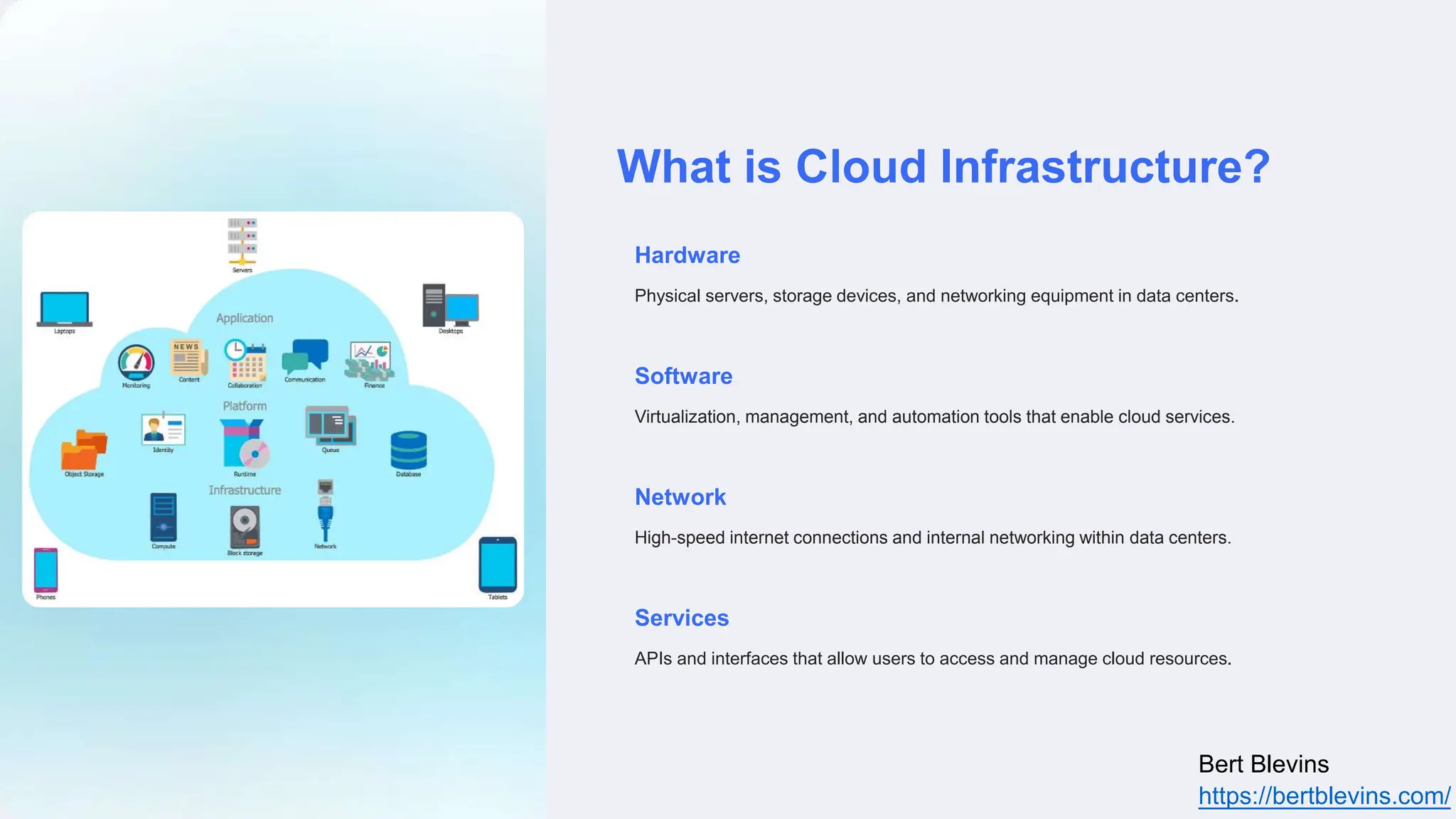
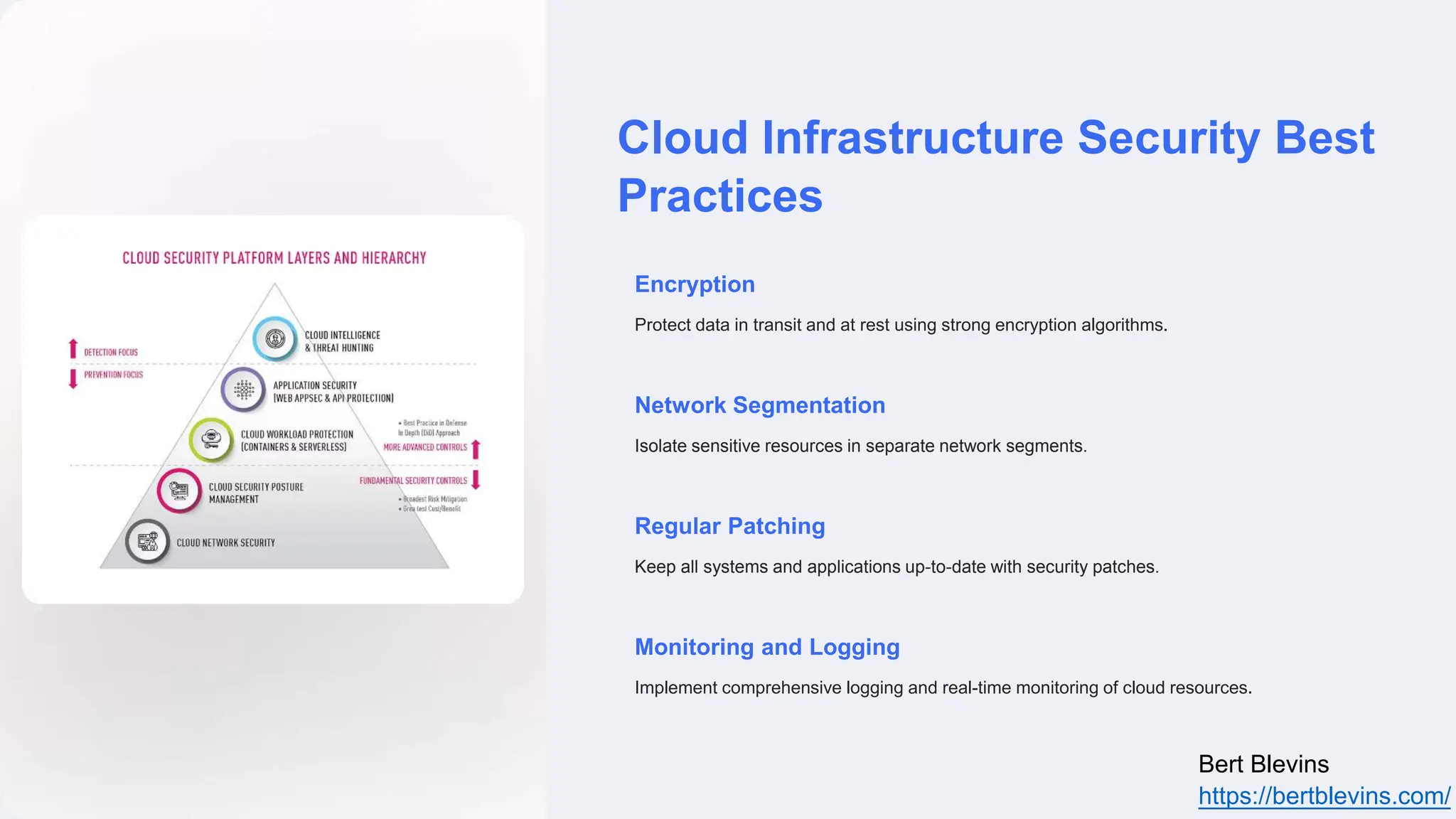
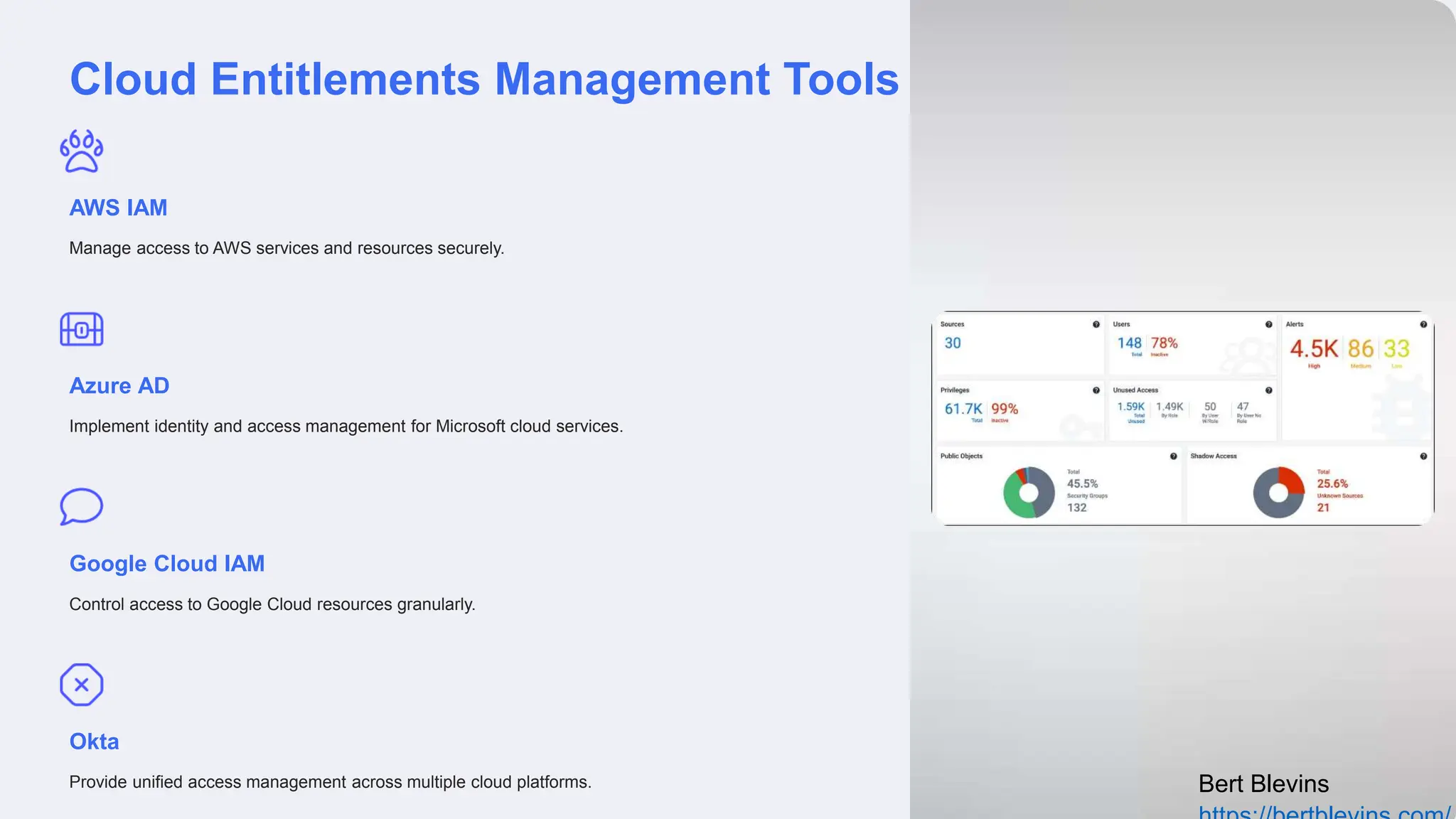
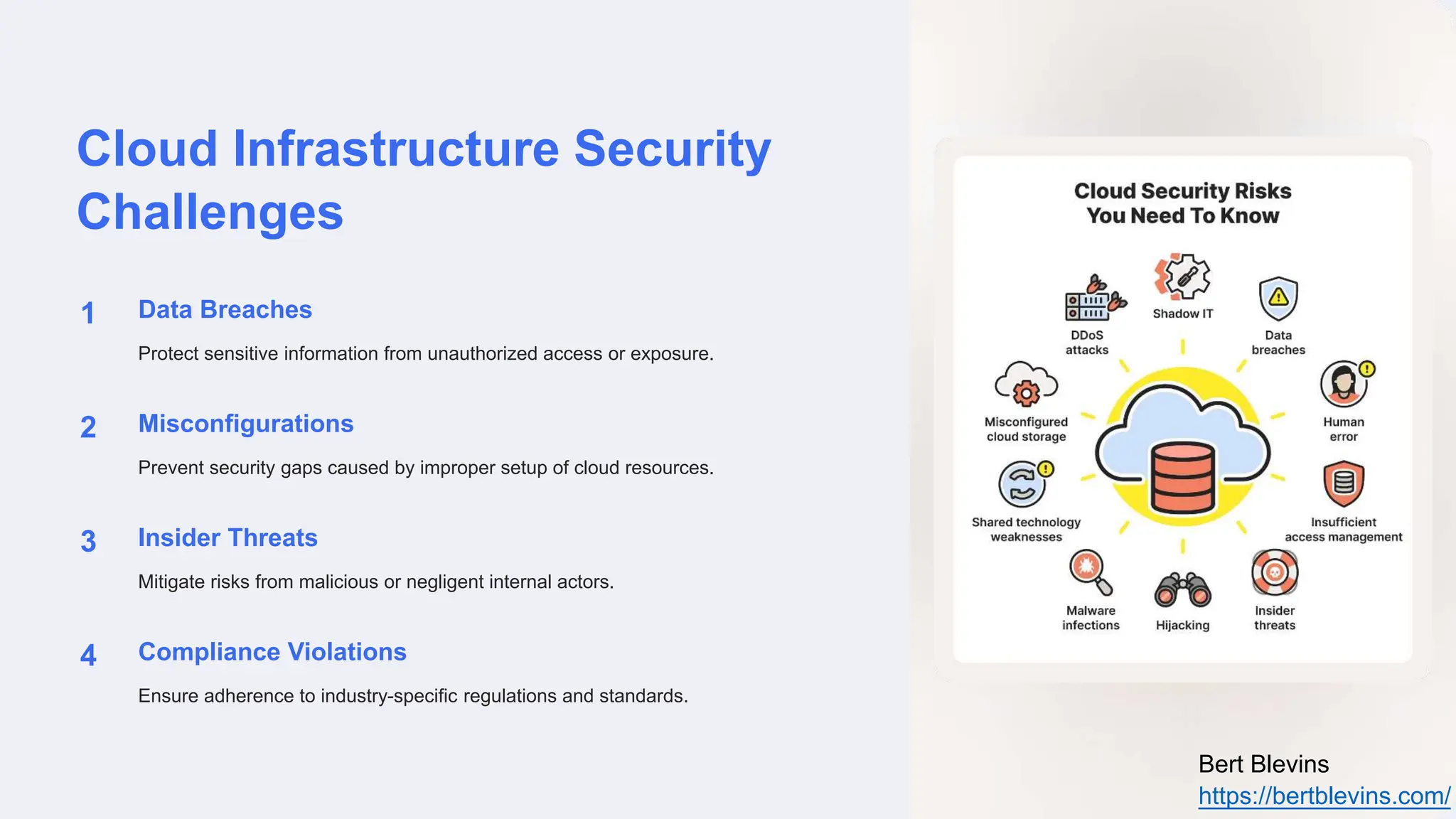
The document discusses privileged access management (PAM) and its importance for modern cloud infrastructure, focusing on scalable computing, security, and compliance. It elaborates on cloud entitlements management and best practices like identity and access management, automated workflows, and continuous monitoring. Additionally, it highlights emerging trends, future challenges, and tools for effective management of cloud resources.