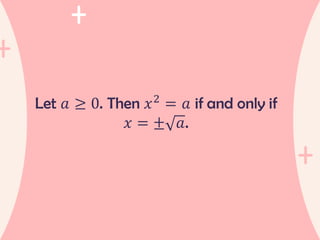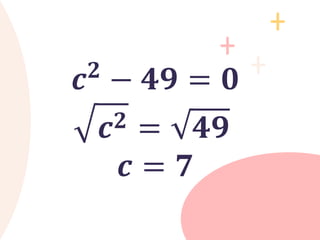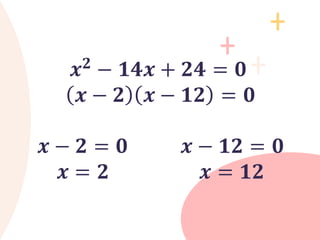The document provides an overview of quadratic equations, defining their standard form and differentiating them from linear equations. It explains methods for solving these equations, such as extracting square roots and factoring, with examples illustrating the application of these methods. Additionally, it includes practice problems and solutions for better understanding of quadratic equations.